Effects of surface density and compaction density on properties of fast charge lithium ion battery
-
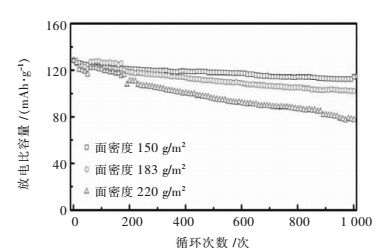
摘要: 以LiCoO2为正极材料制备成软包电池,探究不同面密度及压实密度对其快速充电性能及循环性能的影响.采用扫描电镜(SEM)及X射线衍射(XRD)技术表征正极材料表面形貌和结构的变化.实验电池以高倍率6 C充电(1 C放电)并测试其电性能.结果表明:随着面密度增加,电池内阻明显增加,放电比容量降低且循环性能变差;面密度从150 g/m2提升到220 g/m2,电池循环1 000次后容量保持率由89.06 %下降到60.45 %.而随着压实密度的提高,循环性能先提升后下降,适当增大压实密度可有效地减小电池内阻并缩短Li+迁移路径,循环性能也有所提升.当压实密度为3.32 g/cm3时,电池循环500次后,容量保持率有91.50 %.Abstract: The effects of cathode bulk density and compaction density on fast charge and cycle properties of the soft package battery, which was prepared by using LiCoO2 as cathode material, were studied. The morphology and structure of the cathode materials were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. The prepared battery was charged at high rate 6 C (discharged at 1 C) to test its electrochemical properties. With the adding cathode surface density, the discharge specific capacity and the cycle performance diminish accompanied with increasing resistance. When the bulk density is increased from 150 g/m2 to 220 g/m2, the battery capacity retention ratio falls from 89.06 % to 60.45 % after 1000 cycles. The cycle performance of LiCoO2 battery increases first and then drops with the adding compaction density. Appropriate increasing of press density can effectively reduce the resistance and shorten the migration path of Li+, which improves the battery's cycle performance. The capacity retention ratio for the battery charged at 6 C and discharged at 1 C with compaction density of 3.32 g/cm3 is 91.50 % after 500 cycles.
-
Keywords:
- lithium ion battery /
- surface density /
- compaction density /
- fast charge /
- high rate
-
0 引言
稀土元素由于其独特的电子层结构,而具有特殊的光电磁性质.随着新材料科技的发展,稀土元素的应用已经由传统的化工、冶金、陶瓷等领域扩展到磁性材料、荧光材料、催化剂等领域[1-4].目前,具有可控粒度的稀土氧化物展现了良好的市场前景,具有大粒度且颗粒分布均匀的稀土氧化物越来越受到关注[5-6].在制备金属钕时,为减少车间细颗粒粉尘和增大电解收率,氧化钕粒径较大、颗粒由小颗粒团聚而成且易于分散为最佳.玻璃工业中,为提高折射率,降低散射,提高玻璃的抗化学腐蚀性,也要求使用颗粒分布均匀的大粒径稀土氧化物.
目前,国内对于稀土化合物的研究主要集中在纳米级别,而对于大粒度稀土氧化物的报道尚不多见[7-9].王嵩龄等[10]以碳酸铈为原料,草酸为沉淀剂,采用硝酸、草酸混合淋洗草酸铈前驱体的方法,制备了D50大于20 μm的氧化铈产品.柳召刚等[11]分别以碳酸铈、氧化钇经酸溶得到的稀土盐溶液为原料,草酸为沉淀剂,制备了D50大于30 μm的氧化铈和D50大于20 μm的氧化钇.文献[12]报道,在用草酸沉淀制备稀土氧化物时,较高的酸度可抑制沉淀反应的快速进行,减小成核速度,相对增大沉淀颗粒的生长速度,易于得到粒度较大的稀土草酸盐前驱体.目前,国内用于制备大粒度稀土氧化物的原料主要为各种稀土碳酸盐、氧化物经酸溶、除杂后的稀土盐溶液,原料准备过程较复杂,工业生产成本较高.
在前期工作中,采用P507-N235双溶剂体系协同萃取稀土,去除了传统稀土萃取的皂化工序,可从源头上解决皂化萃取过程中氮氨排放问题,大幅度降低酸碱消耗,实现无氨排放和余酸利用[13].选取盐酸作为反萃剂,针对P507-N235-磺化煤油-环己烷体系的反萃性能进行了研究,确定了最佳的稀土萃取反萃工艺[14].结果表明,用3 mol/L的盐酸反萃稀土负载有机相时,稀土单级反萃率可达到98 %以上,此时稀土反萃余液中盐酸浓度可达2.3~2.5 mol/L.在上述工作的基础上,进一步设计以草酸直接沉淀稀土反萃余液制备大粒度稀土氧化物,在省去制备稀土盐溶液的酸溶、除杂工序的同时,达到充分利用反萃余液中的盐酸的目的.本文主要研究草酸直接沉淀P507-N235-磺化煤油-环己烷体系氯化钕反萃余液的影响因素,探究反萃余液中残留的有机相对前驱体粒度的影响,确定制备大粒度氧化钕的最佳工艺,实现了稀土无皂化萃取-反萃-反萃余液制备大粒度稀土氧化物整个工艺的有序衔接,为工业应用提供借鉴.
1 试验
1.1 氧化钕样品制备
原料为分析纯的草酸、P507-N235-磺化煤油-环己烷体系氯化钕反萃余液(盐酸浓度:2.3~2.5 mol/L).将草酸以一定的速度滴加到含有微量有机相的氯化钕反萃余液中,分别用水浴锅和电子搅拌器控制反应的温度和转速,得到的草酸钕前驱体经陈化、过滤、洗涤、干燥后,置于马弗炉中煅烧得到大粒度氧化钕.
1.2 样品性能表征
以OME LS-230型激光粒度仪对样品进行粒度分析;以ZEISS EVO MA 10型扫描电镜对样品进行形貌分析;以DIAMOND6000型差热仪对样品进行差热分析(氩气气氛,升温速率10 ℃/min);以Magna IR-750型光谱仪对样品进行红外分析;以Rigaku D/Max2500型转靶X射线衍射仪对样品进行物相分析.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 沉淀过程中不同反应条件对前驱体粒度的影响
2.1.1 反应温度
沉淀反应中,温度是影响颗粒大小的因素之一.当反应温度较低时,溶液过饱和度相对较大,但溶质分子的能量较低,晶粒的生成和生长速度都较慢,易于形成小颗粒.随着温度的升高,溶液过饱和度减小,黏度降低,晶粒的生长速度大大加快.继续升高温度,溶质分子动能增加过快,不利于形成稳定的晶粒,晶粒的生长速度又趋于下降.由图 1(a)可知,前驱体的粒径随着温度的升高先增加后减小.30~50 ℃范围内,晶粒粒径随着温度的升高而增大.继续升高温度,50~70 ℃范围内,晶粒粒径随着温度的升高而减小.在50 ℃时,溶液过饱和度相对较小,晶粒生长速度较快,且能形成稳定的晶粒,草酸钕前驱体粒径达到最大值,选择的最佳制备温度为50 ℃.
2.1.2 搅拌速度
搅拌速度较低时,溶液局部过饱和度增大,晶核生成速度快,生长速度较小,易于形成小颗粒,且颗粒大小分布不均匀.适当加快搅拌速度,可降低局部过饱和度,同时使溶液浓度一致,易于得到粒径分布均匀的大颗粒沉淀.继续增大搅拌速度,有利于颗粒的均匀分布,但沉淀粒子间的碰撞增加也会导致颗粒破碎,形成较小的粒子.由图 1(b)可知,搅拌速度在100 r/min到300 r/min范围内,前驱体粒径随着搅拌速度的增大而增大.继续增大搅拌速度,300 r/min到500 r/min范围内,颗粒间碰撞明显增多,前驱体粒径变小.当搅拌速度为300 r/min时,溶液浓度均匀且颗粒不会被打碎,前驱体粒径达到最大值,选择的最佳搅拌速度为300 r/min.
2.1.3 沉淀剂滴加速度
当沉淀剂缓慢加入时,溶液中沉淀粒子过饱和度较低,成核速度慢,晶粒生长速度较快,易于形成大颗粒.加快沉淀剂的滴加速度,溶液浓度增大,成核速度加快的同时晶粒加速聚集,粒子的生长以聚集长大为主.加料速度过快,溶液局部过饱和度过高,晶核迅速生成,不利于形成大颗粒.由图 1(c)可知,沉淀剂滴加速度在2 mL/min时,溶液过饱和度较小,得到的颗粒尺寸较大,但沉淀剂滴加速度太慢,不利于控制生产成本.滴加速度在2~9 mL/min范围内,前驱体粒径随着沉淀剂加入速度的加快先减小后增大,在9 mL/min时前驱体粒径达到最大值.继续加快沉淀剂的滴加速度,滴加速度在9~16 mL/min内,溶液过饱和度增大,晶核的生成速度大于生长速度,生成的颗粒较小.考虑生产效率,选择的最佳沉淀剂滴加速度为9 mL/min.
2.1.4 陈化时间
溶液在沉淀完全后静置时,大颗粒和小颗粒同时存在,由于小颗粒在溶液中的溶解度大于大颗粒,小颗粒不断溶解,溶液中的阴阳离子就在大颗粒上沉积,导致大颗粒不断长大,因此延长陈化时间有利于得到大颗粒.随着陈化时间的延长,大小颗粒的溶解、长大达到一个动态平衡,颗粒的变化越来越小,最后趋于稳定.由图 1(d)可知,草酸钕前驱体粒径随着陈化时间的延长而增大.0~24 h范围内,前驱体粒径随着陈化时间的延长显著增加.陈化时间超过24 h,颗粒粒径增加放缓,颗粒的变化越来越小.考虑到生产实际,选择的最佳陈化时间为24 h.
按上述实验确定的最佳条件,即反应温度50 ℃,搅拌速度300 r/min,沉淀剂滴加速度9 mL/min,陈化时间24 h下,用草酸沉淀P507-N235-磺化煤油-环己烷体系氯化钕反萃余液,制备草酸钕前驱体.该条件下制备的前驱体形貌及粒度分布如图 2所示,前驱体为团聚体,由小颗粒团聚形成,中心粒径D50达到100 μm以上.
2.2 反萃余液中残余有机相对前驱体粒径的影响
实验中所用稀土料液为盐酸反萃负载有机相得到的氯化钕反萃余液,反萃余液中可能存在的微量有机相直接影响前驱体沉淀颗粒的大小.为了验证反萃余液中有机相的存在,采用红外光谱分析论证.实验分别提取P507-N235-磺化煤油-环己烷混合有机相以及氯化钕反萃余液进行红外光谱分析,结果如图 3所示.
混合有机相中,煤油和环己烷没有特征官能团,P507的主要官能团是磷氧基P=O,当该基团上连接有氧原子时,特征峰在1 267 cm-1附近.N235是叔胺类萃取剂,胺类萃取剂中起萃取作用的活性基团是叔胺基R3N-,特征峰在1 096 cm-1附近[15].如图 3所示混合有机相的峰值来看,在1 200 cm-1附近出现了磷氧基P=O的特征峰,1 035 cm-1附近出现了碱性基团叔胺基R3N-的特征峰,基本接近理论上的特征峰位置.反萃余液中1 208 cm-1和1 035 cm-1附近出现了微弱的峰值,分别对应于混合有机相中磷氧基P=O及叔胺基R3N-的特征峰,表明反萃余液中有微量残余的混合有机相.
为了对比研究反萃余液中残留的有机相对前驱体粒度的影响,以直接配制、不含有机相的氯化钕溶液为原料,在相同条件下制备草酸钕前驱体.图 4所示为2种情况下的前驱体粒度分布图.可以看出,以反萃余液为原料制备的前驱体粒径明显较大,这可能是由于残留在反萃余液中的有机相成分充当了粒子长大助剂的作用,沉淀反应发生时,残留的有机相一方面引起溶液黏度增大,颗粒移动相对缓慢,前驱体沉淀聚集形成大颗粒;另一方面,残余的有机相可在溶液中形成桥联作用,使前驱体颗粒互相聚集长大[16].
2.3 大颗粒氧化钕的制备
为了确定草酸钕前驱体煅烧得到氧化钕的最佳温度,分别在600 ℃、700 ℃、800 ℃、900 ℃下煅烧前驱体得到粉体.图 5为不同温度煅烧粉体的XRD图谱,可以看出在700 ℃时前驱体煅烧产物谱图出现氧化钕的特征峰,与氧化钕标准衍射卡(01-074-2139)峰型基本一致,可以断定煅烧产物为氧化钕,只是衍射峰还不是很强.随着煅烧温度的升高,在800 ℃时,样品衍射峰更加明显,强度增强,宽度变窄,峰型与氧化钕标准衍射卡完全一致.继续升高煅烧温度,衍射峰变化不明显,说明800 ℃时灼烧产物已形成稳定的氧化钕晶相,因此确定草酸钕前驱体的最佳灼烧温度为800 ℃.
进一步研究前驱体的热分解过程,在氩气气氛、升温速率为10 ℃/min条件下,获取了草酸钕前驱体的热分解TG-DTG曲线(图 6).由前驱体热分解TG-DTG曲线可以看出,草酸钕的分解为多级反应.由DTG曲线可知,前驱体在起始温度到395 ℃范围内,有3个失重峰,对应的是吸附水的挥发和前驱体发生解脱水反应失去结晶水,由TG曲线可知,这一阶段失重率为23 %,和理论计算值25.4 %接近.在397 ℃到740 ℃范围内,前驱体有一个较大的失重过程,对应的是草酸钕发生分解生成氧化钕的反应,由TG曲线得此阶段失重率为28 %,接近理论计算值29.6 %.740 ℃以后,出现失重平台,达到失重平衡,前驱体完全分解成氧化钕,不再出现差热变化.上述结果与XRD分析结果一致.
将草酸钕前躯体煅烧温度固定为800 ℃,煅烧时间经过实验确定为2 h.该条件下制备的氧化钕形貌及粒度分布如图 7所示,氧化钕为团聚体,由小颗粒聚集长大形成,体积中心粒径D50为50~55μm,基本成正态分布.与草酸钕前驱体相比,颗粒尺寸变小,形貌上有延续性.
3 结论
1)采用P507-N235-磺化煤油-环己烷无皂化萃取体系氯化钕反萃余液为原料,可充分利用料液中的盐酸,残留在反萃余液中的有机相成分充当了粒子长大助剂的作用,利于制备大粒度氧化钕.
2)反应温度50 ℃,搅拌速度300 r/min,沉淀剂滴加速度9 mL/min,陈化时间24 h下得到100 μm以上的草酸钕前驱体,在800 ℃下煅烧保温2 h可得到大粒度氧化钕,其体积中心粒径D50为50~55 μm,粒度分布均匀.
3)本工艺操作简单,可作为稀土萃取反萃的后续工艺,实现了无皂化萃取-反萃-反萃余液制备大粒度稀土氧化物整个工艺的有序衔接.
-
表 1 电池内阻及容量保持率
Table 1 The internal resistance and capacity retention of the LiCoO2 batteries
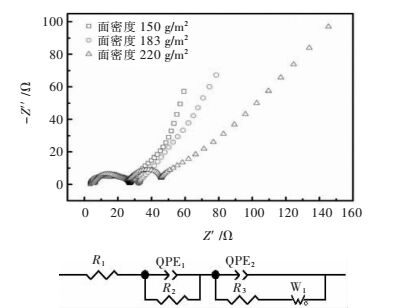
正极面密度/(g·m-2) 循环前内阻/Ω 循环后内阻/Ω 容量保持率/% 150 34 45.0 89.06 183 62 97.0 79.63 220 65 151.9 60.45 表 2 扣式电池电阻拟合数据
Table 2 Fitting data of EIS pattern for button cells
正极面密度/(g·m-2) R1 /Ω R2 /Ω R3 /Ω 150 1.439 1.236 3.682 183 2.049 3.484 7.401 220 2.344 5.360 14.57 表 3 不同面密度的正极电解液吸附量
Table 3 Results of absorbing electrolyte value with different bulk densities
正极面
密度/(g·m-2)极片料
质量/mg电解液吸
附量/mg电解液吸附
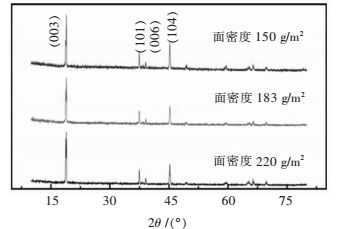
比例/%150 8.4 4.6 0.55 183 9.8 5.1 0.52 220 13.0 6.6 0.51 表 4 XRD谱图拟合精修数据
Table 4 Rietveld refinement dates of XRD
样品面密度/(g·m-2) a /Å c /Å d(003) V /Å 220 2.816 14 14.062 27 4.687 8 96.58(5.047 9) 183 2.813 22 14.062 64 4.683 9 96.38(5.058 2) 150 2.814 51 14.044 64 4.683 6 96.35(5.060 1) 0 2.814 02 14.028 21 4.671 8 96.2(5.067 7) 表 5 电池内阻及容量保持率(4 C)
Table 5 The internal resistance and capacity retention of the LiCoO2 batteries (4 C)
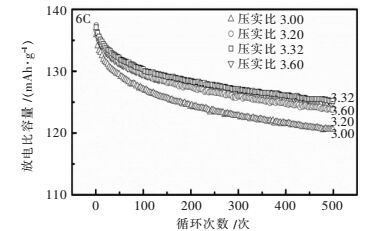
压实密度/(g·cm-3) 极片厚度/μm 分容后内阻/Ω 循环后内阻/Ω 容量保持率(500次) 3.00 75 75.1 91.3 88.74 % 3.20 71 63.2 76.3 90.10 % 3.32 70 59.1 70.5 91.50 % 3.60 66 61.6 78.1 90.32 % -
[1] GOODENOUGH J B, PARK K S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: a perspective[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(4): 1167-76. doi: 10.1021/ja3091438
[2] WAKIHARA M. Recent developments in lithium ion batteries[J]. Materials Science & Engineering Reports, 2001, 33(4):109-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927796X01000304
[3] 廖春发, 郭守玉, 陈辉煌.锂离子电池正极材料的制备研究现状[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2003, 4(2): 34-37. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=200302012 [4] KANG K, MENG Y S, BREGR J, et al. Electrodes with high power and high capacity for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. ChemInform, 2006, 37(20): 977-80. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7293588_Electrodes_with_High_Power_and_High_Capacity_for_Rechargeable_Lithium_Batteries
[5] ZAGHIB K, DONTIGNY M, GUERFI A, et al. Safe and fast-charging Li-ion battery with long shelf life for power applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(8):3949-3954. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.11.093
[6] 周文彩, 李金洪, 姜晓谦.磷酸铁锂制备工艺及研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报, 2010, 29(1): 133-137. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201001031.htm [7] 钟海江, 唐有根, 卢周广, 等. LiFePO4锂离子电池的高倍率充放电性能[J].电池, 2012, 42(3):28-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DACI201203012.htm [8] 钟盛文, 钟风娣, 张骞.锂离子正极材料LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2的合成与掺杂Al的性能研究[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2013, 4(4):11-16. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=2013040002 [9] YOSHIO M, NOGUCHI H, ITOH J I, et al. Preparation and properties of LiCoyMnxNi1-x-yO2, as a cathode for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 90(2):176-181. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(00)00407-9
[10] OH S, LEE J K, BYUN D, et al. Effect of Al2O3, coating on electrochemical performance of LiCoO2, as cathode materials for secondary lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 132(1/2):249-255. https://koreauniv.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/effect-of-alsub2subosub3sub-coating-on-electrochemical-performanc
[11] 梅佳, 钟盛文, 张骞, 等.高性能LiCoO2的制备与性能表征[J].电源技术, 2007, 31(2):128-130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJS200702010.htm [12] OHZUKU T, UEDA A, NAGAYAMA M, et al. Comparative study of LiCoO2, LiNiCoO2 and LiNiO2 for 4 volt secondary lithium cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1993, 38(9):1159-1167. doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(93)80046-3
[13] 吕之阳, 冯瑞, 赵进, 等.高倍率锂离子电池负极材料:氮掺杂碳纳米笼[J].化学学报, 2015, 73(10):1013-1017. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB201510006.htm [14] 宋怀河, 杨树斌, 陈晓红.影响锂离子电池高倍率充放电性能的因素[J].电源技术, 2009, 33(6):443-448. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJS200906014.htm [15] SINGH M, KAISER J, HAHN H. Thick electrodes for high energy lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(7):A1196-A1201. doi: 10.1149/2.0401507jes
[16] 刘润, 庄卫东, 班丽卿, 等.影响锂离子电池电极性能的一些因素[J].稀有金属, 2016(10):1066-1075. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXJS201610015.htm [17] 唐艳, 欧庆祝, 刘恒, 等.极片面密度和压实密度对Li3V2(PO4)3/C电化学性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(12):3404-3413. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201512018.htm [18] YU D Y W, DONOUE K, INOUE T, et al. Effect of electrode parameters on LiFePO4 cathodes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2006, 153(153):A835-A839. http://jes.ecsdl.org/content/153/5/A835.short?related-urls=yesl153/5/A835c153/5/A835
[19] 刘小虹.锂离子电池快速充电及高倍率放电性能[J].电源技术, 2011, 35(7):768-771. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJS201107008.htm [20] SINGH M, KAISER J, HAHN H. A systematic study of thick electrodes for high energy lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 782:245-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.10.040
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 宫子琪,郑理银. 含Sc超高强度铝合金成分优化及组织性能研究. 有色金属科学与工程. 2025(01): 75-84 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 肖镭,赵雪,王聪,高炳亮. NaF-AlF_3体系热导率的有限元数值模拟. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(01): 15-24 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 曹洪志,李琳,闫丽珍,王天石,陈帅,唐斯琪. 4047硅铝合金激光焊微观组织和力学性能分析. 焊接技术. 2023(11): 14-18+145 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 袁建伟,陈翌庆,余俊超,张凯旋,周锐. 高硅铝合金Al-20Si-xCu热裂行为及其机理. 中国有色金属学报. 2022(11): 3294-3305 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 董屹盛,吕洪玉. 高硅铝合金的研究现状及展望. 轻合金加工技术. 2021(02): 11-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孔令晨,冯胜强,董天顺,冯阳. A356铝合金表面Al-25Si等离子喷涂层的组织和耐磨性能研究. 轻合金加工技术. 2021(04): 54-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘米丰,任卫朋,赵越,陈韬,王盈莹. 一种集成无源电容式高硅铝合金基微波功率芯片载体技术. 电子元件与材料. 2021(11): 1112-1117 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: