Dissipative particle dynamics of the sadsorption propertiesof compound additives on the surface of dicalcium silicate
-
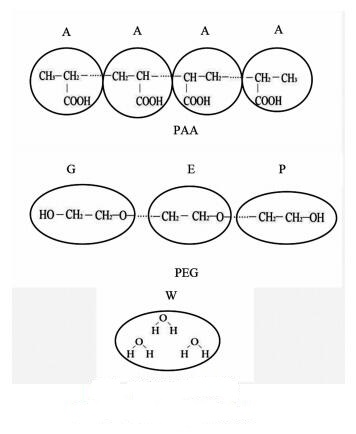
摘要: 采用耗散粒子动力学模拟方法(DPD)研究了聚丙烯酸(PAA)与聚乙二醇(PEG)复配添加剂在硅酸二钙表面的吸附性能。为了合理地表征聚合物与硅酸二钙表面的相互作用,聚合物与表面的相互作用通过匹配分子动力学(MD)计算得到的过剩吸附量与DPD计算得到的过剩吸附量来确定,从而实现介观与微观尺度之间的耦合。研究结果表明,PAA5:PEG5复配添加剂吸附效果、驱替水分子的能力以及自身吸附稳定性皆强于单一添加剂PAA、PEG。在PAA5:PEG5复配添加剂在吸附过程中,聚合物PAA与PEG之间存在着协同作用,使其抑制硅酸二钙分解的效果较优。Abstract: Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD) method was used to study the adsorption properties of polyacrylicacid (PAA) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) compound additives on the surface of dicalcium silicate. in order to reasonably characterize the interaction between polymer and dicalcium silicate surface, mesoscopic polymer-surface interactions are determined by matching the surface excess, as computed with atomistic molecular dynamics (MD), with those for DPD, thus realizing a coupling between the mesoscopic and atomistic scales. The results showed that the optimal ratio of compound additive is 5:5, which features better adsorption effect, water displacement ability and self-adsorption stability than that of single PAA or PEG additive. in the adsorption process of PAA5:PEG5 composite additive, there is a synergistic effect between polymer PAA and PEG, which makes it the best inhibitor for decomposition of dicalcium silicate.
-
0 引言
锂离子电池凭借其高能量密度、长循环寿命、对环境友好等优势已成为一种应用广泛的电池[1-2]。但是锂离子电池的高成本、低安全性和苛刻的生产条件等问题使其应用受到了限制,难以应用于大规模的储能系统。可充电的水系锌离子电池作为一种具有低成本、高安全性、对环境友好和较高的能量密度等特点的储能设备成为近年来的热门研究对象,而且有望成为大规模储能设备的候选之一[3-5]。
由于金属锌负极具有储量丰富、成本低廉、较低的标准电极电势(约为-0.76 V)、冶炼与加工工艺较为成熟和超高的理论体积能量密度(5 851 mAh/cm3)等优点,水系锌离子电池通常直接使用纯金属锌箔作为电池负极[6-9]。然而在实际应用中,金属锌负极还面临着诸多挑战。对于锂、钠、钾、镁、锌等纯金属负极,在电池的充放电过程中,倾向于形成较为粗糙和不均匀的表面,而随着循环时间的增加,金属离子在负极不断发生沉积/溶解反应,金属电极表面容易形成枝晶[10]。在锌离子电池中,锌枝晶容易刺破电池隔膜导致电池短路,若枝晶从负极脱落进入电解液中,则会与电极失去电接触变成无电化学活性的死锌,从而极大地影响电池的可逆容量、库仑效率和循环稳定性[7, 11]。因此,寻找一种无枝晶的负极材料是发展高性能水系锌离子电池的关键之一。
为了抑制锌枝晶的生长获得高度可逆的水系锌离子电池负极材料,研究者研究了3D结构设计[12-13],涂覆高导电性涂层或与高导电性材料复合[14-15],制备锌合金负极[16-17]等策略对锌负极进行改性,这些策略均取得了不错的效果。然而这些改性策略大多原料成本较高、制备工艺复杂,难以大规模应用。与上述策略相比,在锌负极表面涂覆氧化物涂层,诱导锌在涂层下均匀沉积,是制备无枝晶负极的一种工艺较为简单却行之有效的锌负极改性策略。以前的研究表明,通过各种方法制备的ZrO2[11]、Al2O3[18]和TiO2[19]涂层改性锌负极均可以有效抑制锌枝晶的生长,改善锌负极的电化学性能,然而使用商业化二氧化钛粉体作为涂层时,其对锌负极的电化学性能改善效果却不太理想。鉴于上述问题,本文制备了一种工艺简单,成本较低的锐钛矿型纳米二氧化钛粉体,将其涂覆到锌箔上制备了改性锌负极,并且通过各种表征手段和测试方法,研究了二氧化钛涂层对锌负极电化学性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 材料的制备
在250 mL的烧杯中加入100 mL的无水乙醇和3 mL的浓氨水,用玻璃棒搅拌混合均匀得到混合溶液。在45 ℃恒温水浴及高速搅拌的条件下,将4.5 mL的钛酸四丁酯在30 min内逐滴缓慢地滴加到该混合溶液中。在持续水浴以及高速搅拌12 h后,得到乳白色的二氧化钛溶胶,之后再将其静置陈化24 h得到白色沉淀物。将白色沉淀物过滤、洗涤、干燥即可得到无定形二氧化钛粉体。最后将无定形二氧化钛粉体置于马弗炉中,以5 ℃/min的升温速率,在空气气氛下450 ℃煅烧5 h制备得到锐钛矿型纳米二氧化钛粉体,简记为a-TiO2。
1.2 材料结构和形貌的表征
使用X射线衍射技术分析材料的晶体结构,采用日本Rigaku D/Max-2500型衍射仪进行测试,扫描的角度范围为10°~90°,步长为0.02°,扫描速率为5(°)/min(靶材为铜靶,λ=0.154 06 nm)。材料和电极表面形貌的观察采用美国MLA650F场发射扫描电子显微镜。
1.3 电化学性能测试
1.3.1 对称电池的组装
实验通过纽扣电池(CR2032型)来评估改性锌负极的电化学性能。将制备得到的锐钛矿型纳米二氧化钛粉体(a-TiO2)和聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)按9∶1的质量比混合在N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)中制成均匀浆料涂覆在锌箔上制备Zn@a-TiO2电极,未改性的纯锌箔记为Bare-Zn电极。采用Zn@a-TiO2作正极和负极,2 mol/L ZnSO4水溶液为电解液,玻璃纤维滤膜(Whatman,GF/A)作为隔膜组装Zn/Zn对称电池。此外,作为对比,采用Bare-Zn作正负极,其他条件不变的情况下组装Zn/Zn对称电池。
1.3.2 全电池的组装
将MnO2、Super P(一种导电炭黑)和PVDF按7∶2∶1的质量比混合在NMP中制成均匀浆料涂覆到钛箔上制备MnO2电极。然后以MnO2电极作正极,分别以Bare-Zn和Zn@a-TiO2电极作负极,2 mol/L ZnSO4+0.1 mol/L MnSO4溶液为电解液,玻璃纤维滤膜(Whatman,GF/A)作为隔膜组装成全电池,分别记为Bare-Zn/MnO2电池和Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池。
1.3.3 电池的电化学性能测试
对称电池和全电池均使用新威电池测试系统进行恒电流充放电测试,测试条件为:恒温25 ℃。电池的循环伏安曲线使用上海辰华CHI760E型电化学工作站记录,测试的电压范围为1.0~1.9 V,扫描速率为0.1 mV/s。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 材料结构分析与形貌表征
图 1(a)所示为a-TiO2粉体的SEM图像,从图 1(a)中可以看出制备得到的a-TiO2粉体的形貌大致为大小不一的球状。a-TiO2的一次颗粒的粒径约为10~20 nm,且形状多为不规则的小球体,但由于材料的分散性欠佳,这些纳米级的一次颗粒团聚成粒径从50 nm到2 μm不等的二次颗粒。由图 1(b)可知,未经过450 ℃煅烧的前驱体无定形TiO2的XRD图谱无明显的衍射峰,为典型的非晶态材料的XRD图谱;而经过450 ℃煅烧后的a-TiO2的XRD图谱衍射峰与锐钛矿型TiO2的标准PDF卡片(PDF No.#84-1286)的特征峰基本一致,且(101)、(200)、(004)晶面对应的3个强峰的强度也基本一致,但衍射峰的半峰宽较大,说明经过煅烧后的材料为锐钛矿型TiO2,但材料的结晶性略差。
2.2 Zn/Zn对称电池性能
组装Zn/Zn对称电池并测试其电化学性能是一种评价改性后的锌负极性能的常用方法。为了验证a-TiO2涂覆层是否可以抑制Zn枝晶的生长,促进Zn的均匀沉积/溶解,以期提高电池容量并且改善电池循环稳定性,分别用Bare-Zn和Zn@a-TiO2电极组装了Zn/Zn对称电池,并进行电化学测试。使用扫描电子显微镜对循环前后的电极形貌进行观察,结合能谱仪进行分析,从微观角度分析Zn的沉积/溶解行为。图 2(a)所示为Zn/Zn对称电池在电流密度为1 mA/cm2,充放电容量为1 mA h/cm2条件下的恒电流充放电测试结果。结果表明Bare-Zn电极在初期的极化电压约为94 mV,且在循环约50 h后极化电压开始大幅增加,这可能是由于Bare-Zn电极表面发生了Zn的析氢反应或是无电化学活性的死锌的增多,导致极化电压升高。而同样的测试条件下Zn@a-TiO2电极的极化电压仅为47 mV,且在稳定循环了520 h后,电极的极化电压几乎没有变化,始终维持在50 mV之内且没有出现短路现象,这表明a-TiO2可以减少副反应的发生,避免锌枝晶的形成,使锌负极的循环寿命大大提高。文献[20]研究表明,通过原子层沉积法制备的超薄二氧化钛涂层改性锌负极可以在电流密度为1 mA/cm2,充放电容量为1 mA h/cm2条件下稳定循环150 h,而涂覆了商业化二氧化钛涂层和高度暴露(001)晶面的二氧化钛保护层的锌负极在相同的测试条件分别可以稳定循环190 h和460 h[19]。因此,与文献[20]的研究结果相比,a-TiO2涂层改性锌负极的循环性能更加优秀。
为了测试Zn@a-TiO2电极的倍率性能,分别在0.25、0.5、1、2、5 mA/cm2电流密度下进行恒电流充放电测试,每次循环的充电时间和放电时间均为1 h。测试结果如图 2(b)所示,可以发现随着电流密度的增大,Bare-Zn电极和Zn@a-TiO2电极的极化电压都在逐步升高。当电流密度达到5 mA/cm2时,Bare-Zn电极的极化电压无法保持稳定;而Zn@a-TiO2电极在所有电流密度下极化电压均可以保持平稳,且在5 mA/cm2的测试结束后,电池依然能在2 mA/cm2的电流密度下稳定循环200 h。这表明在不同电流密度下,改性锌负极的循环稳定性均高于未改性的金属锌负极。
图 3(a)和图 3(b)分别展示了电解液在Bare-Zn电极和Zn@a-TiO2电极表面接触角的大小。可以发现,电解液在2种电极表面的接触角大小有明显差异,经过测量电解液在Bare-Zn电极上的接触角为108°,在Zn@a-TiO2电极上的接触角为70°。接触角越小,说明电解液对材料表面的润湿性越好,电解液对Zn@a-TiO2电极的润湿性优于对Bare-Zn电极的湿润性,这也意味着电解液中的Zn2+可以较为容易地穿过二氧化钛涂层在锌箔表面沉积。
Zn/Zn对称电池测试结果表明,涂覆了a-TiO2涂层的Zn@a-TiO2负极的电化学性能明显优于未改性的Bare-Zn。为了探究其原因,将Zn/Zn对称电池拆解,取出极片清洗干净后分别对循环前后的电极进行了SEM测试。图 4(a)和图 4(b)分别为循环前和循环50 h后的Bare-Zn电极的SEM图像,可以看出在循环前Bare-Zn电极表面较为平整,无明显的凸起与裂纹,而循环50 h后的Bare-Zn电极表面变得十分粗糙,密集分布着杂乱无序的片状物,这些片状物是充放电过程中在电极表面沉积、生长的金属锌晶粒。这些晶粒大小不一,生长的取向也各不相同,这会造成循环过程中电极表面电场分布不均,晶粒凸起部分比底部的Zn基底更容易发生Zn的沉积。随着循环时间的增长,凸起部分容易形成纵向生长的锌枝晶,导致电池容量下降甚至短路,Bare-Zn电极较差的电化学表现也证实了这一观点。图 4(c)展示了循环520 h后Zn@a-TiO2电极的表面形貌,可以发现电极表面上较为平整的为二氧化钛涂层,虽然有少数裂纹,但未观察到明显的凸起。将电极表面的裂纹处进行放大,可以发现在二氧化钛涂层下,锌晶粒取向较为一致地沉积在金属锌箔表面(图 4(d))。这表明二氧化钛涂层可以诱导锌在涂层下平整均匀地沉积,有效限制锌枝晶的产生,从而使电池获得稳定的电化学表现。
2.3 全电池电化学性能分析
分别使用Bare-Zn和Zn@a-TiO2作为负极,MnO2作为正极组装了Zn/MnO2全电池并对其进行电化学测试,对比了二氧化钛涂层改性锌负极和未改性锌负极在全电池中的电化学性能。文献[21]研究表明,在以Mn基材料为正极的水系锌离子电池的电解液中加入Mn2+可以抑制Mn基材料的溶解,提高电池的循环稳定性,因此Zn/MnO2全电池使用的电解液为2 mol/L ZnSO4+0.1 mol/L MnSO4溶液。图 5(a)为Zn/MnO2电池在1.0~1.9 V的电压范围内,扫描速率为0.1 mV/s时的循环伏安(CV)曲线。可以看出Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池与Bare-Zn/MnO2电池的CV曲线几乎完全重合,这表明a-TiO2涂层在充放电过程中不参与电极反应,因此不会影响电池中发生的氧化还原反应。
图 5(b)和图 5(c)分别是Zn/MnO2全电池的0.5 A/g电流密度下的循环性能图和对应的第100次循环的充放电曲线。从中可知,在0.5 A/g的电流密度下,Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池的初始放电比容量为189.08 mA h/g,略高于Bare-Zn/MnO2电池的180.65 mA h/g。随着充放电循环次数的增长,Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池的容量衰减速度明显低于Bare-Zn/MnO2电池,在100次循环后,Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池的容量保持率为82.53%,远高于Bare-Zn/MnO2电池的容量保持率(67.22%),库仑效率(CE)是研究金属负极性能的关键参数,其定义为每个循环周期的放电容量与充电容量的比值,对比2种电池的库仑效率可以发现,Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池库仑效率非常稳定,而Bare-Zn/MnO2电池的库仑效率波动明显,且在60次循环后降低到80%~90%的范围内。同时,观察第100次循环时的充放电曲线可以发现Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池的极化电压明显小于Bare-Zn/MnO2电池。这些结果均表明改性锌负极能明显提高全电池的电化学性能。测试了电池在不同电流密度下的放电比容量,如图 5(d)所示,结果表明在0.2、0.5、1、2 A/g的电流密度下,Zn@a-TiO2/MnO2电池的放电比容量均略高于Bare-Zn/MnO2电池,而在5 A/g大电流下的结果则相反。这可能是由于二氧化钛涂层的存在使得Zn@a-TiO2电极的导电性降低,导致其在大电流密度下的电化学性能表现欠佳。
3 结论
1)通过XRD、SEM、EDS等表征手段和Zn/Zn对称电池与Zn/MnO2全电池电化学性能测试,评估了锐钛矿型二氧化钛涂层对锌负极性能的改善效果。结果表明,二氧化钛涂层可以诱导锌在涂层下稳定均匀沉积,抑制锌枝晶的形成。使用改性后的锌负极组装的Zn/Zn对称电池可在1 mA/cm2的电流密度下稳定循环520 h以上,这一表现明显优于未改性锌负极。
2)分别使用未改性锌负极与二氧化钛涂层改性锌负极组装了Zn/MnO2全电池并进行了电化学性能测试。结果显示,使用改性锌负极组装的全电池在0.5 A/g电流密度下循环100次后容量保持率为82.53%,远高于用未改性锌负极组装的全电池的容量保持率(67.22%)。表明在金属锌电极表面涂覆二氧化钛涂层是一种成本低廉、工艺简单且行之有效的锌负极改性策略。
-
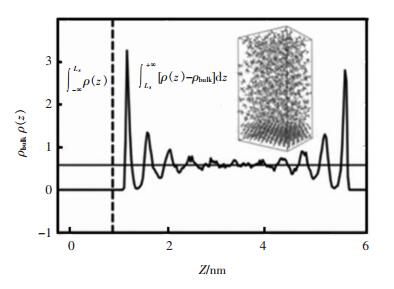
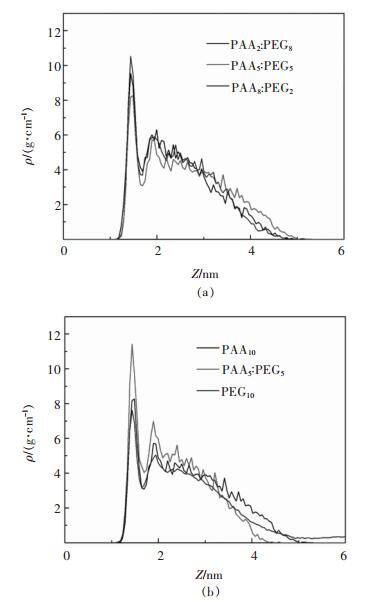
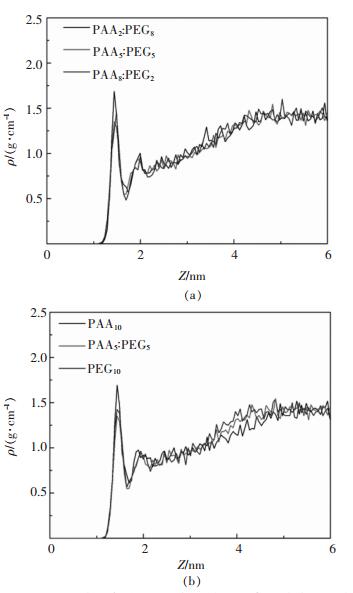
表 2 MD模拟的表面过剩吸附量(Γ′(MD)),液相珠子与硅酸二钙表面的DPD相互作用参数(ais),相同类型珠子之间的相互作用DPD参数(aii)
Table 2 MD simulation of excess surface adsorption quantity (Γ'(MD)), liquid phase on the surface of the beads and dicalcium silicate DPD interaction parameters (ais), and the interaction between the same types of beads DPD parameters (aii)

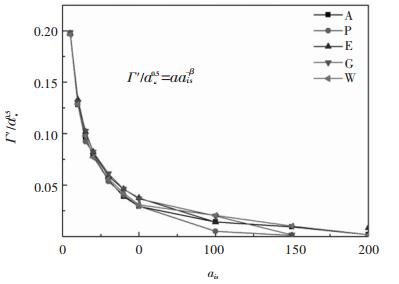
表 3 DPD中所用的斥力参数aii,aij和ais
Table 3 Repulsion parameters aii, ai and ais used in DPD

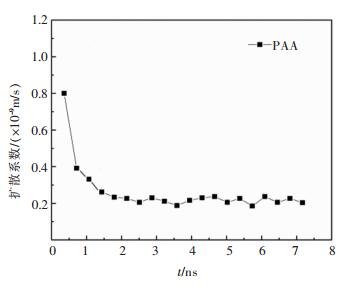
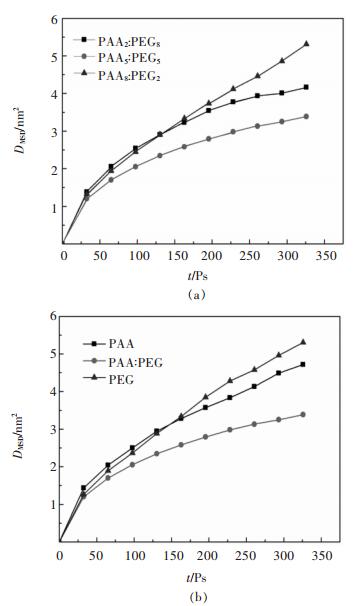
表 4 聚合物吸附层的扩散系数
Table 4 Diffusion coefficient of polymer adsorption layer

-
[1] 毕诗文.氧化铝生产工艺[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2006. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1095.2012.00057 [2] 杨重愚.轻金属冶金学[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2014. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0958.2010.05.011 [3] 王亮.提高熟料净溶出率的措施[J].轻金属, 2015(6):19-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qjs201506005 [4] 权昆, 武福运.铝酸钠溶液中硅酸二钙的分解及抑制[J].有色矿冶, 2005, 21(2):29-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysky200502009 [5] 尤晶.添加剂抑制熟料溶出二次反应的研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2005. [6] 任根宽.二次反应抑制剂及其添加工艺技术研究[J].轻金属, 2008(5):16-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qjs200805005 [7] 刘欣.添加剂抑制熟料溶出二次反应的研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2008. [8] 张玉衡.新型抑制熟料溶出二次反应抑制剂的合成及其抑制机理研究[D].赣州: 江西理工大学, 2019. [9] 康立武.烧结法熟料溶出过程中抑制二次反应的研究[D].赣州: 江西理工大学, 2010. [10] 张程忠, 于海燕, 李光柱, 等. PEG对烧结法熟料溶出过程二次反应的影响[J].轻金属, 2007(12):13-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qjs200712004 [11] 张程忠, 于海燕, 董宝才, 等.聚合物AY在硅酸二钙-铝酸钠溶液体系中的吸附和分布[J].轻金属, 2008(2):48-52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qjs200802003 [12] 丁婷婷.表面活性剂在β-2CaO·SiO2界面吸附行为热力学与电化学研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2011. [13] YU H Y, PAN X L, DING T T, et al. Adsorption of sodium polyacrylate at interface of dicalcium silicate-sodium aluminate solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(10):2323-2326. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61015-7
[14] 刘涵.聚合物在硅酸二钙表面吸附的分子动力学研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2011. [15] 佟志芳, 胡斌, 肖成, 等.聚丙烯酸在硅酸二钙表面吸附的分子动力学模拟[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2016, 7(6):25-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxysjs201606005 [16] TONG Z F, XIE Y B, ZHANG Y H. Molecular dynamics simulation on the interaction between polymer inhibitors and β-dicalcium silicate surface[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 259: 65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.018
[17] TONG Z F, ZHANG Y H, XIE Y B. Interaction mechanism between copolymer inhibitor and β-dicalcium silicate surface based on molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Molecular Physics, 2020, 118(2):1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1080/00268976.2019.1597196
[18] 张程忠.抑制熟料二次反应添加剂的研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2008. [19] HOOGERBREGGE P J, KOELMAN J M V A. Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics[J]. Europhys Leet, 2007, 19(3):155. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/19/3/001
[20] KACAR G, PETER E A J F, WITH G D. Mesoscopic simulations for the molecular and network structure of a thermoset polymer[J]. Soft Matter, 2013, 9(24):5785. doi: 10.1039/c3sm50304f
[21] KACAR G, PETER E A J F, WITH G D. A generalized method for parameterization of dissipative particle dynamics for variable bead volumes[J]. Europhys Leet, 2013, 102(4):40009. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/102/40009
[22] KACAR G, PETER E A J F, WITH G D. Structure of a thermoset polymer near an alumina substrate as studied by dissipative particle dynamics[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(40):21028. doi: 10.1021/jp409106m
[23] 刘亮. 2-MBI与SDBS协同缓蚀机理的实验与分子模拟研究[D].北京: 中国石油大学, 2015. [24] ALDER B J, GASS D M, WAINWRIGHT T E. Studies in molecular dynamics. VIII. the transport coefficients for a hard log phere Fluid[J]. Chem Phys. 1970, 53(10):3813-3826. doi: 10.1063/1.1673845
[25] CAO B Y, DONG R Y. Nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation of shear viscosity by a uniform momentum source-and-sink scheme[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2012, 231(16):5306-5316. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2012.04.017
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 范璐平,张情,张所为,陈哲. 水系锌离子电池中锌负极表面涂层的研究进展. 山东化工. 2025(05): 159-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蒋瑞,陈泰强. 锌离子化海泡石涂层锌负极的制备与性能. 广州化学. 2024(01): 49-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蔡志勇,文璟,王日初,彭超群. 增强体表面改性在高导热金属基复合材料中的应用. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(02): 237-255 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 徐杰,阮挺婷,马全新,孙蓉,路胜利. 水系锌离子电池负极改性策略研究进展. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(04): 513-526 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 周飞. 船用高比表面积二氧化钛核复合光催化材料研究. 舰船科学技术. 2023(12): 47-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李尚颖,王春源,卫文飞,汪洋. 凹凸棒石包覆的锌电极的制备及其对电池性能的影响. 硅酸盐学报. 2023(10): 2617-2625 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 范敏敏,罗成玲,薛裕华. 水系锌电池Se@Zn负极的制备及性能. 广州化学. 2023(06): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: