First-principles design of cation-doped H-Nb2O5 negative electrode material and its electrochemical performance investigation
-
摘要:
铌基氧化物负极材料因具有优异的锂离子扩散速率而备受关注,但铌基氧化物导电性较差,严重限制了其大规模应用。本研究运用第一性原理计算方法,采用VASP软件包结合Hubbard修正的广义梯度近似(GGA + U)计算了不同阳离子掺杂对H-Nb2O5的态密度带隙的影响,结果表明,掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+能改善H-Nb2O5电子结构,将其带隙由纯相H-Nb2O5的0.35 eV分别降低至0、0.1、0.17 eV。在此基础上,采用固相法分别制备了掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+的H-Nb2O5,并对其结构及电化学储锂机理进行了研究。其中,Ni2+掺杂H-Nb2O5展现出较优的电化学性能,在2.5 C条件下放电比容量达203 mAh/g;在50 C条件下容量仍保持在89 mAh/g;25 C条件下3 000次循环中每次容量损失率仅为0.002 1% 。锂离子迁移势垒计算结果表明,Ni2+掺杂H-Nb2O5的迁移势垒为0.674 eV,远低于纯相H-Nb2O5的0.847 eV。
Abstract:Niobium-based oxide negative electrode materials have attracted much attention because of their excellent lithium-ion diffusion rate, but their poor electrical conductivity severely limits their large-scale application. In this study, the effects of different cationic doping on the bandgap of H-Nb2O5 state density were calculated by using the VASP software package and Hubbard modified generalized gradient approximation (GGA + U). The results show that Ni, Co and Ag can improve the electronic structure of H-Nb2O5 and reduce the band gap compared to pure phase H-Nb2O5 from 0.35 eV to 0, 0.13 and 0.17 eV, respectively. On this basis, H-Nb2O5 doped with Ni, Co and Ag was prepared using the solid phase method, and its structure and electrochemical lithium storage mechanism were studied, respectively. The experimental results show that Ni-doped H-Nb2O5 exhibits the best electrochemical performance among the doped H-Nb2O5 anodes. The specific discharge capacity reaches 203 mAh/g at 2.5 C. The capacity remains at 89 mAh/g at 50 C. The capacity loss rate per 3000 cycles is only 0.002 1% under the 25 C condition. The calculation results show that the migration barrier of Ni-doped H-Nb2O5 is 0.674 eV, much lower than 0.847 eV of pure H-Nb2O5.
-
随着便携式电子设备和电动汽车的快速发展,对高能量密度、高功率密度、高安全性和良好的循环稳定性的锂离子电池(LIBs)的需求已经十分迫切[1-4]。负极材料是锂离子电池的关键材料,也是决定锂离子电池性能的重要因素之一[5]。传统的石墨负极材料因具有资源丰富、价格低廉、理论容量较高、循环稳定性良好等特点而广泛应用于商用锂离子电池中[6]。然而,石墨负极材料仍存在诸多缺点,如锂离子扩散速率慢、脱嵌锂所引起的体积变化而易破坏材料结构,以及活性高而易与电解液反应生成较厚的固体电解质界面层,表现出较差的倍率性能[7]。此外,石墨嵌锂电位较低(约为0.1 V vs Li/Li+),放电过程中容易形成锂枝晶而造成短路或爆炸等安全问题[8]。因此,开发具有高安全性和高功率特性的新型负极材料对于下一代锂离子电池的发展至关重要。
氧化铌具有电位平台高、无毒环保、热力学稳定性好、循环寿命长等优点,其独特的结构优势、较好的倍率性能和循环稳定性使其在电化学储能和转换技术中具有良好的应用前景[9]。然而,氧化铌材料的电子导电性较差,导致其在高电流密度下循环时可逆容量较低。此外,氧化铌材料的充放电平台并非绝对平坦,相对于其他合金或转化型化合物,其理论容量较低。因此,氧化铌材料的研究主要集中于如何改善其电子导电性和离子传输性,包括通过调控材料的形貌和结构、掺杂和表面工程等方法。为了简化实验路径和降低成本,需要深入研究材料性能的本质。通过建立理论模型,发挥第一性原理在实验中的指导作用,可以有针对性地设计电极材料,并为实验的开展提供理论支撑。第一性原理计算预测氧化物电极材料的电化学性能,验证假设,能有效减少试错实验的数量,简化实验路径,并提高实验效率[10]。
本研究利用VASP软件包,采用第一性原理计算方法,在理论计算的指导下,对H-Nb2O5进行结构调控,构建锂离子传输通道,分析了不同阳离子掺杂对H-Nb2O5的电子结构和离子传输性的影响。计算结果表明,掺杂Ni、Co和Ag能有效降低H-Nb2O5带隙,改变电极材料的电子结构,提高电子及离子扩散速率。经过实验进一步验证,具备较低带隙的阳离子掺杂H-Nb2O5具有较高的比容量和优异的倍率性能。本研究通过理论计算为实验的展开提供思路,减少了探索性实验,为选择阳离子掺杂H-Nb2O5作为负极材料提供了理论依据,大幅降低实验成本、减少探究时间,为电池负极材料的研究提供了新思路。
1 实验与仿真
1.1 Ni、Ag或Co掺杂H-Nb2O5材料的制备
称取3份21 mmol铌粉(纯度99.5%,300目(即粒径0.05 mm),上海麦克林生化科技有限公司),分别与1.13 mmol镍粉(纯度99.5%,300目,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)、硝酸银(纯度99.8%,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司)或硝酸钴(纯度99.0%,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司)混合后,加入15 mL异丙醇,以200 r/min的转速球磨8 h。将所得混合溶液在8 000 r/min的条件下离心5 min,倒掉上清液,将所得样品在80 ℃条件下干燥12 h,得到混合前驱物。称取0.8 g混合前驱物在600 ℃保持5 h后,再以10 ℃/min的升温速度升至1 100 ℃并保持3 h,自然冷却后即可获得Ni、Ag或Co掺杂H-Nb2O5的电极材料[11-12],分别标记为Ni@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5。
1.2 材料表征测试
采用JSM-5601LV型扫描电子显微镜(日本电子株式会社)观察H-Nb2O5、Ni@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5的微观形貌;采用D8型X射线粉末衍射仪(Cu靶,Kα射线,电压40 kV,电流40 mA,扫描范围10°∼80°,德国布鲁斯公司)分析所制备材料的晶体结构。
1.3 电极制备及电化学测试
以NMP为溶剂制备了含有70%(质量比,下同)活性材料、20%乙炔黑和10% PVDF的电极浆料。将浆料均匀涂布在铜箔上,然后在80 °C下真空干燥12 h,并将其切割成直径为12 mm的电极片。每个电极片上的活性材料负载约为1.6 mg/cm2。以所制备电极为正极,金属锂片为负极,多孔聚丙烯膜(Celgard 2500)为隔膜,在充满氩气且水氧含量低于0.001‰的手套箱中组装成CR2025纽扣电池。其中,所使用电解液由体积比为1∶1∶1的六氟磷酸锂(LiPF6)、碳酸二乙酯(DMC)和碳酸二甲酯(DEC)组成。搁置12 h后进行电化学测试。
在Neware BTS-7.6.0电池充放电测试仪(深圳新威尔电子有限公司)上进行充电和放电性能以及恒电流放电/充电测试,电压范围为1.00∼3.00 V,电流测试密度为0.1 A/g。采用CHI760E电化学工作站(上海辰华仪器有限公司)进行电化学阻抗谱(EIS)和循环伏安(CV)测试,EIS测试范围为0.01~100.00 kHz,CV测试的扫描速率为0.5 mV/s,电压测试范围为1.00∼3.00 V。
1.4 第一性原理计算
第一性原理计算基于密度泛函理论(DFT),采用VASP模拟包完成。电子与离子相互作用由投影缀加平面波(PAW)方法处理[13-15],采用广义梯度近似(GGA + U)的Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof(PBE)方案分析电子交换相关能,Ni、Co和Ag的Hubbard U值分别设置为6.4、3.3、3.0 eV,平面的截止能量波设置为500 eV[16]。布里渊区由Monkhorst-Pack取样,构型弛豫用3 × 3 × 1的k点,用更密集的6 × 6 × 1的k点进行电子性质分析,作用在任何原子上的力小于0.02 eV/Å(1 Å = 0.1 nm),能量汇聚小于 1 × 10‒5 eV[17],Li+迁移势垒采用VASP过渡态(CI-NEB)方法计算[18]。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 材料结构
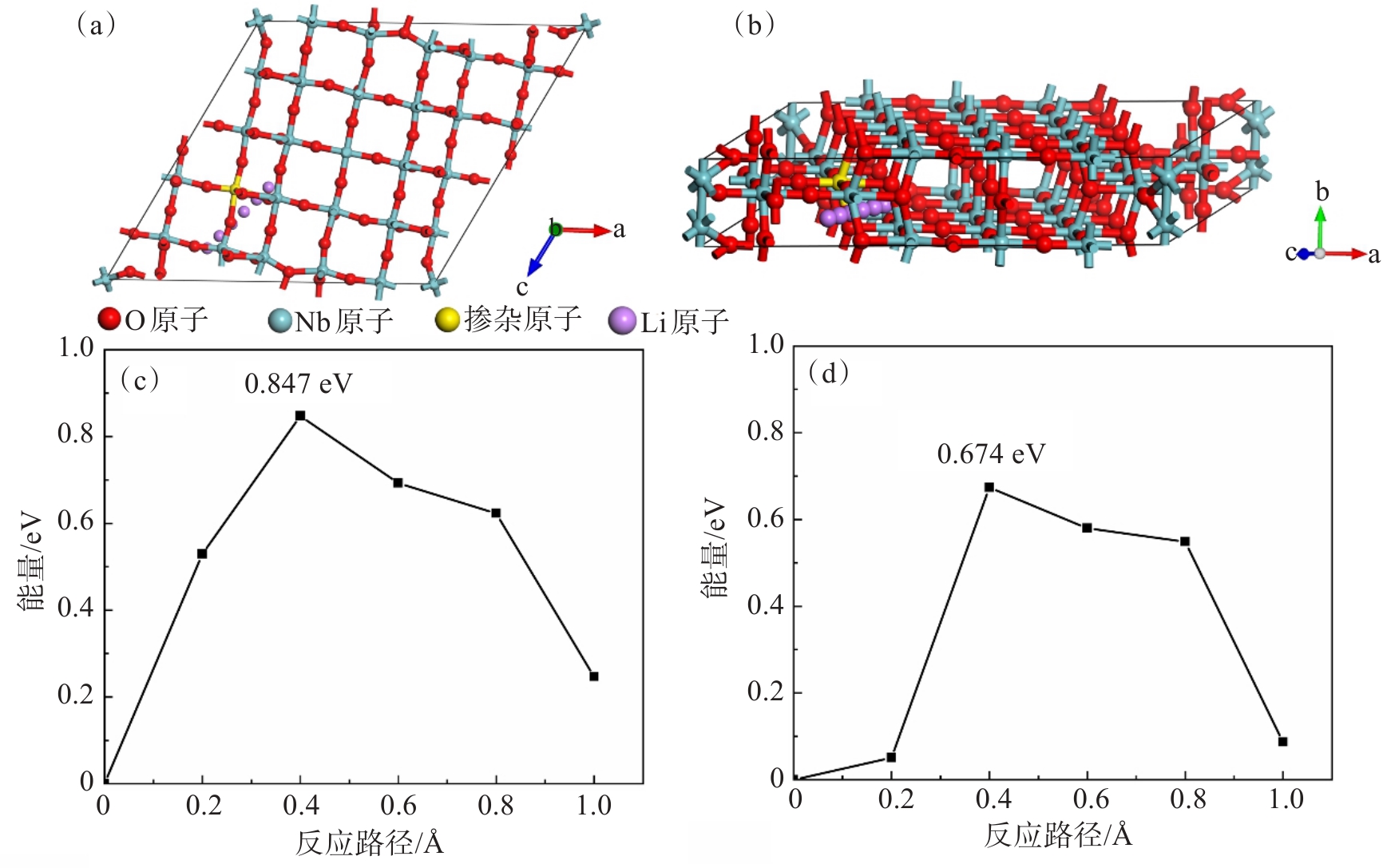
H-Nb2O5晶胞结构的俯视图和侧视图分别如图1(a)和图1(b)所示,为典型的单斜晶体结构,其晶格常数a = 21.153 Å, b = 3.823 Å, c = 19.357 Å, ɑ = γ = 90°,β = 120°。该晶体结构属于第10号P2/M空间群,晶胞中包含28个Nb原子,70个O原子[19]。H-Nb2O5是一种单斜多晶型化合物,晶型不会随着温度变化而转变,属于Wadsley-Roth族的晶体剪切结构。这种三维开放框架能够实现Li+的快速扩散,倍率性能较好。阳离子取代Nb掺杂后H-Nb2O5晶胞结构的俯视图和侧视图如图1(c)和图1(d)所示,掺杂阳离子后,氧化铌的晶体结构基本保持不变。以Ni掺杂H-Nb2O5为例,结构优化后,其晶格常数为a = 21.389 Å,b = 3.987 Å, c = 19.610 Å,与掺杂前相比晶格常数增大,这是因为与铌原子相比半径更大的阳离子会使晶格膨胀,导致晶格常数增加。晶格常数的增大也将更有利于Li+的扩散。
2.2 电子结构
导电率低的问题严重制约了氧化铌负极材料的应用,通过掺杂金属离子可降低氧化铌带隙,并有望大幅提升氧化铌电极材料的导电率,从而使其获得优异的电化学性能。纯相H-Nb2O5的电子态密度(DOS)如图2(a)所示,导带与价带分离,带隙为0.35 eV,费米能级位于价带的顶部,为典型的绝缘体或宽带隙半导体特性。通过掺杂不同金属阳离子(Ni2+、Cu2+、Mn2+、Cd2+、Co2+、Ag+、Fe2+、Zn2+)对H-Nb2O5进行改性,所获得材料的态密度如图2(b)—图2(i)所示。如图2所示,阳离子掺杂可以有效改变H-Nb2O5带隙大小,掺杂阳离子为Cu2+、Mn2+、Cd2+、Fe2+、Zn2+时,材料的带隙分别为0.79、0.57、0.83、0.52、0.97 eV,这可能是由于掺杂的阳离子改变了材料导电性,使载流子的浓度减小,带隙变宽[20];当掺杂阳离子为Ni2+时,所获得的材料无带隙;当掺杂阳离子为Co2+和Ag+时,其带隙分别为0.13 eV和0.17 eV,远小于纯相H-Nb2O5带隙宽度(0.35 eV)。掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后,费米能级向导带移动,带隙减小,这种减小的带隙将促进电荷载流子从价带迁移到导带,有利于提高电化学性能[21]。计算结果表明,掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+减少了H-Nb2O5的带隙宽度,费米能级的偏移可能是n型半导体的掺杂所致。本研究选择对H-Nb2O5分别掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+,并对所制备的材料进行表征以及电化学测试。
![]() 图 2 H-Nb2O5及不同金属阳离子掺杂后H-Nb2O5的态密度:(a)纯相H-Nb2O5;(b)Ni@Nb2O5;(c)Cu@Nb2O5;(d)Mn@Nb2O5;(e)Co@Nb2O5;(f)Cd@Nb2O5;(g)Ag@Nb2O5;(h)Fe@Nb2O5;(i)Zn@Nb2O5Figure 2. State density of H-Nb2O5 doped with different metal cations: (a) pure phase H-Nb2O5; (b) Ni@Nb2O5; (c) Cu@Nb2O5; (d) Mn@Nb2O5; (e) Co@Nb2O5; (f) Cd@Nb2O5; (g) Ag@Nb2O5; (h) Fe@Nb2O5; (i) Zn@Nb2O5
图 2 H-Nb2O5及不同金属阳离子掺杂后H-Nb2O5的态密度:(a)纯相H-Nb2O5;(b)Ni@Nb2O5;(c)Cu@Nb2O5;(d)Mn@Nb2O5;(e)Co@Nb2O5;(f)Cd@Nb2O5;(g)Ag@Nb2O5;(h)Fe@Nb2O5;(i)Zn@Nb2O5Figure 2. State density of H-Nb2O5 doped with different metal cations: (a) pure phase H-Nb2O5; (b) Ni@Nb2O5; (c) Cu@Nb2O5; (d) Mn@Nb2O5; (e) Co@Nb2O5; (f) Cd@Nb2O5; (g) Ag@Nb2O5; (h) Fe@Nb2O5; (i) Zn@Nb2O52.3 表征与形貌
由纯相H-Nb2O5的扫描电子显微镜(SEM)图(图3(a))可见,H-Nb2O5颗粒呈不规则形状,由尺寸约为500 nm的晶粒紧密堆积形成10~15 μm的颗粒。图3(b)所示为纯相H-Nb2O5和掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后制备材料的XRD图谱,放大位于23.9°处的(110)晶面衍射峰可见,掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后,该峰均向左偏移,说明该晶面间距变大[22]。图3(c)、图3(g)、图3(k)所示分别为Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的SEM图像,Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5材料的形貌与H-Nb2O5相比基本无变化。相应的EDS图谱(图3(d)—图3(f)、图3(h)—图3(j)、图3(l)—图3(n))表明材料中元素分布均匀,并进一步证实了Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5中除了含有Nb和O元素外,还分别包含掺杂的Ni、Co、Ag元素。
![]() 图 3 (a)纯相H-Nb2O5的SEM图;(b)纯相H-Nb2O5、Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的XRD图;(c-n)Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的SEM图和EDS元素图谱Figure 3. (a)SEM diagram of pure phase H-Nb2O5; (b) XRD patterns of pure phase H-Nb2O5, Ni@Nb2O5, Co@Nb2O5, Ag@Nb2O5; (c-n) SEM and EDS element Atlas images of Ni@Nb2O5, Co@Nb2O5, Ag@Nb2O5
图 3 (a)纯相H-Nb2O5的SEM图;(b)纯相H-Nb2O5、Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的XRD图;(c-n)Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的SEM图和EDS元素图谱Figure 3. (a)SEM diagram of pure phase H-Nb2O5; (b) XRD patterns of pure phase H-Nb2O5, Ni@Nb2O5, Co@Nb2O5, Ag@Nb2O5; (c-n) SEM and EDS element Atlas images of Ni@Nb2O5, Co@Nb2O5, Ag@Nb2O52.4 电化学性能
通过电化学阻抗谱测试(EIS)探究了H-Nb2O5中掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后,所制备材料的电子和离子传输性能(图4(a))。高频区域的半圆对应于电荷转移电阻(Rct),而低频区域中的倾斜直线代表Warburg电阻[23]。纯相H-Nb2O5的电阻为282 Ω,掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后,电极材料的电阻分别降低至55、236、274 Ω,材料的电导率均有效提高,此结果与DFT计算结果一致。
![]() 图 4 H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni、Co、Ag前后:(a)在频率范围0.1~100 kHz的EIS图谱;(b)在0.5 mV/s扫速下,1.0~3.0 V电压范围的CV曲线;(c)1~50 C电流密度下的倍率性能;(d)在2.5 C时的循环性能;(e)在25 C电流密度下的长循环性能Figure 4. After doping Ni, Co and Ag with H-Nb2O5: (a) EIS spectra in the frequency range 0.1-100 kHz; (b) CV curve results from 1.0 V to 3.0 V voltage range at 0.5 mV/s sweep speed; (c) magnification performance at 1-50 C current density; (d) cycle performance at 2.5 C; (e) long cycle performance at 25 C current density
图 4 H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni、Co、Ag前后:(a)在频率范围0.1~100 kHz的EIS图谱;(b)在0.5 mV/s扫速下,1.0~3.0 V电压范围的CV曲线;(c)1~50 C电流密度下的倍率性能;(d)在2.5 C时的循环性能;(e)在25 C电流密度下的长循环性能Figure 4. After doping Ni, Co and Ag with H-Nb2O5: (a) EIS spectra in the frequency range 0.1-100 kHz; (b) CV curve results from 1.0 V to 3.0 V voltage range at 0.5 mV/s sweep speed; (c) magnification performance at 1-50 C current density; (d) cycle performance at 2.5 C; (e) long cycle performance at 25 C current density为了评估所制备Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5和Ag@Nb2O5的储锂性能,在扫速为0.5 mV/s、电压为1.0∼3.0 V的条件下,进行了循环伏安特性曲线测试(图4(b))。在1.60~1.76 V处的一对强阴极/阳极峰可归属于Nb5+/Nb4+的氧化还原转变,伴随着Li+的嵌入/脱嵌[24];位于1.42~1.47 V的弱峰归属于Nb4+/Nb3+的价态变化[25]。此外,位于1.90~2.00 V的弱氧化还原反应峰也归属于Nb5+/Nb4+。
在1~50 C不同的电流密度下,分别测试了H-Nb2O5、Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5和Ag@Nb2O5的倍率性能,结果如图4(c)所示,Ni@Nb2O5的倍率性能最优,当倍率从1 C增至25 C时,Ni@Nb2O5电极的容量从179.7 mAh/g降至114.4 mAh/g。即使电流密度增加至50 C的超高倍率,Ni@Nb2O5的容量仍可以达到89 mAh/g。当电流密度恢复到1 C时,比容量恢复到179.0 mAh/g,与初始比容量(179.7 mAh/g)相比几乎没有衰减,表明Ni@Nb2O5电极材料具有极其优异的可逆性和稳定性。Ni@Nb2O5的速率稳定性归因于其具有优异的电子导电性,这使得Li+具有更好的速率耐受性和更快的动力学反应速率。综上,H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+改性后,优良的电子和离子传输性能使得H-Nb2O5倍率性能更加优异。
H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后的循环性能如图4(d)所示,Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5在2.5 C的电流密度下稳定循环200次后,仍分别具有203、181、164 mAh/g的高比容量,均优于H-Nb2O5(153 mAh/g),表明Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的结构稳定,并提升了H-Nb2O5的电化学性能。在25 C的电流密度下测试了长循环性能,结果如图4(e)所示,经过3 000次充放电后,掺杂前H-Nb2O5具有87 mAh/g的放电比容量,而Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5分别具有120、108、93 mAh/g的高放电比容量,Ni@Nb2O5每次容量的损失率仅为0.002 1%。一系列的电化学测试反应表明,H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后进一步提高了其电子和离子传输效率,提高了电化学性能及锂离子存储性能,展现出阳离子掺杂的Nb2O5作为高性能锂离子电池负极材料的巨大应用潜力。为了更深层次探究H-Nb2O5电化学储锂优化机制,采用VASP等软件对H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni、Co、Ag前后进行计算分析。
2.5 电荷密度与锂离子迁移
通过VASP计算分析了H-Nb2O5、Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的电荷得失和成键情况。Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5掺杂位点差分电荷密度图如图5(a)—图5(c)所示,青色部分表示电荷密度减小,黄色部分表示电荷密度增加。Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5掺杂位点电荷密度图如图5(d)—图5(f)所示,红色部分表示电子分布最多,蓝色部分表示没有电子。
本研究采用CI-NEB计算了H-Nb2O5和带隙变化最大的Ni@Nb2O5在嵌锂过程中的迁移势垒。图6(a)和图6(b)所示分别为模拟Li+在Ni@Nb2O5沿c轴方向迁移路径的主视图和侧视图。Li+从H-Nb2O5结构的表面迁移至其内部需克服0.847 eV的迁移势垒(图6(c));Li+从Ni@Nb2O5表面迁移至其内部需克服0.674 eV的迁移势垒(图6(d)),小于Li+在H-Nb2O5中的迁移势垒,说明添加Ni2+改善了Li+的转移能力,使得Li+迁移势垒降低,这与前文的分析和掺杂Ni能够改善H-Nb2O5导电性的实验结果一致。Ni@Nb2O5比H-Nb2O5具有更低的扩散势垒。本研究利用Li+沿某一路径的迁移步长和所遇到的迁移势垒估算出Li+沿该路径的扩散系数:
,其中,d为Li+迁移距离,V为尝试频率,EA为势垒,kB为玻尔兹曼常数,T为温度[26]。据此可以计算出室温附近 (300 K) H-Nb2O5的扩散系数约为1.83 × 10-8 cm2/s,Ni@Nb2O5的扩散系数约为1.47 × 10-5cm2/s。 3 结论
基于第一性原理分别计算H-Nb2O5掺杂不同阳离子(Ni2+、Cu2+、Mn2+、Cd2+、Co2+、Ag+、Fe2+、Zn2+)后的电子态密度变化情况。结果表明,掺杂Ni2+、Co2+、Ag+后,所制备的Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5负极材料的带隙分别减少至0、0.13、0.17 eV,带隙的减小更有利于电子的传输。Ni@Nb2O5、Co@Nb2O5、Ag@Nb2O5的电化学测试结果表明,掺杂后的H-Nb2O5材料在放电比容量的循环稳定性和导电性均优于纯相H-Nb2O5,其中,Ni@Nb2O5表现最优异。Ni@Nb2O5的迁移势垒远小于纯相H-Nb2O5,相应的Li+的扩散系数为1.47 × 10‒5cm2/s,表明Li+在Ni@Nb2O5较纯相H-Nb2O5中的迁移速率更高。基于第一性原理计算金属阳离子掺杂前后H-Nb2O5的电子结构,并筛选出最佳的掺杂阳离子,此过程可大幅减少实验的探索时间,有效节约实验成本。本实验结果与第一性原理计算结果一致,验证了计算方法的可靠性。本研究为铌基氧化物负极材料第一性原理计算指导实验的研究范式提供了思路与方法。
于桂红 -
图 2 H-Nb2O5及不同金属阳离子掺杂后H-Nb2O5的态密度:(a)纯相H-Nb2O5;(b)Ni@Nb2O5;(c)Cu@Nb2O5;(d)Mn@Nb2O5;(e)Co@Nb2O5;(f)Cd@Nb2O5;(g)Ag@Nb2O5;(h)Fe@Nb2O5;(i)Zn@Nb2O5
Fig 2. State density of H-Nb2O5 doped with different metal cations: (a) pure phase H-Nb2O5; (b) Ni@Nb2O5; (c) Cu@Nb2O5; (d) Mn@Nb2O5; (e) Co@Nb2O5; (f) Cd@Nb2O5; (g) Ag@Nb2O5; (h) Fe@Nb2O5; (i) Zn@Nb2O5
图 4 H-Nb2O5掺杂Ni、Co、Ag前后:(a)在频率范围0.1~100 kHz的EIS图谱;(b)在0.5 mV/s扫速下,1.0~3.0 V电压范围的CV曲线;(c)1~50 C电流密度下的倍率性能;(d)在2.5 C时的循环性能;(e)在25 C电流密度下的长循环性能
Fig 4. After doping Ni, Co and Ag with H-Nb2O5: (a) EIS spectra in the frequency range 0.1-100 kHz; (b) CV curve results from 1.0 V to 3.0 V voltage range at 0.5 mV/s sweep speed; (c) magnification performance at 1-50 C current density; (d) cycle performance at 2.5 C; (e) long cycle performance at 25 C current density
-
[1] DENG S, ZHU H, LIU B, et al. Synergy of ion doping and spiral array architecture on Ti2Nb10O29: a new way to achieve high‐power electrodes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(25): 2002665.
[2] DING H, SONG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Niobium-based oxide anodes toward fast and safe energy storage: a review[J]. Materials Today Nano, 2020, 11: 100082.
[3] YANG Y, ZHAO J B. Wadsley-roth crystallographic shear structure niobium-based oxides: promising anode materials for high-safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(12): 2004855.
[4] TAO R M, ZHANG T Y, TAN S S, et al. Insight into the fast-rechargeability of a novel Mo1.5W1.5Nb14O44 anode material for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(36): 2200519.
[5] SHEN F, SUN Z T, HE Q G, et al. Niobium pentoxide based materials for high rate rechargeable electrochemical energy storage[J]. Materials Horizons, 2021, 8(4): 1130-1152.
[6] YANG C, YU S, LIN C F, et al. Cr0.5Nb24.5O62 Nanowires with high electronic conductivity for high-rate and long-life lithium-ion storage[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(4): 4217-4224.
[7] LEI C R, QIN X, HUANG S Y, et al. Mo-doped TiNb2O7 microspheres as improved anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chem Electro Chem, 2021, 8(17): 3379-3383.
[8] WU Z C, GUO M, YAN Y T, et al. Reducing crystallinity of micrometer-sized titanium-niobium oxide through cation substitution for high-rate lithium storage[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(22): 7422-7430.
[9] YAN L T, RUI X H, CHEN G, et al. Recent advances in nanostructured Nb-based oxides for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(16): 8443-8465.
[10] 凡杰, 谢刚, 田林, 等. ZnS掺杂Fe2+电子结构第一性原理计算及对矿物浸出的影响[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2021, 12(2): 1-7. [11] CHEN X L, CUI P, CHEN X L, et al. W6+-doped Nb2O5 as high-rate anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 967: 171846.
[12] FU Q F, ZHU X Z, LI R J, et al. A low-strain V3Nb17O50 anode compound for superior Li+ storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 30: 401-411.
[13] YUAN T, SOULE L K, ZHAO B T, et al. Recent advances in titanium niobium oxide anodes for high-power lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(11): 13321-13334.
[14] ZHENG Y, QIU W J, WANG L J, et al. Triple conductive wiring by electron doping, chelation coating and electrochemical conversion in fluffy Nb2O5 anodes for fast-charging Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(25): 2202201.
[15] SHAN L T, WANG Y R, LIANG S Q, et al. Interfacial adsorption-insertion mechanism induced by phase boundary toward better aqueous Zn-ion battery[J]. Information Material, 2021, 3(9): 1028-1036.
[16] SPADA D, ARAMINI M, FITTIPALDI M, et al. Spectroscopic techniques and DFT calculations to highlight the effect of Fe3+ on the properties of FeNb11O29, anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2022, 126(9): 4698-4709.
[17] PREEFER M B, SABER M, WEI Q L, et al. Multielectron redox and insulator-to-metal transition upon lithium insertion in the fast-charging, wadsley-roth phase PNb9O25[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(11): 4553-4563.
[18] 李立清, 周润, 龙慧婷, 等. 基于密度泛函理论的氢氧化镁(101)表面改性机理研究[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2023, 14(4): 447-453. [19] CHEN H T, CHENG H Y, LIU H C, et al. Design of phase interface and defect in niobium-nickel oxide for ultrafast Li-ion storage[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 147(1): 145-152.
[20] TIAN K D, WANG Z X, DI H X, et al. Superimposed effect of La doping and structural engineering to achieve oxygen-deficient TiNb2O7 for ultrafast Li-ion storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(8): 10478-10488.
[21] CHEN Y, PU Z Y, LIU Y B, et al. Enhancing the low-temperature performance in lithium ion batteries of Nb2O5 by combination of W doping and MXene addition[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 515(1): 230601.
[22] FU Q F, LI R J, ZHU X Z, et al. Design, synthesis and lithium-ion storage capability of Al0.5Nb24.5O62[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 34(7): 19862-19871.
[23] LIU Y Q, YAN Y, LI K, et al. A high-areal-capacity lithium-sulfur cathode achieved by a boron-doped carbon-sulfur aerogel with consecutive core-shell structures[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(8): 1084-1087.
[24] XIA R, ZHAO K N, KUO L Y, et al. Nickel niobate anodes for high rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(1): 2102972.
[25] SHEN F, SUN Z T, ZHAO L, et al. Triggering the phase transition and capacity enhancement of Nb2O5 for fast-charging lithium-ion storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(25): 14534-14544.
[26] 林传金,郑锋,朱梓忠. 锂离子电池正极材料Li2FeO2的电子结构性质和Li扩散[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(15): 140-147.




 下载:
下载: