Study on ferrous ions oxidation by zinc electrolytic anode slime
-
摘要:
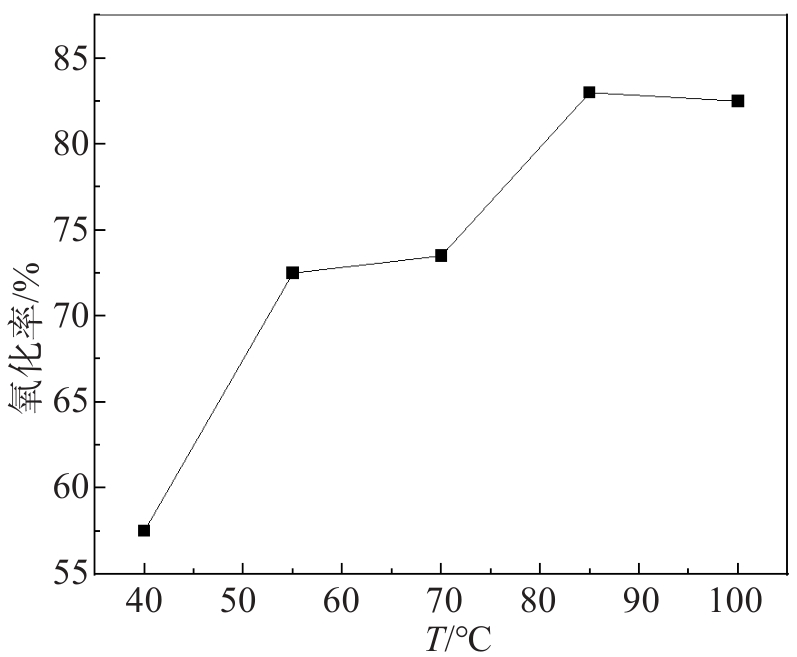
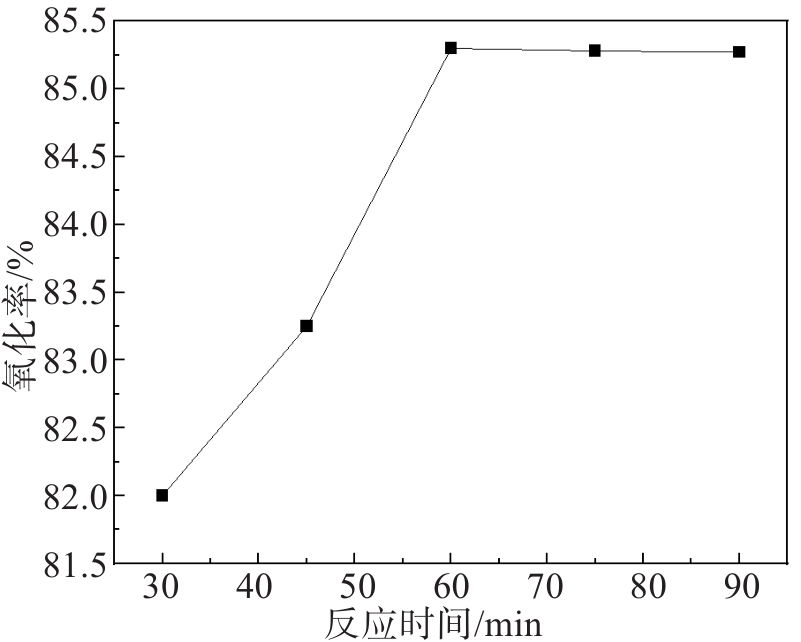
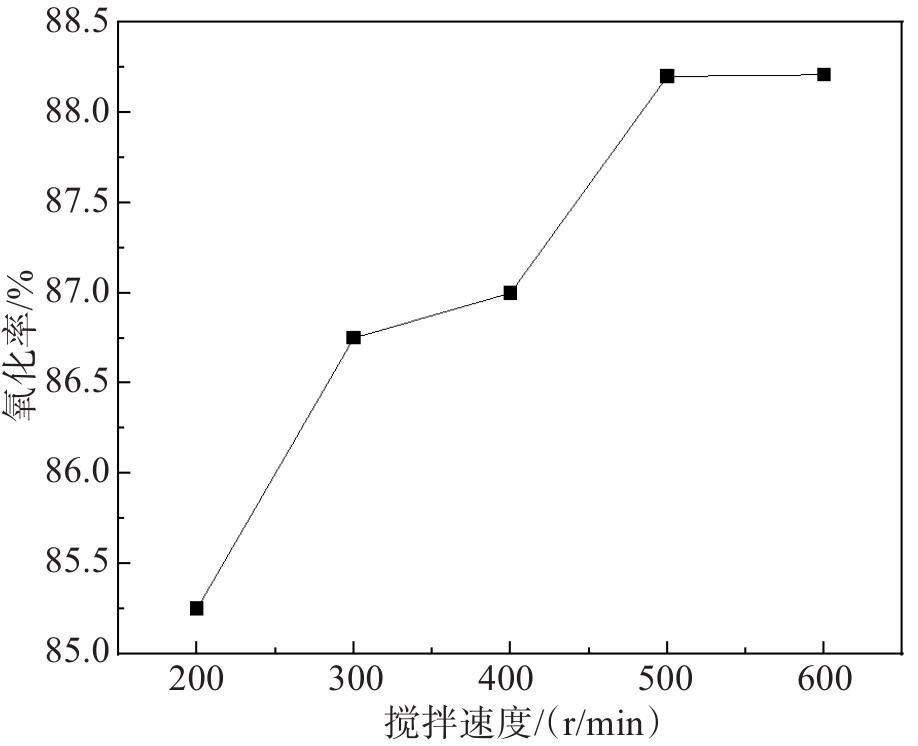
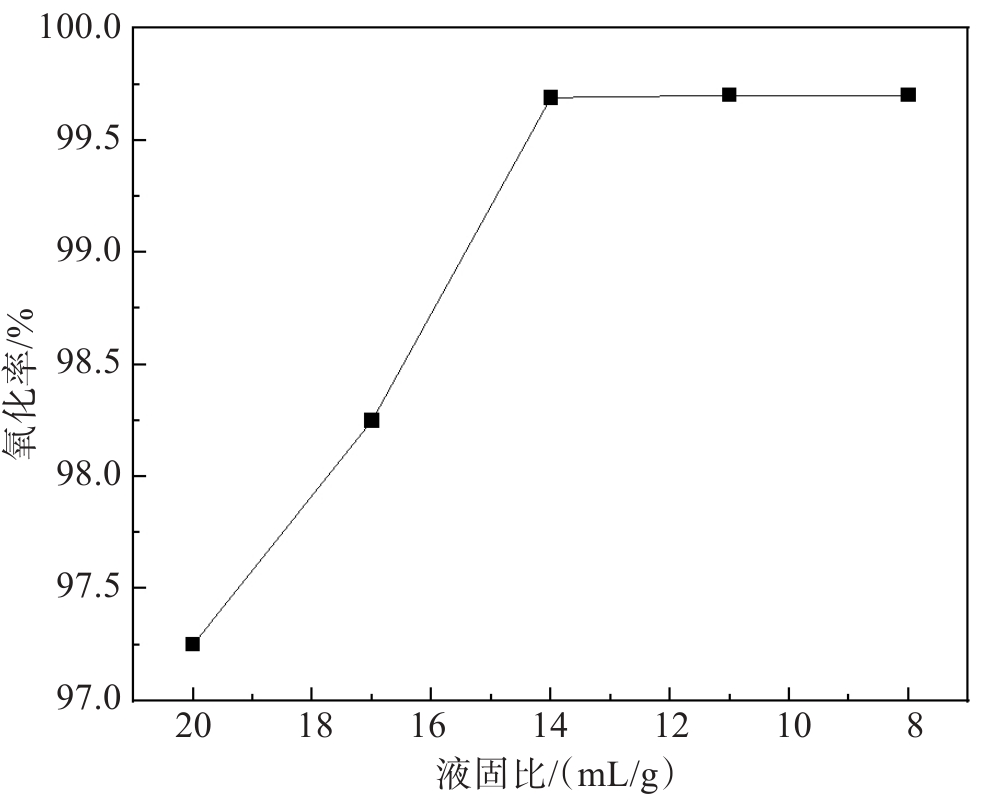
文中采用主要成分为MnO2的锌电解阳极泥氧化锌焙砂浸出液中的亚铁离子,达到除铁的目的。研究了锌电解阳极泥氧化亚铁离子过程中的反应温度、反应时间、搅拌速度、阳极泥粒径、液固比等工艺条件对亚铁离子氧化率的影响。实验结果表明,在反应温度为85 ℃、反应时间为60 min、搅拌速度为500 r/min、阳极泥粒径为0.154 mm、液固比为14∶1(单位:mL/g)的较优工艺条件下,亚铁离子的氧化率高达99.80%。此工艺使锌冶炼企业产生的电解阳极泥得到了高效利用,不仅充分利用了资源、降低了生产成本,同时解决了固废堆存引起的环境问题。
Abstract:In this study, the zinc electrolysis anode slime with MnO2 obtained as the main component at the zinc electrowinning process was used to oxidize the ferrous ions in the leaching solution of zinc calcine. The effects of reaction temperature, reaction time, stirring speed, particle size of anode slime and liquid-solid ratio on the oxidation ratio of ferrous ions were studied. The experimental results show that the oxidation ratio of ferrous ions reaches as high as 99.80 % under the optimal conditions of reaction temperature of 85 ℃, reaction time of 60 min, stirring speed of 500 r/min, anode mud particle size of 0.154 mm and liquid-solid ratio of 14∶1. This process not only makes full use of resources and reduces production costs but also solves the environmental problems caused by solid waste storage, achieving the efficient utilization of the electrolytic anode slime produced by zinc smelting enterprises.
-
Keywords:
- zinc anode slime /
- manganese dioxide /
- ferrous ion /
- oxidation ratio
-
钇铁合金主要用于钕铁硼永磁体的添加剂[1],铸造领域[2]、球化剂[3]、核燃料稀释剂等.用钇铁合金变质剂可提高耐磨件的工体寿命[4],由此可见,钇铁合金正在各个领域被广泛使用[5].然而在大多数稀土铁合金中非稀土杂质的检测都已制定了相应的国家或行业标准分析方法[6]但由于钇铁合金为新型产品,对该产品中非稀土杂质的测定仍无相应的国家或行业标准.随着钇铁合金在各领域广泛应用,对其非稀土杂质(铝、硅、钙、镁、锰)的检测也将越来越重要.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-AES)分析技术自20世界60年代问世以来,并因其具有的检出限低,基体效应小,精密度高,灵敏度高,线性范围宽以及多元素同时分析等诸多优点而得以广泛应用[7-8].所提方法研究了采用电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-AES)[9]、基体匹配法[10-11]测定钇铁合金中铝、硅、钙、镁、锰,方法简单、快捷、准确.
1 试验
1.1 仪器与试剂
ULTIMA 2电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱仪.标准溶液:取1.0000 g/L被测元素储备溶液,采用逐级稀释法分别配制成100 mg/L、10 mg/L单一标准溶液,盐酸(1+9)介质.
盐酸为优级纯, 试验用水为超纯水(电阻率18 MΩ·cm)
1.2 仪器工作条件
输出功率为1.0 kW,反射功率小于2 W,观测高度14 mm,高斯积分,冷却气流量12 L/min,护套气0.3 L/min,进样速率1.0 mL/min,积分时间0.3~0.5 s.
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 标准溶液的配制
配置二套标准, 一套为基体匹配(用于测定样品);一套为不带基体(用于测定试剂空白).
采用基体匹配方法配制标准溶液,基体为2.0000 g·L-1金属钇与金属铁(其中:铁35%、钇65%)混合溶液.用多元素含量阶梯配制方式配成3个标准溶液系列,3个标准溶液中铝、硅、钙、镁、锰各为0、1.00、2.00 mg/L,盐酸(1+19)介质,用作样品检测;另采用不加基体方法配制标准溶液,用多元素含量阶梯配制方式配成3个标准溶液系列,3个标准溶液中铝、硅、钙、镁、锰各为0、1.00、2.00 mg/L,盐酸(1+19)介质,用作试剂空白检测.
1.3.2 样品制备及检测
称取钇铁合金样品0.2000g于100 mL烧杯中,加盐酸(1+1)溶液10 mL,低温加热分解清亮,取下冷却,用水定容于100 mL容量瓶中,混匀,同时以相同条件制试剂空白.用相应标准溶液,按仪器工作条件对样品与试剂空白进行检测.最后结果扣除试剂空白.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 分析谱线的选择
谱线的选择主要考虑无基体干扰、共存元素干扰、激发电位低、根据光谱线波长表[12-13]预选出几条强度大的谱线进行轮廓扫描,选出一条背景平坦、信倍比大、的分析谱线[14].各元素分析线的选择见表 1.
表 1 各元素的分析线及检出限Table 1. Analytical spectral lines and detection limits of the elements元素 分析线/nm 检出限ρ/(mg·L-1) 测定下限ρ/(mg·L-1) Al 396.152 0.015 0.050 Si 288.158 0.016 0.053 Ca 393.366 0.0042 0.014 Mg 279.553 0.0034 0.011 Mn 257.610 0.0043 0.014 2.2 共存元素干扰试验
选用钇铁合金53JYFe01样品为试验对象.分别在样品中单一加入共存元素(Al、Si、Ca、Mg、Mn)量,加入量为一般钇铁合金样品最高出现含量的2.5倍(即5.00 mg/L),进行干扰试验.实验证明,各共存元素在5.00 mg/L含量时,在所选用分析谱线范围内互不干扰.见表 2.
表 2 共存元素干扰试验Table 2. Coexisting element interference test项目 Al Si Ca Mg Mn 53JYFe01原含量 0.837 0.858 0.0100 0.072 0.454 Al加入5.00 mg/L / 0.855 0.0102 0.071 0.457 Si加入5.00 mg/L 0.840 / 0.0097 0.072 0.456 Ca加入5.00 mg/L 0.830 0.850 / 0.070 0.453 Mg加入5.00 mg/L 0.838 0.856 0.0103 / 0.460 Mn加入5.00 mg/L 0.835 0.860 0.0105 0.078 / 注:空白处表示加入的干扰元素正好是所对应的共存元素,固不列数据. 2.3 标准溶液的基体匹配
1)基体匹配法相对于去基体法,在分析结果上并无明显差异.见表 3以钇铁合金53JYFe01为例,分别列出了基体匹配法与去基体法结果.基体匹配法相对于去基体法最大的差异是:前者步骤简单而后者步骤繁琐,繁琐的步骤引起误差的概率也随之增大.
表 3 基体匹配与去基体结果对比Table 3. Matrix matching and matrix results contrast方法 Al
/(mg·L-1)Si
/(mg·L-1)Ca
/(mg·L-1)Mg
/(mg·L-1)Mn
/(mg·L-1)基体匹配法 0.837 0.858 0.0100 0.072 0.0454 去基本法 0.821 0.840 0.0091 0.070 0.0439 2)基体匹配法可以消除盐效应.溶液的粘度等物理性质均随溶液含盐的增加而增大,从而影响溶液的进样量、雾化效率及气溶胶传输效率并最终影响谱线强度.消除盐效应的根本方法是基体匹配,保持标准溶液和分析溶液有相同的含盐量[15].试验采用基体匹配配制方式,很好的解决了盐效应.
由于工业化生产的钇铁合金产品中,钇-铁比例一般为65%-35%之间,所以方法以此比例为基体研究对象.而在工业生产中钇-铁比例也不能排除存在波动,为了使方法的适用范围更广泛,因此增加基体波动影响试验.分别配制钇-铁比例为60%-40%与70%-30%的基体,其他杂质各为0.10 g/L进行测定.实验证明钇-铁基体比例在60%~40%与70%~30%之间变化时对测定无明显影响,见表 4.
表 4 钇-铁基体比例在60%~40%与70%~30%波动影响实验Table 4. Effects of matrix proportion of Y and Fe on determination results元素 参照值/(mg·L-1) 钇-铁(60%~40%)
测定值/(mg·L-1)钇-铁(70%~30%)
测定值/(mg·L-1)Al 0.100 0.103 0.102 Si 0.100 0.109 0.097 Ca 0.100 0.103 0.100 Mg 0.100 0.102 0.101 Mn 0.100 0.105 0.098 2.3 仪器工作条件和工作参数的选择
在化学实验中,影响实验结果的因素多,所波及的水平和所需实验次数也多.如果进行所有的实验,不但在成本上造成浪费,且给实验者带来许多无须有的麻烦,而最终还不一定选择到最佳的条件组合.正交试验正是克服以上的不足,它利用一种科学的表格──正交表来安排实验,以期获得满意的效果[16].所提方法根据影响测定的主要因素,采用4因素3水平正交设计,按L9(34)正交表安排试验.以(I-Ib)和I/Ib的综合值为评价指标,选择最佳仪器工作条件和工作参数,因Si的谱线相对较弱,则以Si线为试样对象,正交设计实验表见表 5,最佳值见1.2仪器工作条件.
表 5 正交设计因素、水平Table 5. Results of orthogonal test for instrumentation conditions水平 功率/kW 观测高度/mm 冷却气流
量/(L·min-1)护套气流
量/(L·min-1)1 0.95 12 12.0 0.20 2 1.0 14 12.5 0.25 3 1.1 15 13.0 0.30 2.4 方法的检出限和精密度
连续测定混合基体空白溶液11次,按3倍标准偏差计算到检出限[17],以10倍的标准偏差作为方法的测定下限,结果见表 1.
按试验方法对钇铁合金样品53JYFe01进行了分析,所得结果见表 6,各元素测定结果的相对标准偏差(n=11)在0.74%~4.58%之间.
表 6 钇铁合金分析结果(n=11)Table 6. Determination results of Y-Fe alloy元素 测定值
/(mg·L-1)RSD% Al 0.837 4.50 Si 0.858 4.58 Ca 0.0100 1.75 Mg 0.072 0.74 Mn 0.454 1.46 2.5 分析结果的准确度试验
因国内尚无钇铁合金标准样品,对钇铁合金样品53JYFe01进行标准加入回收试验,试验结果见表 7.
表 7 钇-铁合金样品53JYFe01进行标准加入回收试验Table 7. Recovery test by standard addition method元素 样品测定
值/(mg·L-1)加入量
/(mg·L-1)测定值
/(mg·L-1)回收率
/%Al 0.837 0.100 0.942 105.0 Si 0.858 0.100 0.961 103.0 Ca 0.0100 0.100 0.106 96.0 Mg 0.072 0.100 0.17 98.0 Mn 0.454 0.100 0.551 97.0 Al 0.837 1.00 1.799 96.2 Si 0.858 1.00 1.852 99.4 Ca 0.0100 1.00 0.964 95.4 Mg 0.072 1.00 1.040 96.8 Mn 0.454 1.00 1.377 92.3 3 结论
各元素测定结果的相对标准偏差(n=11)在0.74%~4.58%之间,回收率在92.30%~105.00%之间.钇-铁基体比例在60%~70%-40%~30%对测定无明显影响.试验证明方法满足钇铁中铝、硅、钙、镁、锰分别在0.003%~0.1%的分析测定.
赵中波 -
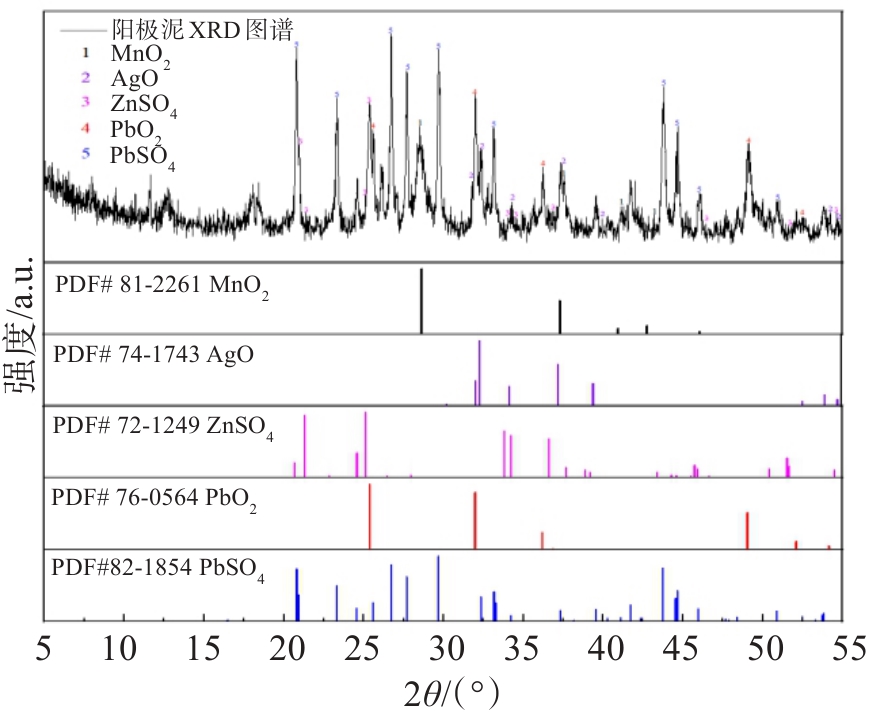
表 1 锌电解阳极泥主要元素含量
Table 1 Main metal composition of zinc electrolytic anode slime
主要元素 Mn Pb Zn Ag O S Na 其他 含量 34.57 9.78 2.21 0.038 35.80 7.493 2.22 7.889 表 2 阳极泥粒径对亚铁离子氧化率的影响
Table 2 Effect of anode slime particle size on oxidation ratio of ferrous ions
阳极泥粒径/mm 亚铁离子氧化率/% 0.355~<0.212 88.43 0.212~<0.154 92.64 0.154~<0.100 97.19 0.100~<0.075 97.21 ≥0.075 97.23 表 3 较优条件重复实验结果
Table 3 Results of repeated experiments under the optimal conditions
项目 氧化率/% 重复实验1 99.79 重复实验2 99.82 重复实验3 99.81 实验平均值 99.807 -
[1] 张家玮,王夏阳,何静.直流电协同锌板置换提镉的工艺实践[J].有色金属科学与工程,2015, 6(5): 22-26, 96. [2] 裴启飞,郭孟伟,邵伟春,等.锌电积体系Zn-MnO2同槽电解电化学分析[J].有色金属科学与工程,2024,15(3):322-331. [3] 铅锌冶金学编委会.铅锌冶金学[M].北京:科学出版社,2003: 410-453. [4] WANG W J, LI R D, YUAN T C, et al. Effects of Ag+ in diaphragm electrolysis on oxygen evolution and corrosion behaviors of Pb and Pb-Ag anodes[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020,192:105254.
[5] WANG W J, YUAN T C, LI R D, et al. Electrochemical corrosion behaviors of Pb-Ag anodes by electric current pulse assisted casting[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019,847:113250.
[6] Review of trends in 2021 zinc[N]. http://www.ilzsg.org/static/statistics.aspx.
[7] 王成彦,陈永强.中国铅锌冶金技术状况及发展趋势:锌冶金[J].有色金属科学与工程,2017,8(1): 1-7. [8] 马菲菲,展宗波.湿法炼锌电解阳极泥综合利用及Mn2+的控制[J].中国有色冶金,2022,51(3): 112-116. [9] ZHONG X C, WANG R X, XU Z F, et al. Influence of Mn2+ on the performance of Pb-Ag anodes in fluoride/choride containing H2SO4 solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017,174:195-201.
[10] 刘一宁,林文军,乔岚,等.一种从锌阳极泥中回收有价金属的方法[P].中国:CN102586599A,2013. [11] 伍永国,张荣荣,陈武超,等.电解锌锰阳极泥回收利用现状[J].广州化工,2022,50(18): 29-31. [12] 周冲冲,牛勤学,白宇峰,等.从锌电解阳极泥中回收锌锰并富集铅银的实验研究[J].中国有色冶金,2017,46(4): 69-72. [13] 吴焱,沈慧庭.改性无机还原剂还原浸出电解锰阳极泥综合回收锰铅研究[J].矿冶工程,2016,36(5): 69-72. [14] 赵兵伍,赵德军,李建福.锌电积阳极泥综合处理的研究[J].云南冶金,2013,42(3): 33-35,40. [15] 向平.锌电解阳极泥锰铅银分离的技术与理论研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2011, 9-10. [16] 廖俊梅.两种含锌二次资源中有价金属的回收研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013. [17] 向平,冯其明,刘朗明,等.物理方法从锌阳极泥中分离锰与铅银矿物工艺研究[J].矿业工程,2010,30(4): 54-57,64. [18] 廖云军,梅光贵,刘荣义.锌电解过程中减少锰离子贫化及对阳极泥返回利用的研究[J].中国锰业,1999,17(1): 30-33. [19] 谢庭芳,罗永光,焦志良,等.提高锌电积阳极泥中锰利用率的研究[J].矿产综合利用,2021(2): 134-140. [20] 沈慧庭,覃华,黄晓毅,等.某含锰冶金渣中锰和铅的综合回收研究[J].金属矿山,2009 (6): 171-175. [21] 梅晶.用电解锌阳极泥制备电池级硫酸锰的工艺研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2014,8-11. [22] 向平,冯其明,钮因健,等.硫化铅还原硫酸浸出锌电解阳极泥中二氧化锰的实验研究[J].湖南有色金属,2010,26(1): 19-23. [23] 牛向东,谭钰凡.响应曲面法优化锌阳极泥还原浸出的工艺研究[J].矿冶,2018,27(3): 65-70. [24] 耿家锐,王振杰,刘安荣,等.锌电解阳极泥中有价金属的提取工艺研究[J].矿冶工程,2019,39(4): 98-101. [25] 徐军.从锌阳极泥中综合回收锌锰并富集铅银的研究[J].湖南有色金属,2013,29(2): 23-26. [26] FAN J L, WANG G, LI Q, et al. Extraction of tellurium and high purity bismuth from processing residue of zinc anode slime by sulfation roasting-leaching-electrodeposition process[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 194: 105348.
[27] 李洪桂.冶金原理 [M].2版.北京:科学出版社,2018.



 下载:
下载: