Surface modification mechanism of magnesium hydroxide (101) based on density functional theory
-
摘要: 近年来,氢氧化镁已广泛应用于制备阻燃材料,但其产品存在表面极性高、易团聚、不易与高分子材料相容等不足。本研究基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的理论计算,对常用改性剂(油酸、硅烷偶联剂G-570(γ-甲基丙烯酰氧基丙基三甲氧基硅烷)以及甲基丙烯酸甲酯(MMA))在氢氧化镁(101)表面的吸附情况进行了模拟,研究了改性剂对氢氧化镁表面的改性机理。吸附能、态密度、差分电荷密度和Mulliken布居电荷等参数的分析结果表明,3种改性剂分子中油酸的吸附能最低,可在氢氧化镁(101)表面稳定吸附,并且吸附的油酸与氢氧化镁(101)表面之间有明显电荷转移,形成Mg-O相互作用,而这种相互作用正是氢氧化镁表面改性的关键。本研究为提高氢氧化镁阻燃材料的性能提供了有价值的理论指导。Abstract: In recent years, magnesium hydroxide has been one of the most widely used flame retardant materials, but its products still have shortcomings, such as high surface polarity, ease of reunion and difficulty in compatibility with polymer materials. In this paper, the adsorption of oleic acid, silane coupling agent G-570 (γ-methacryloxy propyl trimethoxysilane) and methyl methacrylate (MMA) on the surface of magnesium hydroxide (101) was simulated by density functional theory (DFT), and the modification mechanism on the surface of magnesium hydroxide was studied. The results were analyzed by adsorption energy, the density of states, differential charge density and Mullikan population charge. The results show that oleic acid has the lowest adsorption energy among the three modifier molecules and can be stably adsorbed on the magnesium hydroxide (101) surface. After adsorption, there is obvious charge transfer between oleic acid and the magnesium hydroxide (101) surface, forming Mg-O interactions, which is the key to the surface modification of magnesium hydroxide. The research results of this paper provide useful theoretical guidance for improving the properties of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant materials.
-
氢氧化镁(Mg(OH)2)因兼具无毒、无味、无腐蚀、阻燃、消烟、热分解温度高(340~450 ℃)和环保等优点,已成为高分子材料阻燃领域中极具前途的阻燃剂之一[1]。但是,目前研发的氢氧化镁阻燃剂还存在如下不足[2]:①产品粒径大,阻燃效率低,实际应用时需大量填充,严重损害材料的力学性能。②产品粒度不均匀,团聚现象严重,不利于在高分子材料中分散。③产品表面极性强,与有机高分子的相容性较差。④以水氯镁石制备的氢氧化镁,氯含量高,作为阻燃剂会产生HCl等有害气体。为弥补上述不足,研究者从制备方法和表面改性方面,对氢氧化镁的形貌、粒径和表面极性等进行了研究。
在改性方面,目前大部分研究集中于改性剂的选择,在制备过程中,通过表面活性剂(硬脂酸钠等)、偶联剂(有机硅烷等)以及表面聚合包覆(聚合物等)降低表面极性和增加与有机高分子的相容性。PIPEROPOULOS等[3]研究了表面活性剂十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)对氢氧化镁结构、形貌和物理性能的影响,结果表明,当CTAB浓度为2.0 mmol/L时,促进形成了分离良好的氢氧化镁颗粒,降低了氢氧化镁的平均粒径;ZHU等[4]采用钛酸酯偶联剂改善氢氧化镁与聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)的相容性,结果表明,直径为0.1~0.5 μm的PET与改性纳米Mg(OH)2颗粒(改性剂含量:10%、20%和30%)相容性良好;YANG等[5]以合成的碳微球包覆氢氧化镁提高其阻燃性能,结果表明,氢氧化镁和碳微球(CMSs)对PET具有协同阻燃作用。虽然这些方法可以在一定程度上改善氢氧化镁的粒径分布和表面极性,但对氢氧化镁生长机制、粒径控制机理和改性剂机理的研究较少,开发存在一定的盲目性。
密度泛函理论(Density Functional Theory,DFT)近几年在材料合成、模拟计算等方面的应用研究取得了较大进展,成为计算凝聚态物理、计算量子化学和计算材料科学的重要根基和中心技术,其应用范围越来越广[6-8]。本研究基于DFT方法,选取了3种常用的氢氧化镁改性剂:油酸[9]、硅烷偶联剂G-570(γ-甲基丙烯酰氧基丙基三甲氧基硅烷)以及甲基丙烯酸甲酯(MMA)[10],计算模拟了这3种物质在氢氧化镁表面的吸附过程,探究氢氧化镁(101)表面的改性机理,并通过吸附能、态密度、差分电荷密度和Mulliken布居电荷分析界面之间的相互作用。
本研究从理论上分析改变氢氧化镁表面极性、提高氢氧化镁与有机材料相容性的改性机理,再结合实际生产,以期制备高分散、高附加值的氢氧化镁阻燃材料。我国盐湖资源丰富,富含大量镁资源,而作为盐湖资源开发废弃物之一的水氯镁石产量很高,大量堆积的水氯镁石不仅极大地浪费了资源,还会形成“镁害”,威胁当地生态环境。因此,利用盐湖废弃水氯镁石制备高性能氢氧化镁阻燃材料,不仅可以保护盐湖地区生态环境,还能增加经济效益,实现废弃水氯镁石的综合利用,对于盐湖资源的高效开发和高值化利用具有重要意义。
1 计算方法和模型建立
1.1 计算方法
本研究采用DFT理论计算方法对氢氧化镁改性机理进行分析。DFT被广泛用于描述分子之间的相互作用[11]。利用Materials Studio软件Adsorption Locator模块中的模拟退火法确定吸附的最佳位置,选择由原子集定义的表面区域,最大吸附距离设置为5 Å(1 Å = 0.1 nm);几何优化则在DMol3模块中进行,采用PBE(Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof)开发的广义梯度近似(Generalized Gradient Approximatio,GGA)泛函计算交换关联能,采用DFT Semi-core Pseudopots处理原子的内层电子,基组为DNP双重数值基组[12]。布里渊区k点网格设置为1 × 1 × 1,自洽收敛为2 × 10‒5 Ha,最大应力为0.005 Ha/Å,最大位移为0.005 Ha[13]。为了评估界面与分子间的相互作用和电荷转移情况,进行了吸附能、态密度、差分电荷密度和布居数的分析[12, 14]。
1.2 模型建立
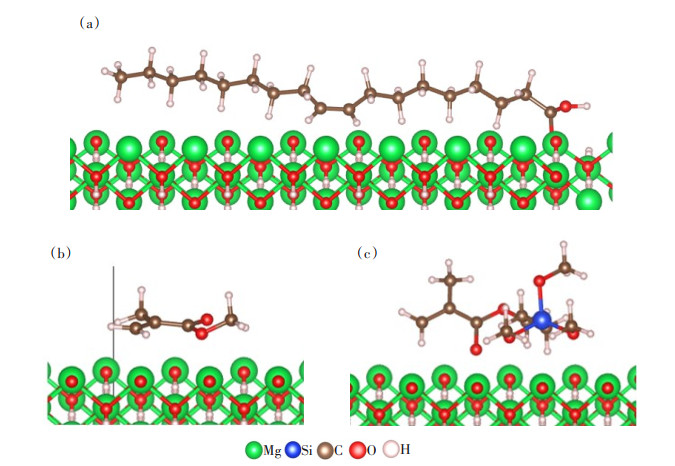
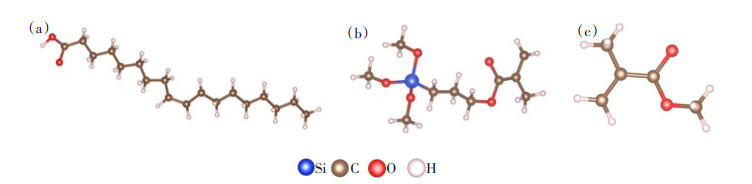
油酸、硅烷偶联剂G-570和MMA模型如图 1所示:图 1(a)为优化后的油酸分子,其分子式为C18H34O2;图 1(b)为优化后的硅烷偶联剂G-570,其分子式为C10H20O5Si;图 1(c)为优化后的MMA,其分子式为C5H8O2。
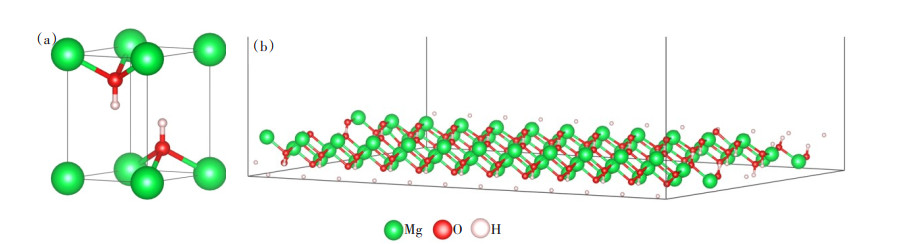
氢氧化镁(101)面模型(图 2(b)):氢氧化镁模型由Materials Pjoject网站下载后优化得到(图 2(a)),氢氧化镁(101)面模型如图 2(b)所示,优化后晶格常数与文献[15]相比较吻合(表 1),其误差低于2%,这表明优化后的结构模型与实际相符合, 本计算方法以及所设置实验参数合理,结果可靠。由于氢氧化镁晶体在(101)面有微观内应变,具有表面极性大、表面能高、晶粒易团聚的特点[16],是氢氧化镁改性研究的重点内容,因此构建了一层6 × 6 × 1氢氧化镁(101)表面模型,真空层厚度设置为30 Å,以避免不必要的潜在相互作用力[17];结构优化后,氢氧化镁(101)面的H-O-Mg和O-Mg-O键角分别为125.3°和110.1°、层间距离为2.335 Å,与文献[18]一致,计算结果合理。
表 1 氢氧化镁晶格常数对比Table 1. Comparison of lattice constants of Mg(OH)2
2 结果与讨论
2.1 稳定性分析
氢氧化镁表面吸附改性剂的稳定性可由吸附能进行判断,若吸附能为负值,则表明吸附为放热反应,吸附能绝对值越大,吸附越稳定[19],计算公式如式(1)所示[20]:

(1) 式(1)中:Ea为吸附能;EMH/abs为氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附改性剂后的能量;EMH为氢氧化镁(101)表面的总能量;Eabs为表面改性剂的总能量。
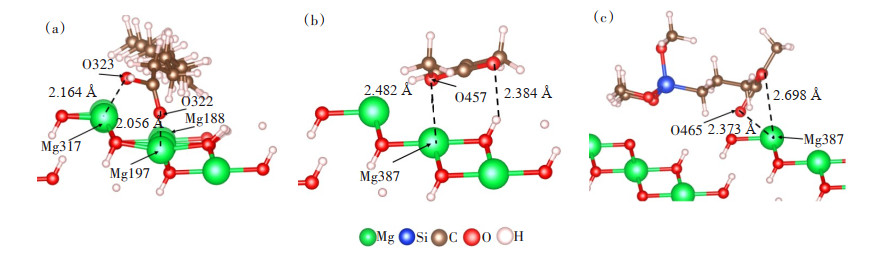
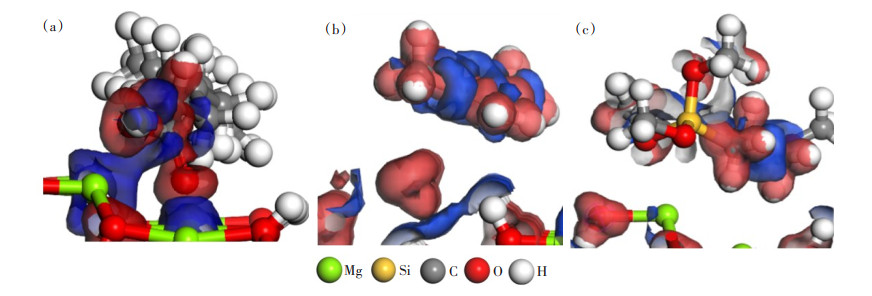
通过吸附定位确定3种改性剂在氢氧化镁(101)表面的最佳吸附位点,即吸附能最低的模型(图 3);然后将所得模型进行几何优化,获得硅烷偶联剂G-570、MMA和油酸吸附在氢氧化镁(101)面的最优结构(图 4);计算得到吸附3种改性剂时的吸附能,结果见表 2。
表 2 氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附改性剂吸附能计算结果Table 2. Calculation results of adsorption energy of magnesium hydroxide (101) surface adsorption modifier
如图 4(a)所示,吸附后油酸与氢氧化镁(101)表面相邻原子之间的距离为2.164、2.056 Å,硅烷偶联剂G-570、MMA与氢氧化镁(101)表面相邻原子之间的距离约为2.5 Å。由于相互作用的强度与距离成反比[21],所以氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附油酸体系的结构稳定性更强。结合表 2数据分析,相比硅烷偶联剂G-570和MMA,氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附油酸体系的吸附能更低,稳定性更好。
2.2 态密度分析
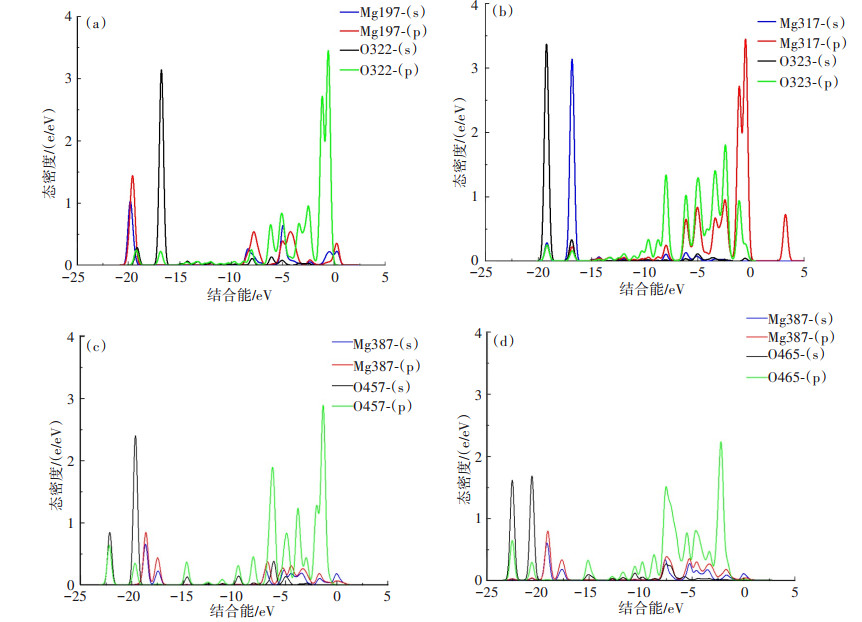
为了进一步揭示吸附质和氢氧化镁之间的相互作用的本质,对吸附后的氢氧化镁进行了基于能带理论的分波态密度分析(Partial Density of States,PDOS)。若相邻原子之间的分态密度在相同能量处出现了尖峰,可用于直观说明吸附质和氢氧化镁(101)表面相邻原子之间的作用强弱[22]。
吸附质和氢氧化镁(101)表面相邻原子之间的PDOS分析如图 5所示,即3种吸附体系中Mg原子和O原子的杂化峰重叠情况。由图 5可见,在-25~5 eV之间,这3种吸附体系的Mg原子和O原子的s、p轨道均存在杂化峰,其中,吸附油酸体系的Mg317和O323之间的杂化峰数量最多,表明氢氧化镁吸附油酸的相互作用力最强,这也与前述实验结果一致。
2.3 差分电荷密度分析
为了更加直观地表征改性剂和氢氧化镁(101)表面之间的相互作用力,对吸附后的电子密度差进行了分析,以揭示吸附过程中电子密度的变化,其计算公式如式(2)所示:

(2) 式(2)中:Δρ为吸附前后的电子密度差;ρabs+MH为吸附后的总电子密度;ρabs为油酸的电子密度;ρMH为氢氧化镁(101)表面的电子密度。
图 6所示为氢氧化镁(101)表面3种吸附体系的差分电荷密度图,电荷减少和电荷密集的区域分别表示为蓝色和红色,等值面为0.05 e/Å。由图 6(a)可见,油酸末端羧基O原子周围电荷比较密集,蓝色区域主要在氢氧化镁(101)表面Mg原子周围,并且油酸与氢氧化镁表面之间电子转移明显,说明在吸附过程中,电子从氢氧化镁(101)表面转移到油酸末端羧基,形成较强的Mg-O相互作用;而MMA(图 6(b))和硅烷偶联剂G-570(图 6(c))与氢氧化镁表面之间的电子转移并不明显,说明并未形成较强的相互作用力。
2.4 Mulliken布居电荷分析
Mulliken布居电荷分析有助于更清晰地研究吸附质在氢氧化镁(101)表面的电子转移情况[23-24],具体分析如表 3所列。
表 3 氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附体系布居电荷分析Table 3. Population charge analysis of magnesium hydroxide (101) surface adsorption system
由表 3可知,3种吸附体系中氢氧化镁(101)表面的Mg原子均失去电子、吸附质的O原子均得到电子,并且与其他2种体系相比,吸附油酸体系的得失电子数最多、电荷转移数最多、相互作用力最大。因此,油酸可稳定吸附在氢氧化镁(101)表面,得益于油酸和氢氧化镁之间能够形成较强的Mg-O相互作用,这也与上述态密度、差分电荷密度和吸附能的分析结果一致。
3 结论
基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的理论计算,对常用改性剂油酸、硅烷偶联剂G-570以及MMA在氢氧化镁(101)表面的吸附情况进行了模拟,研究了改性剂对氢氧化镁表面的改性机理。吸附能、态密度、差分电荷密度和Mulliken布居电荷等参数的分析结果表明,3种改性剂分子均可吸附在氢氧化镁(101)表面,以降低表面能,其中,油酸的吸附能最低,可在氢氧化镁(101)表面稳定吸附,并且吸附后油酸与氢氧化镁(101)表面之间发生了明显的电荷转移,形成Mg-O相互作用。改性剂通过这种相互作用稳定吸附在氢氧化镁表面,改变了氢氧化镁表面极性,提高氢氧化镁与高分子材料的相容性。本研究为提高氢氧化镁阻燃材料的性能研究提供了理论参考。
-
表 1 氢氧化镁晶格常数对比
Table 1 Comparison of lattice constants of Mg(OH)2

表 2 氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附改性剂吸附能计算结果
Table 2 Calculation results of adsorption energy of magnesium hydroxide (101) surface adsorption modifier

表 3 氢氧化镁(101)表面吸附体系布居电荷分析
Table 3 Population charge analysis of magnesium hydroxide (101) surface adsorption system

-
[1] 曹雨微, 逯登琴, 宋学文, 等. 氢氧化镁阻燃材料改性工艺研究现状[J]. 盐科学与化工, 2019, 48(9): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHYH201909001.htm [2] PILARSKA A A, KLAPISZEWSKI Ł, JESIONOWSKI T. Recent development in the synthesis, modification and application of Mg(OH)2 and MgO: a review[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 319: 373-407. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.07.009
[3] PIPEROPOULOS E, MASTRONARDO E, FAZIO M, et al. Enhancing the volumetric heat storage capacity of Mg(OH)2 by the addition of a cationic surfactant during its synthesis[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 215: 512-522. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.047
[4] ZHU Y M, WANG Y, SHA L, et al. Design of antibacterial polyethylene terephthalate masterbatch functionalized by modified nano-Mg(OH)2[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(46): 46755. doi: 10.1002/app.46755
[5] YANG Y, NIU M, LI J, et al. Preparation of carbon microspheres coated magnesium hydroxide and its application in polyethylene terephthalate as flame retardant[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2016, 134: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.09.019
[6] LIU S B, ZHANG X J. Chemical concepts from density functional theory[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2018, 34(6): 563-566.
[7] 何桂春, 蒋巍, 项华妹, 等. 密度泛函理论及其在选矿中的应用[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2014, 5(2): 62-66. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2014.02.011 [8] PACCHIONI G, CLOTET A, RICART J M. A theoretical study of the adsorption and reaction of SO2 at surface and step sites of the MgO (100) surface[J]. Surface Science, 1994, 315(3): 337-350. doi: 10.1016/0039-6028(94)90137-6
[9] ASADI A, ASADI M, SIAHMARGOI M, et al. The effect of surfactant and sonication time on the stability and thermal conductivity of water-based nanofluid containing Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles: an experimental investigation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 108: 191-198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.12.022
[10] 李芮地, 王晨, 南婷婷, 等. Mg(OH)2-BA-MMA对PVC硬制品加工性及热稳定性影响[J]. 现代塑料加工应用, 2021, 33(5): 25-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSL202105007.htm [11] LEE S G, CHOI J I, KOH W, et al. Adsorption of β-d-glucose and cellobiose on kaolinite surfaces: density functional theory (DFT) approach[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2013, 71: 73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.11.002
[12] 王群, 林小龙, 孙静, 等. 有机添加剂柠檬酸与乙二胺四乙酸吸附在Mg(0001)表面的计算模拟研究[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2022, 39(3): 38-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZYF202203006.htm [13] KWON S, CHOI J I, LEE S G, et al. A density functional theory (DFT) study of CO2 adsorption on Mg-rich minerals by enhanced charge distribution[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2014, 95: 181-186. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2014.07.042
[14] 凡杰, 谢刚, 田林, 等. ZnS掺杂Fe2+电子结构第一性原理计算及对矿物浸出的影响[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2021, 12(2): 1-7. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2021.02.001 [15] AZUMA K, ODA T, TANAKA S. Vibrationanalysis of O-H stretching mode in Mg(OH)2, Ca(OH)2, LiOH and NaOH by plane-wave pseudopotential DFT calculation[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2011, 963(1): 215-220. doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2010.10.029
[16] 刘春英, 冯锡兰, 李汝奕, 等. 片状氢氧化镁阻燃剂的制备、表面改性及其测试[J]. 当代化工, 2021, 50(1): 76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHH202101026.htm [17] 张新明, 刘建才, 唐建国, 等. 铝晶体自由表面的稳定性计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(10): 1759-1765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ200910010.htm [18] ZHANG D Y, ZHANG P X, SONG S H, et al. Simulation of magnesium hydroxide surface and interface[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 612: 315-322. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.05.198
[19] WANG Q, WANG M H, WANG K F, et al. Molecular mechanisms of interactions between BMP-2 and graphene: effects of functional groups and microscopic morphology[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 525: 146636. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146636
[20] 景晓环, 郭瑞华, 安胜利, 等. 乙醇在Pt低指数晶面吸附的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2022, 46(2): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXJS202202009.htm [21] WANG Q, WANG M H, WANG K F, et al. Interactions of anionic and neutral serine with pure and metal-doped graphene studied by density functional theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2016, 29(4): 437-444.
[22] 王群, 孙玉希, 曹宇, 等. 含硫氨基酸与本征及缺陷石墨烯表面的相互作用[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2020, 37(3): 323-330. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZYF202003003.htm [23] ZHENG X F, LIU L Z, NIE Z Y, et al. The differential adsorption mechanism of hexahydrated iron and hydroxyl irons on a pyrite (1 0 0) surface: a DFT study and XPS characterization[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 138: 215-225.
[24] WANG Q, SHE W Q, LU X, et al. The interaction of hyaluronic acid and graphene tuned by functional groups: a density functional study[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2019, 1165: 112559.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 王浦璠,邓道繁,陈果,张慧宁,廖春发. 基于第一性原理的Fe(111)/Al_2O_3(0001)界面稳定性研究. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(02): 158-166 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 曾书航,王泽艳,李智力,廖杰,李嘉霖,何东升,唐远,付艳红. 基于BP神经网络的聚丙烯/氢氧化镁复合材料阻燃性能预测模型. 塑料科技. 2024(05): 18-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘航辰,陈海停,刘若涵,赵鹏博,赵志朋,刘俊琪,胡浩. 第一性原理设计阳离子掺杂H-Nb_2O_5负极材料及其电化学性能研究. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(05): 732-739 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 王诗雯,鲁杨帆,丁朝,李建波,陈玉安,谭军. Ti基催化剂改性Mg基储氢材料的研究进展. 稀有金属. 2023(12): 1642-1656 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: