Selective roasting transformation to extract lithium from LiNi0.815Co0.15Al0.035O2 anode material of waste Tesla battery
-
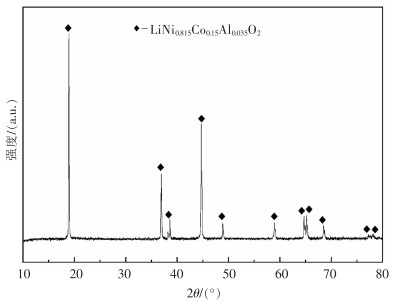
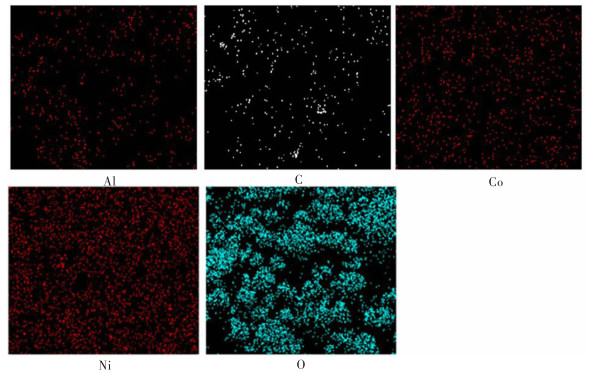
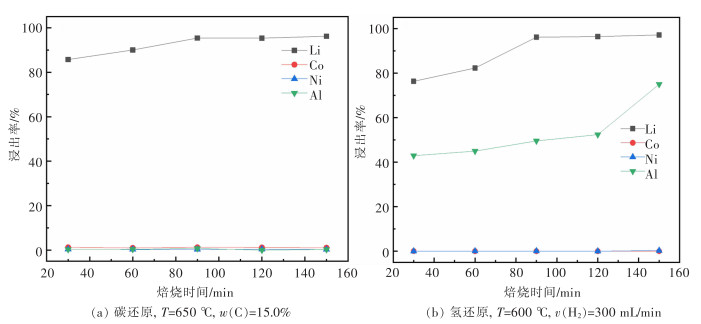
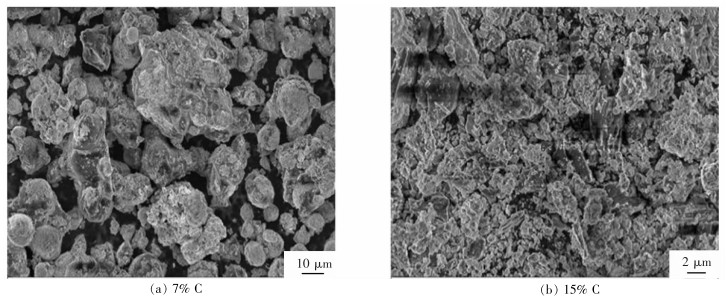
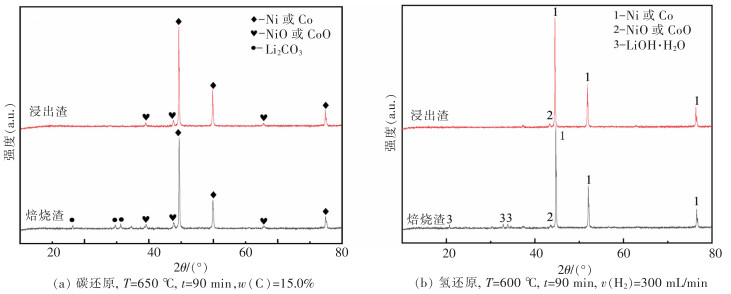
摘要: 在“碳达峰碳中和”战略目标下,新能源产业受到国家政策的大力扶持,我国锂电新能源产业迅猛发展,作为新能源汽车核心部件的锂离子电池的产量及报废量持续增加。废旧三元锂电池含大量的有价金属和危险废物,对其综合回收利用兼具经济和环境效益。传统火法工艺存在能耗高、锂损失率大、污染重等缺点,而常规湿法工艺亦存在流程长、净化工序复杂、锂综合回收率低、废水量大等问题。现阶段研究多以LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2(NCM) 三元正极材料为研究对象,而针对新型含铝特斯拉电池物料的回收鲜有报道,因此以典型的特斯拉三元正极材料LiNi0.815Co0.15Al0.035O2(NCA) 为原料,以碳和氢气为还原剂,采用“还原焙烧转型-选择性提锂”工艺对废旧锂电池中的锂进行选择性提取回收,并从还原焙烧及浸出方式、能耗和环保等方面进行对比。结果表明:采用碳还原焙烧选择性提锂工艺,在碳含量为15.0%、温度为700 ℃、焙烧时间为90 min的条件下,Li、Ni、Co、Al的提取率分别为97.84%、0.45%、0.36%、0.75%;采用氢还原焙烧选择性提锂工艺处理NCA物料,转型温度较低,在相同焙烧时间下,在焙烧温度500 ℃、氢气流速300 mL/min的条件下,Li提取率为95.97%,Al的提取率为8.65%,Ni、Co提取率均小于0.5%,同时产物中无CO、CO2等污染气体产生。因此,氢还原焙烧具有较大的工业应用潜力。Abstract: To achieve the goals for "carbon peaking and carbon neutrality", the new energy industry has been strongly supported by national policies. With the rapid development of China's lithium new energy industry, the production and scrap volume of lithium-ion batteries, the core components of new energy vehicles, have been increasing. The comprehensive recycling of ternary lithium batteries, containing a large amount of valuable metals and hazardous wastes, are of both economic and environmental benefits. The traditional pyrometallurgy has the disadvantages of high energy consumption, high lithium loss rate and heavy pollution, and the routine hydrometallurgy also has the problems of long process, complex purification process, low comprehensive lithium recovery rate and a large amount of wastewater. At present, LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 (NCM) ternary anode materials are taken as the main research objects, while the recovery of new aluminum-containing Tesla battery materials is rarely reported. Therefore, with the typical Tesla ternary anode material LiNi0.815Co0.15Al0.035O2 (NCA) as raw material, carbon and hydrogen reducing agents, the lithium in waste lithium batteries was selectively extracted and recovered by reduction and roasting transformation—selective lithium extraction processes. Comparisons were conducted from the perspectives of reduction roasting and leaching methods, economic cost and environmental aspects. The results show that, by carbon reduction and roasting-selective lithium extraction process, the extraction rates of Li, Ni, Co and Al are 97.84%, 0.45%, 0.36% and 0.75%, respectively, at a carbon content of 15.0%, temperature of 700 ℃ and roasting time of 90 mins. The transition temperature is rather low when NCA materials are treated by hydrogen reduction roasting selective lithium extraction process. The extraction rate of Li is 95.97% and that of Al 8.65%, but the extraction rates of Ni and Co are both less than 0.5% at a roasting temperature of 500℃, hydrogen flow rate of 300 mL/min in the same roasting time. Meanwhile, no pollution gas such as CO and CO2 is generated in the products. Therefore, hydrogen reduction roasting has a large potential for industrial applications.
-
Keywords:
- spent lithium battery /
- carbon reduction /
- hydrogen reduction /
- water leaching separation /
- lithium
-
底吹熔炼炉是一种卧式圆筒形熔池熔炼炉,高压富氧空气从底部鼓入熔池,产生的气泡流剧烈搅拌熔体,并与之发生氧化反应[1]。底吹熔炼炉的搅拌能力强,熔池内反应速度快,炉渣中的金属含量低,氧气利用率和吸热效率高,广泛用于铜、铅、锑等金属的捕集冶炼[2]。在熔池熔炼过程中,气泡和熔体的多相流动决定了反应效率和冶金炉窑的安全使用寿命。由于高温熔池内部的气泡、铜锍、渣及下料颗粒的运动过程难以观察,而数值模拟方法能够通过理论计算得到熔池内实时参数分布,已成为一种解决氧气底吹炼铜问题的重要研究方法[3-7]。
近年来,研究者通过数值模拟及实验方法对铜熔池熔炼过程进行了研究。李晟等[8]采用流体体积方法对铜锍转炉熔池内造铜期吹炼过程中气液两相流动进行单喷嘴数值模拟,研究了气体喷入熔体时的喷流运动现象和性质、气流穿透距离、风口压力变化、风口侧壁面剪切应力分布和气含率分布规律。郭学益等[9-10]采用VOF多相流模型研究底吹氧气熔池熔炼过程中气泡的生长和破裂行为,分析了熔池内部相分布、气泡的形状、生长频率、直径,以及变形、融合、破裂等过程,对氧枪的枪位布置方式进行优化。王书晓等[11]采用水模型实验研究了铜底吹炉氧枪喷口蘑菇头生成过程,发现蘑菇头的大小、孔隙率以及形成稳定蘑菇头所需时间受气流速度的影响较大,受氧枪倾角的影响较小。XIAO等[12]研究了不同气体流速和熔池深度下底吹熔池喷嘴几何结构对进出口压降的影响,发现喷嘴水力直径和孔口尺寸对压降的影响较大。邓伟鹏等[13]针对生物柴浸没燃烧熔池熔炼建立了计算模型,分析了熔池内气泡轨迹为曲线和气泡形状变化。SHUI等[14-16]利用水模型实验,通过两种不同密度且互不融合的液体研究了底吹炉渣眼大小的影响因素,并且开发了数学模型对渣眼的产生区域进行模拟研究,得出混合时间与气流速度及熔池深度的关系式。李小龙等[17]为定量描述熔炼过程中乳化现象,根据相似原理建立了侧吹炼铜物理模型,考察了气体流量对熔池内乳化层的形成、乳化液滴尺寸分布的影响规律,建立了传质界面面积α的估算方法。LIU等[18]根据相似性原理建立了双侧吹水模型实验台,并模拟计算了气液两相流动过程中气流速度、氧枪浸没深度和角度的影响。董择上等[19]对底吹铜熔炼炉内气-渣-铜锍三相流动过程进行仿真模拟,对炉内气液两相流动规律、炉内各相速度场、熔炼炉喷溅机理进行分析,获得炉内各流动区域特征。余跃[20]对底吹炉渣-铜锍-粗铜-空气四相的流动过程进行数值模拟,研究了气体流量对铜底吹炉吹炼过程的影响。穆亮照等[21]针对国内单体最大铜底吹熔炼炉存在的熔炼效率低、渣含铜过高等问题,模拟了气-锍-渣多相流场,对氧枪数量和熔池深度进行了优化。
尽管目前已有大量水模型及模拟研究,但大多只针对熔池气-液体两相流动过程,对熔池内气泡、铜锍、渣等多相流动特性的研究较少。氧气底吹炼铜在生产运行中存在渣眼位置不稳定、渣含铜偏高、渣金分离效果差等问题,导致生产效率降低,阻碍了氧气底吹炼铜工艺进一步发展。为进一步探究实际底吹炉内气-锍-渣多相并存条件下各相的运动规律以及气泡、铜锍、渣层在熔池内的动态分布,本文建立了三维底吹熔池熔炼模型,对炉内空气-铜锍两相和空气-铜锍-渣三相的流动进行数值模拟,为优化生产参数、提高冶炼效率和炉体结构改造提供了理论依据。
1 数学模型
1.1 控制方程
大量数值模拟实践[22-25]表明,流体体积分数模型VOF(Volume of Fluid)对于预测射流破碎、流体中大泡的运动和气液界面的稳态和瞬态处理具有优良的表现。本文研究气-锍-渣三相流动,各相为互不相融的流体,且存在相界面,因此,选用VOF多相流模型。各相的连续性方程如下:

(1) 式(1)中:p、q为不同的相;ρq为第q相的密度;t为时间;α为体积分数;U是流场中任一点的流速;


VOF模型中,各相共用单一速度场,动量守恒方程为:

(2) 式(2)中:g为重力加速度;μ为有效黏度;F为作用在控制体的体积力。
由于铜锍体积分数最大,计算时将铜锍设为主相,气泡设为第一次相,计算三相流动时,渣层设为第二次相。
底吹熔炼过程的高压气体由氧枪进入熔池时为射流,在吹炼区形成强烈的搅拌漩涡,该过程为湍流流动。由于熔池内存在大量气泡和漩涡,使用标准k-ε湍流模型误差较大,而Realizable k-ε湍流模型能更好地描述气泡尺寸的变化,模拟复杂的湍流问题[18]。因此,本文采用Realizable k-ε湍流模型进行模拟计算。
1.2 边界条件
本文以1∶12的水口山炉水力学实验台为基础建立三维模型,模型长1250 mm,内径300 mm,喷嘴直径为5 mm,底部共有9个竖直氧枪[22]。对计算区域划分网格,底部熔池区域进行加密处理,网格数量1 575 675个,三维网格及喷口区横截面网格如图 1所示。
氧枪的入口设为速度入口,烟气出口设为自由出流。使用煤油、水、空气模拟渣、铜锍和富氧空气,其物性参数如表 1所列。初始液面高度90 mm。
表 1 物性参数Table 1. Physical parametersof liquid phases
2 模型求解及结果验证
2.1 模型的求解
利用数值模拟软件Fluent对建立的水口山底吹炉模型进行求解。采用PISO算法对速度进行耦合,压力基分离器的格式采用PRESTO格式,动量方程选用一阶迎风格式,最短时间步长为0.001 s。
2.2 模型的验证
利用水模型试验台得到的气泡流照片[15]对比模拟计算得出的二维XY截面的气液相分布,如图 2所示, 模拟得到的气泡流形状和液面波动形状均与水模型实验相吻合,因此,所建立的模型能够正确反映熔池内流动特性。
为了验证网格的独立性,对建立的三维几何模型重新划分网格,网格数量分别为1 053 680个和1 976 924个。在第一个氧枪喷口处设置一个速度监测点,如图 3所示。
利用不同数量的网格进行计算,得出不同监测点的速度。如图 4所示,在0.3 s后气泡上升到液面,流动稳定。由于监测点为气液两相湍流流动,因此流速无法保持恒定,处于波动状态。网格数为2×106个和1.5×106个的监测点平均速度较为接近,而网格数为1×106个的监测点速度相比网格数2×106个和网格数1.5×106个有较大偏差。因此,在考虑精算精度以及计算速度的情况下,本文采用1.5×106个网格数量进行模拟计算。
3 模拟结果分析
3.1 气液两相流动特性
气液两相模型仅考虑气体和水,用于模拟在熔炼炉加料位置还没有渣生成时富氧空气和铜锍的两相流动特性。为了详细分析熔池内流场特性,在三维模型内取XY方向第二个氧枪横向截面和YZ方向穿过炉膛中心的纵向截面,如图 5所示。
当空气连续稳定喷入熔池内,XY和YZ横向截面的两相分布和流线图如图 6所示,由XY截面相分布图可见,空气连续喷入熔池中形成稳定上升的气泡流。当气泡从底部上升到熔池表面,液面产生波动,并向炉壁侧传播。液面波动会不断冲刷炉壁内侧,导致炉壁耐火材料的损耗。从XY截面流线可见,气泡流的上升导致熔池内氧枪左右两侧各形成一个大漩涡,实现了对熔池的持续搅动,左右侧漩涡的位置基本对称。从YZ截面相分布图可见,由于各个喷口距离较近,喷口区气泡流在上升过程中相互影响较严重。熔炼区气泡流对熔体进行强烈搅拌,最右侧氧枪喷口的气泡会流动到炉膛中部的沉降区。熔炼区液面波动幅度较大,左侧炉壁受到冲刷较严重,右侧液面波动较轻微,因此液面波动对左侧炉壁冲刷比右侧炉壁更剧烈,左侧炉壁耐火材料损耗更严重。
3.2 气液渣三相流动特性
气液渣三相模型使用空气、水和煤油模拟在熔炼区产生渣层时富氧空气、铜锍和渣层的三相流动特性。当空气连续稳定喷入熔池内,XY截面的三相分布、流线图、三维液面波动图和渣相体积分数分布图如图 7所示。
图 7(a)中最下层红色区域为模拟铜锍层,中间绿色区域为渣层,上部蓝色区域为气相。当空气体由底部连续喷入炉内后,形成的气泡流在溶池中快速上升,并穿过铜锍层和渣层,将最上层的渣层吹开形成渣眼,对比图 6可知,当液面出现渣层时液面波动幅度更小。由图 7(b)可见,当渣层存在时在喷枪左右侧也会形成两个漩涡,对比图 6可知,渣层存在时生成的漩涡面积较小,表明搅动的程度减弱。图 7(d)中间红色区域为渣层。当气泡流稳定上升时,渣眼面积几乎维持稳定,靠近壁面处渣层较厚,渣线位置较稳定,保证了加料时炉料能够落入渣眼,并与铜锍进行快速反应。熔炼区氧枪喷出的气泡流将渣层吹开,大部分渣被推向沉降区,小部分渣被推向左侧炉壁,最左侧氧枪气流甚至无法吹开渣层形成稳定的渣眼。因此,加料口不宜设置在靠近炉壁左侧,以防物料直接进入渣层,不利于化学反应的进行。由于氧枪间距较小,不同氧枪气泡流相互影响,右侧氧枪气泡流吹开的渣眼逐渐融合,同时有部分渣被卷入吹炼区铜锍中。沉降区由于没有气泡搅动,渣相和金属相实现分层,渣层厚度维持不变。由图 7(c)也可见熔炼区液面波动较剧烈,而沉降区液面波动较小。
4 不同操作参数对熔池流动过程的影响
以三维三相模型为研究对象,模拟计算不同气流速速度、铜锍深度和渣层厚度对炉内流场的影响。
4.1 气流速度对流场的影响
当铜锍深度为90 mm,渣层厚度10 mm,气流速度分别为0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9、1.1、1.3 m/s,计算得到在熔池达到稳定状态后不同气流速度下XY和YZ截面空气-铜锍-渣三相分布,如图 8所示。由XY截面可见,随着气流速度增大,渣层容易被漩涡卷吸到铜锍层中,液面波动高度不断增大,渣眼尺寸不断增大。在气流速度达到1.3 m/s时熔池出现了轻微的喷溅现象。这是由于气流速度越大,鼓入熔池中的气泡尺寸越大,大气团直接从熔池底部冲出液面,造成较大的液面波动,容易导致熔体喷溅。此外,气流速度过大,进入熔池的气泡团聚效应严重,生成的大气团比表面积较小,降低了熔池内富氧空气与铜锍的造渣反应速率。由YZ截面可见,气流速度越大,炉内漩涡搅拌越剧烈,左侧滞留的渣越少,渣层被漩涡推向熔池右侧,渣层长度缩短,厚度增大。但是,当速度达到1.3 m/s时,渣层出现波动,可能造成排渣不稳定。
根据XY截面相分布图和流线图计算得出不同速度下液面波动高度、渣眼直径和旋流强度,如图 9和图 10所示。
由图 9可见,随着气流速度增大,液面波动高度线性增加,即液面波动越剧烈;气流速度增大,渣眼直径不断增大,当气流速度到达一定程度时,渣眼直径保持不变。由图 10可见,随着气流速度增大,旋流强度几乎线性增大,即气流对熔池的搅拌越剧烈。
综上可知,随着气流速度增大,气泡流对熔池的搅拌程度逐渐强烈。但是,气流速度过大不仅容易造成熔体喷溅,气泡尺寸增大导致弥散程度降低,可能会导致反应速率下降,渣层在沉降区出现波动,造成排渣不稳定。因此,在实际生产中应将氧枪喷口气流入口速度控制在合理范围内,既可以降低电耗,提高气-液反应速率,又可以防止液面喷溅事故,保证顺利排渣。
4.2 铜锍深度对流场的影响
底吹熔炼炉多为周期性生产,如果加料不足或不及时排锍,会造成铜锍深度发生变化。假设气流速度保持0.3 m/s不变,渣层厚度保持10 mm,铜锍深度分别为90、110、130、150、170、190 mm。模拟得到不同铜锍深度条件下稳定流动状态熔池内XY和YZ截面的空气-铜锍-渣三相分布及XY截面的流线图,如图 11所示。
由图 11中XY截面三相分布图可知,由于气流速度不变,随着铜锍厚度增加,气泡到达液面的距离增大,因此熔池内气含率提高,气泡的分布范围也随铜锍深度的增加而变大,有利于气-液反应的进行。由YZ截面三相分布图可知,渣层主要集中在沉降区。随着铜锍深度增加,沉降区渣层不断向右侧炉壁聚集,渣层逐渐变得短且厚,说明增加铜锍深度有助于沉降区炉渣的聚集,有利于排渣。对比图 8可知,铜锍厚度增大不会引起沉淀区渣层波动。但是,随着铜锍深度增大,熔炼区域搅动更加剧烈,部分渣层被卷入铜锍层中,导致渣中含铜过高。
根据图 11可以计算得出不同速度下液面波动高度、渣眼直径和旋流强度,如图 12和图 13所示。
由图 12可知,随着铜锍深度增大,熔池液面波动高度逐渐增大,渣眼尺寸逐渐变小;当熔池深度继续增大,渣眼尺寸急剧减小,甚至闭合,导致无法加入物料。由图 13可知,随着铜锍深度增大,漩涡中心位置逐渐上移,旋涡的搅拌范围变大,旋流强度越大,即漩涡发展更加充分,对熔池的搅拌越剧烈。
综上所述,随着铜锍深度增大,气流产生的旋涡搅拌范围增大,旋流强度越大,波动高度逐渐增大,渣层变得短且厚,有利于排渣。但是,当熔池深度增大到一定程度,渣眼直径急剧减小,铜锍卷渣程度增大,会导致无法下料,并且渣中含铜过高。因此,在实际生产过程中需要及时排放铜锍,保持铜锍厚度在一定范围内,以防进料直接进入渣层。
4.3 渣层厚度对流场的影响
在生产过程中,如果加料过多或者不及时排渣会造成渣层厚度发生变化。假设气流速度保持0.3 m/s不变,铜锍深度保持90 mm,渣层厚度分别为10、20、30、40、50、60 mm。模拟得到稳定流动状态下不同渣层厚度时熔池内XY和YZ截面空气-铜锍-渣三相分布以及XY截面流线图,如图 14所示。
由图 14中XY截面三相分布图可知,由于渣层密度更小,黏性系数更大,液面波动逐渐变小,气泡主要存在于铜锍层中。随着渣层厚度增加,熔池内气含率明显增大。气泡尺寸随着渣层厚度增加而增大,这是因为气泡在通过黏度较大的渣层时上升速度较慢,而在铜锍层的气泡上升速度较快,导致小气泡融合成尺寸更大的气泡,不利于气液反应进行。当渣层厚度大于20 mm时,渣层中包含了少量铜锍,导致渣含铜较高。当渣层较薄时,气泡流能够将渣层吹开,靠近壁面处渣层较厚,在中间形成稳定的渣眼。当渣层厚度大于20 mm时,渣眼逐渐闭合,渣层厚度继续增加时,渣眼消失,炉料无法顺利进入铜锍层。此时,需要及时排渣或增大气流速度,以保证形成稳定的渣眼。
由XY截面流线图可知,随着渣层厚度增大,在铜锍层和渣层都会产生漩涡。渣层中产生漩涡也会导致铜锍被卷入渣中,造成渣含铜过高。由YZ三相分布图可知,随着渣层厚度增加,渣眼逐渐减小,渣层从沉降区不断向熔炼区延伸,直至最右侧氧枪上方。由于气泡流在铜锍层和渣层同时产生漩涡,导致熔炼区卷渣现象越来越严重。
综上所述,随着渣层厚度增大,尽管渣层波动稳定,有利于排渣,但铜锍层内气泡尺寸增大,气含率提高,渣眼尺寸急剧减小,甚至消失,漩涡同时出现在铜锍和渣层内,导致卷渣严重。因此,在实际生产中需要及时排渣,以防下料直接进入渣层。
5 结论
本文采用数值模拟方法计算了铜底吹熔池熔炼过程多相流动过程,分析了熔池内空气-铜锍-渣三相流动规律,主要结论如下:
1)建立了三维底吹熔池熔炼炉的数学模型,并采用ANASY-FLUENT软件对模型进行求解,使用水模型实验结果对模拟结果进行了验证。
2)模拟了熔池内气-液两相和气-液-渣三相流动,得出气泡流的上升导致熔池内氧枪左右两侧各形成一个基本对称的大漩涡,喷口距离较近时,漩涡相互重叠;熔炼区液面波动幅度较大,而沉降区波动较轻微,对左侧炉壁冲刷比右侧炉壁更剧烈,因此,左侧炉壁耐火材料损耗更严重。渣层漩涡的搅动程度减弱,大部分渣被推向沉降区,渣层厚度维持不变。
3)以三相模型为研究对象模拟计算气流速速度、铜锍深度和渣层厚度对炉内流场的影响。入口气流速度越大,气泡流对熔池的搅拌程度越强烈;但是,气流速度过大容易造成熔体喷溅,渣层出现波动,不利于顺利排渣,气泡弥散程度降低,导致反应速率下降。随着铜锍深度增加,旋涡搅拌范围增大,旋流强度越强,渣层变得短且厚,有利于排渣;但是,当熔池深度增大到一定程度,渣眼直径急剧减小,导致无法下料,并且铜锍卷渣程度增大。随着渣层厚度增加,铜锍层内气泡尺寸增大,气含率提高,渣眼尺寸急剧减小,甚至消失,漩涡同时出现在铜锍层和渣层内,导致卷渣严重。
-
表 1 废旧NCA锂电池正极物料化学成分
Table 1 The Chemical composition of waste NCA lithium battery cathode materials

-
[1] SWAIN B. Recovery and recycling of lithium: a review[J]. Separation & Purification Technology, 2017, 172: 388-403.
[2] SONOC A, JESWIET J. A Review of Lithium supply and demand and a preliminary investigation of a room temperature method to recycle lithium-ion batteries to recover lithium and other materials[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2014, 15: 289-293. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2014.06.006
[3] ALEXANDRU, SONOC, JACK, et al. Opportunities to improve recycling of automotive lithium ion batteries[J]. Procedia Cirp, 2015, 29: 752-757. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2015.02.039
[4] GRUBER P W, MEDINA P A, KEOLEIAN G A, et al. Global lithium availability[J]. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 2011, 15(5): 760-775. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00359.x
[5] 林若虚. 锂离子电池正极材料简介及标准布局浅析[J]. 中国金属通报, 2021(8): 107-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSTB202108053.htm [6] 李方昊, 杨建元. 废旧锂电池正极材料回收研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2021, 41(1): 90-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDHG2021S1019.htm [7] MESHRAM P, PANDEY B D, MANKHAND T R. Extraction of lithium from primary and secondary sources by pre-treatment, leaching and separation: A comprehensive review[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 150: 192-208. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.10.012
[8] A T T, A D S, C H O, et al. Distributions of lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride battery elements in copper converting[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 168: 399-409. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.051
[9] ZHENG Y, SONG W, Mo W T, et al. Lithium fluoride recovery from cathode material of spent lithium-ion battery[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(16): 8990-8998. doi: 10.1039/C8RA00061A
[10] ZENG X, LI J, SINGH N. Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery: a critical review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 10(44): 1129-1165.
[11] ZHANG X, XIE Y, LIN X, et al. An overview on the processes and technologies for recycling cathodic active materials from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Mater. Cycles Waste Manage, 2013, 15(4): 420-430. doi: 10.1007/s10163-013-0140-y
[12] HEYDARIAN A, MOUSAVISM, VAKILCHAP F, et al. Application of a mixed culture of adapted acidophilic bacteria in two-step bioleaching of spent lithium-ion laptop batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 378: 19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.12.009
[13] TIRRONEN T, SUKHOMLINOV D, OBRIEN H T, et al. Distributions of lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride battery elements in copper converting[J]. Clean. Prod, 2017, 168: 399-409. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.051
[14] 周弋惟, 陈卓, 徐建鸿. 湿法冶金回收废旧锂电池正极材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 85-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ202201007.htm [15] XIN Y, GUO X, CHEN S, et al. Bioleaching of valuable metals Li, Co, Ni and Mn from spent electric vehicle Li-ion batteries for the purpose of recovery[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 116: 249-258. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.001
[16] DUTTA D, KUMARI A, PANDA R, et al. Close loop separation process for the recovery of Co, Cu, Mn, Fe and Li from spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 200: 327-334. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.02.022
[17] ORDONEZ J, GAGO E J, GIRARD A. Processes and technologies for the recycling and recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 60: 195-205. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.363
[18] 陈艳, 胡显智. 电子废料中贵金属的回收利用方法[J]. 中国矿业, 2006(12): 102-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA200612030.htm [19] TORKAMAN R, ASADOLLAHZADEH M, TORAB MOSTAEDI M, et al. Recovery of cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries by using acidic and basic extract ants in solvent extraction process[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 186: 318-325. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.06.023
[20] CHEN M, WANG R, QI Y, et al. Cobalt and lithium leaching from waste lithium-ion batteries by glycine[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 482: 228942. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228942
[21] MUSARIRI B, AKDOGAN G, DORFLING C, et al. Evaluating organic acids as alternative leaching reagents for metal recovery from lithium-ion batteries[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 137: 108-117. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.03.027
[22] 崔鹏媛, 俞小花, 冯天意, 等. 废旧三元锂电池正极材料的回收再生研究[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(6): 151-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS202206019.htm [23] QUIJADA-MALDONADO E, OLEA F, R SEPúLVEDA, et al. Possibilities and Challenges for ionic liquids in hydrometallurgy[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 251: 117289.
[24] YADAV D, BANERJEE R. A comparative life cycle energy and carbon emission analysis of the solar carbon thermal and hydrometallurgy routes for zinc production[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 229, 577-602.
[25] PENG C, LIU F, WANG Z, et al. Selective extraction of lithium (Li) and preparation of battery grade lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) from spent Li-ion batteries in nitrate system[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 415(3): 179-188.
[26] NAN J, HAN D, ZUO X. Recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion batteries with chemical deposition and solvent extraction[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 152(12): 278-284.
[27] HU J T, ZHANG J l, LI H X, et al. A promising approach for the recovery of high value-added metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 351(3): 192-199.
[28] LIU F P, PENG C, MA Q X, et al. Selective lithium recovery and integrated preparation of high-purity lithium hydroxide products from spent lithium-ion batteries-ScienceDirect[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 259: 118181.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 闫红杰,黄正宗,郝澳,夏韬,刘柳. 基于DPM-VOF耦合的高铅渣底吹还原炉内多相流动数值模拟. 中国有色金属学报. 2025(02): 607-620 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨世亮,肖清泰,徐建新,王华. 有色金属熔池熔炼过程混沌流非线性强化研究进展综述. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 1-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曹赓,赵俊学,王冠杰,郑江华,宗红星,李彬,崔雅茹. 镍冶炼渣中铁资源回收研究现状及发展分析. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(04): 471-478 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 戴鹏飞,张斌,黎显俊,尹一鸣,吴怡康,李明周. 高温铜渣风淬造粒实验研究及铜渣液滴冷凝过程的数值模拟. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(05): 650-659 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 张磊,潘从元,汪勇. LIBS成分检测与Ausmelt数模系统协同优化铜熔炼用氧实践. 铜业工程. 2023(06): 181-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: