The microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy
-
摘要: 采用选区激光熔化(SLM)技术成形Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金。研究了激光打印参数及热处理工艺对Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金显微组织与力学性能的影响。研究结果表明, 打印态Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金组织具有显著的各向异性特征: 建造面熔池为鱼鳞状, 晶粒为大尺寸柱状晶; 扫描面熔池则为条带状, 晶粒为小尺寸柱状晶与等轴晶。SLM成形的Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金存在大量热裂纹, 严重影响合金力学性能。但热处理后, Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金力学性能显著提高。经过热处理后合金的维氏(HV)硬度由91.70提升至144.27, 抗拉强度由183.71 MPa提升至257.53 MPa。
-
关键词:
- 选区激光熔化 /
- Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金 /
- 显微组织 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: The selective laser melting (SLM) was applied to prepare an Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the selective laser melted Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy was investigated before and after heat treatment. The results showed that the printed Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy had an anisotropic microstructure: a fish-scale-like molten pool, large columnar grains at the building plane, and small strips of grains with equiaxed grains at the scanning plane. A large number of hot cracks were found in the alloy, resulting in poor mechanical properties. However, after heat treatment, the performance of the alloy was significantly improved. After heat treatment, the Vickers hardness of the alloy increased from 91.70 to 144.27, and the tensile strength increased from 183.71 MPa to 257.53 MPa.-
Keywords:
- selective laser melting /
- Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy /
- microstructure /
- mechanical properties
-
0 引言
选区激光熔化(Selective Laser Melting, SLM)是一种典型的增材制造技术。近年来, SLM发展迅速, 已成为金属材料增材制造的主流技术之一。SLM首先通过软件将三维模型二维化, 利用高能激光束将平铺的金属粉末快速熔化并凝固, 并逐层打印最终成形为立体零部件[1-2]。与传统金属材料成形工艺相比, SLM技术具有成形精度较高、材料消耗少、可成形高复杂零部件等优点[3]。增材制造7xxx系铝合金因强度高、韧性好的特点, 在航空航天领域具有巨大应用潜力[4]。目前, 对传统牌号的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金SLM成形性能的研究发现, 其抗拉强度通常只有200 MPa, 力学性能不及传统变形铝合金[5-7]。而且, 由于SLM Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金中存在大量微裂纹, 热处理后的合金强度提高不明显, 限制了该体系合金的应用。Al-Zn-Mg-Sc系合金属于热处理强化高强度铝合金, 稀土元素Sc的加入, 不仅能显著地细化合金的晶粒和提高强度, 亦能提高合金的抗热裂性能, 从而显著地改善铝合金的可焊性、抗蚀性以及抗中子辐射损伤作用[8], 在航空航天领域具有较好的应用前景。然而, 目前关于Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金激光增材制造成形的研究较为匮乏。SLM成形Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金组织与性能研究尚处于探索阶段。
基于此, 本研究采用SLM技术制备Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金, 研究SLM打印工艺对合金冶金缺陷及组织性能的影响规律, 并探索SLM打印态合金的热处理强化工艺, 旨在为激光增材制造Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金未来工程应用提供理论和试验依据。
1 实验材料及方法
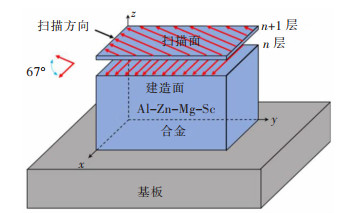
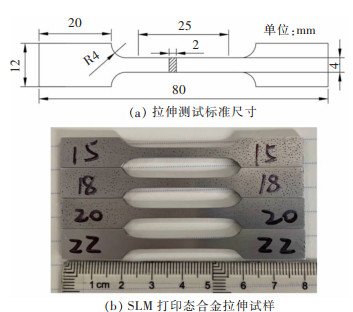
实验原材料为气雾化Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金粉(过筛的粒度是48 μm), 其化学成分如表 1所列。采用选区激光熔化技术成形合金块体, 如图 1所示。SLM参数为: 扫描速度200~1 200 mm/s, 激光功率160~360 W, 铺粉层厚均为0.05 mm, 扫描间距均为0.1 mm, 基板预热100 ℃。为探究热处理工艺对合金的强化作用, 设计了3种热处理工艺, 如表 2所列。采用ZEISS Axio Scope Al型金相显微镜观察合金的缺陷及微观组织, 采用EBSD(HKL Nrodlys Max2)表征成形合金的织构形态。为测试合金力学性能, 将成形合金加工成截面尺寸为4 mm×2 mm标距长度25 mm的拉伸试样(图 2), 并采用UTM/CMT5105电子万能力学试验机测试。采用200HVS-5维氏硬度计表征合金的显微硬度(载荷1 kg, 保持时间15 s)。
表 1 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金粉末化学成分Table 1. The chemical composition of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy powder 表 2 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的热处理工艺Table 2. The heat treatment processes for Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy
表 2 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的热处理工艺Table 2. The heat treatment processes for Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy
2 结果与讨论
2.1 SLM工艺参数对Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金冶金缺陷的影响
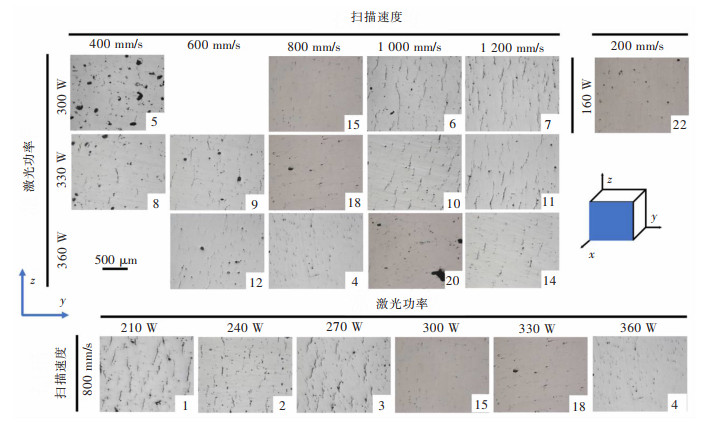
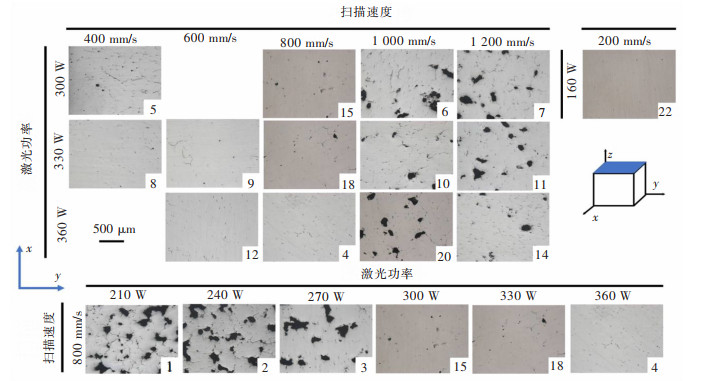
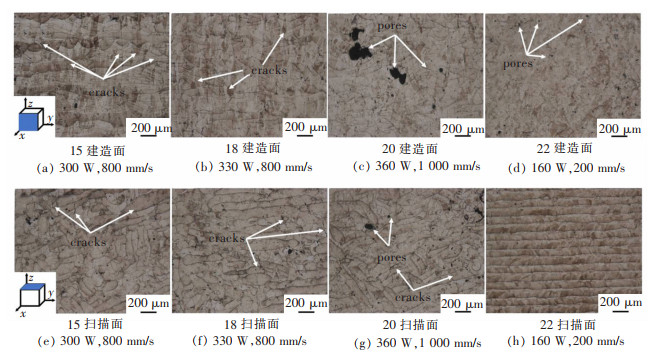
设置不同激光功率与扫描速度参数, 通过SLM成形Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金试样。试样扫描面(xoy面)与建造面(yoz面)的金相组织如图 3、图 4所示。由图 3可知, 裂纹主要集中于建造面, 且沿建造方向扩展。当扫描速度为800 mm/s、激光功率为300 W时, 合金建造面裂纹缺陷数量最少。由图 4可知, 孔隙缺陷主要集中于扫描面。当激光功率恒定时, 扫描面的孔隙缺陷数量随扫描速度增加而增加。当扫描速度恒定时, 扫描面孔隙缺陷数量随激光功率增加而减少。当激光功率与扫描速度均较小(160 W, 200 mm/s)时, 合金扫描面及建造面孔隙及裂纹缺陷均较少。铝合金SLM成形过程中, 激光功率较高但扫描速度较低时, 激光的能量输入较高, 高能激光束熔反冲压力使得熔池稳定性下降, 液态金属沿着熔池内壁上下振荡, 激光束移除后发生快速凝固, 并在熔池底部产生空腔[9]。当激光功率较低但扫描速度较高时, 会因为激光束能量输入不足导致合金粉末不能完全熔化, 产生不规则的键孔[9]。此外, 打印过程由于冷速过快或激光能量密度过低还会导致粉末未熔或保护气体未能及时逸出而产生气孔缺陷[10]。因而, 图 3、图 4中高激光功率低扫描速度下形成的微孔为键孔, 而低激光功率下形成的较大孔隙为气孔。由图 3、图 4可知, Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金SLM成形过程微裂纹主要形成于建造面。裂纹为影响SLM Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金力学性能的主要缺陷。
2.2 选区激光熔化Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金显微组织
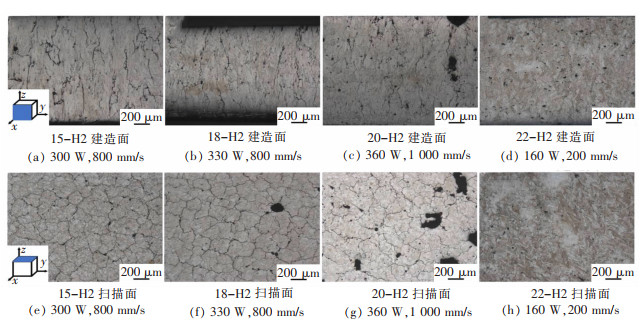
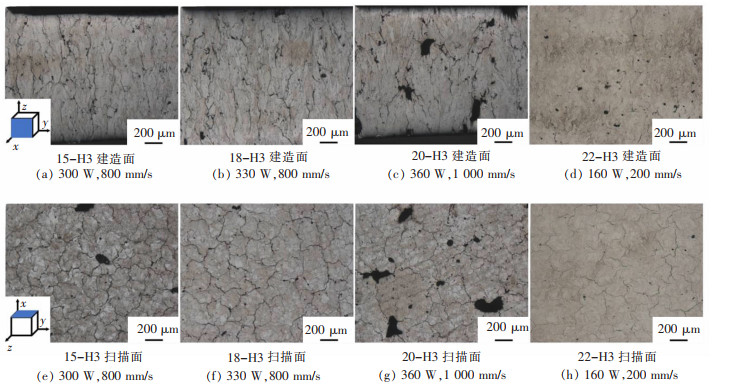
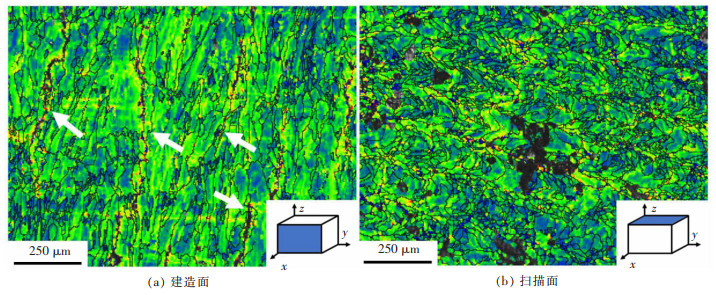
图 5所示为原始打印态合金的金相组织, 可在扫描面上观察到条带状、短棒状的熔池痕迹, 而建造面上的熔池痕迹则为鱼鳞状。其中, 22号试样扫描速度慢、激光能量密度高, 导致扫描面上沿激光扫描方向存在温度梯度, 导致其扫描面形成比较明显的柱状晶。而15号、18号、20号试样激光扫描速度较快、温度梯度较小, 导致扫描面的晶粒沿温度梯度生长不明显, 形成等轴晶。图 6、图 7所示为经过H2、H3工艺热处理后的Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金金相组织。经热处理, 合金组织形貌出现变化。热处理后打印态合金上较为明显的熔池痕迹减弱甚至消失, 出现显著的晶粒形貌与缺陷。
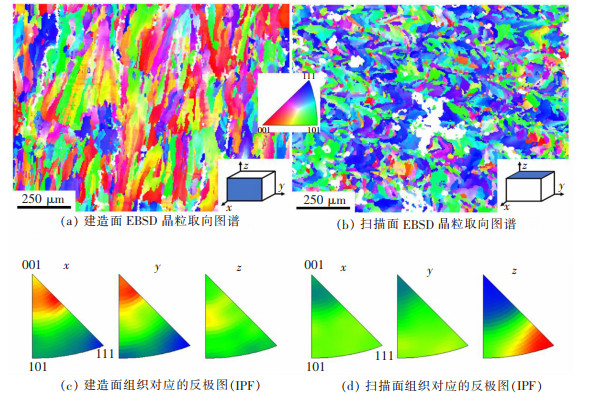
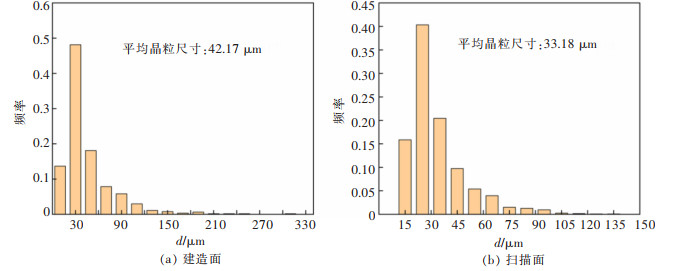
图 8所示为打印态Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金电子背散射衍射(EBSD)图谱。图 9所示为打印态合金建造面和扫描面的晶粒尺寸分布图。由图 8(a)、图 9(a)可知, 试样建造面的晶粒主要为尺寸较大的柱状晶, 平均晶粒尺寸为42.17 μm。打印过程中激光束沿着建造方向(oz)熔化金属粉末, 在该方向产生较大温度梯度, 致使晶粒沿oz方向生长, 最终在建造面形成大尺寸柱状晶组织[11]。从图 8(b)、图 9(b)中可观察到扫描面的熔池痕迹。熔池内的晶粒为较短的柱状晶及小尺寸等轴晶, 平均晶粒尺寸为33.18 μm, 小于建造面晶粒尺寸。结合22号试样的金相组织图 5(d)可发现, 扫描面的小柱状晶呈一定角度指向熔池中心。这是由于在SLM过程中, 激光束在熔化金属粉末并向前移动过程中形成了特定的温度梯度, 即热量沿着激光束运动的反方向散失, 导致晶粒沿着温度梯度向激光束运动的方向生长[12], 形成了小范围的柱状晶组织。此外, SLM过程中, 由于在建造方向和扫描方向均存在温度梯度, 最终导致合金形成明显的织构, 如图 8(c)、图 8(d)所示。在建造方向(oz)上, 合金组织具有典型的[111]择优生长取向。
通过打印态Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的金相组织图(图 3、图 4)可以观察到, 扫描面与建造面均存在裂纹缺陷, 但建造面裂纹较扫描面多。根据液膜理论, 晶界是凝固最后阶段不同晶粒相互接触而产生的, 晶界处的液膜易受凝固收缩的张力而最终产生热裂纹[13-14]。一般认为, 晶间裂纹在大角度晶界处更容易形成。图 10所示为打印态合金建造面与扫描面的晶界局部取向差分布图, 可观察到建造面的裂纹均形成于大角晶界处(图 10(a)中白色箭头), 说明在大角度晶界处更易形成裂纹缺陷。此外, 在建造面(图 5)中可观察到有裂纹分布在熔池的中心区域, 且两相邻熔池中心裂纹的间距与扫描间距相近。AKASH等也观察到了类似的现象, 并认为这是由于打印过程中熔池中心能量输入最高[15], 当激光束移除后, 极快的冷却速度会产生较大的热应力, 使相邻晶粒彼此分离, 极高的冷却速度导致液态金属无法有效地填充两晶粒间隙而最终产生裂纹[13]。因而, 有学者认为, 裂纹萌生于熔池中心, 建造面晶界裂纹也是由熔池中心的裂纹引起的[15]。
2.3 热处理对SLM Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金力学性能的影响
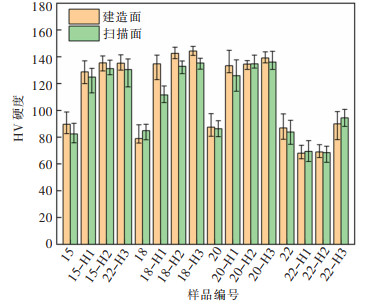
图 11所示为SLM Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金热处理前后的显微维氏硬度。合金建造面与扫描面的硬度相近, 不存在明显的硬度各向异性。经热处理后, 试样的硬度均有大幅度的提升。其中, 试样18经H3热处理后显微HV硬度达144.27。而22号试样硬度经H1和H2热处理后硬度反而有所降低, 经H3热处理后硬度提升不明显。热处理对合金硬度的影响出现较大差异, 可能与SLM打印参数有关。粉末SLM过程中, 激光束能量密度输入可由式(1)计算[16]:

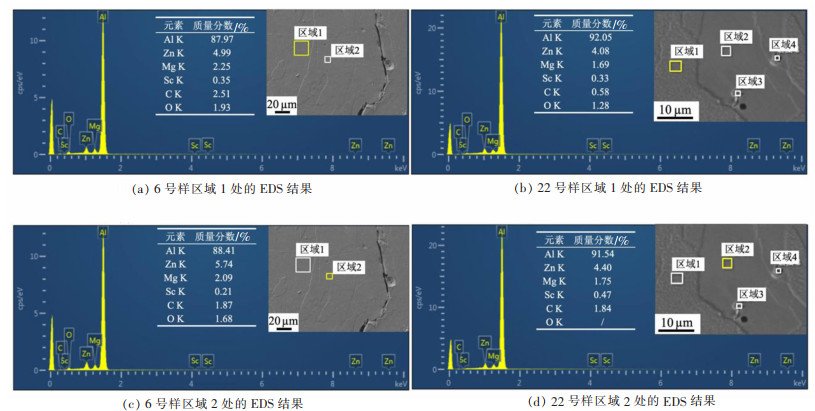
(1) 式(1)中: P为激光功率; h为扫描间距; v为扫描速度; t为层厚。通过式(1)可计算得到15号、18号、20号、22号4个试样打印过程激光能量输入密度分别为: 156、171、150、333 J/mm3。可见, 22号试样激光能量密度显著大于其余合金试样。当能量密度输入过高时, 会导致合金Zn、Mg元素严重烧损, 降低合金Zn、Mg元素含量, 造成合金成分变化, 从而导致合金硬度的降低[17-18]。图 12所示为不同激光能量密度成形试样的EDS面扫描分析结果。可见, 激光成形后的合金Zn、Mg元素含量均低于SLM成形前粉末中Zn、Mg含量(见表 1)。而且, 高激光能量密度成形试样22中, Zn、Mg元素含量均低于低激光能量密度成形的6号试样。尤其是Zn元素, 打印过程中挥发验证导致其含量显著低于原料粉末。因此, 22号试样热处理后的硬度提升不明显有可能是由于能量密度输入过高使得合金元素烧损所导致的。
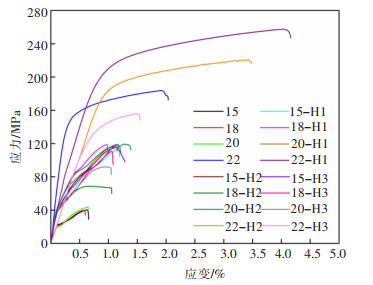
图 13所示为SLM Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金热处理前后的拉伸应力应变曲线。表 3所列为合金拉伸性能数据。可见, SLM Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金经过热处理后拉伸性能显著提升。其中, 22号试样经H2热处理后, 抗拉强度最高值由原始状的183.71 MPa提升至257.53 MPa。而15号、18号、20号试样中孔隙、裂纹缺陷较多(图 2、图 3), 导致3个试样热处理后的抗拉强度、屈服强度以及延伸率依然不高, 且不及22号试样。
表 3 热处理前后Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的拉伸性能Table 3. The tensile properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy before and after heat treatment
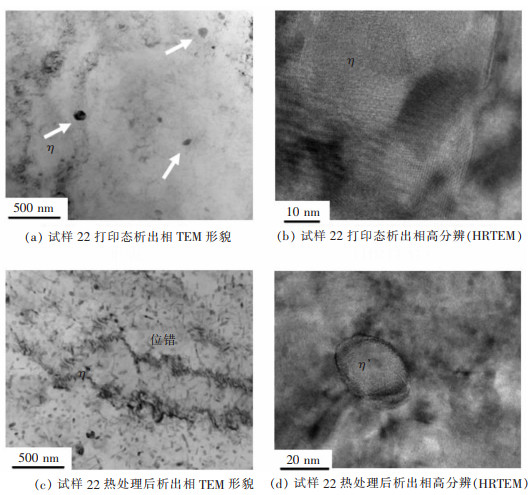
图 14所示为原始状态与热处理后合金22号试样的TEM图。从图 14(a)中可以看到打印态合金内部存在少量大颗粒析出相, 通过透射高分辨图像可判断其尺寸约为100 nm(图 14(b))。此为典型的平衡相-η相。在热处理的固溶阶段大尺寸的η相重新溶解到铝合金基体内部。在时效阶段, 大量小尺寸η'相(约20 nm)析出并弥散分布在合金内部及晶界处, 如图 14(c)所示。这些弥散分布的η'相颗粒不仅起到了第二相强化的作用, 同时对晶粒内部位错和晶界起到了钉扎作用(图 14(c))[19-20]。这解释了为何SLM成形Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金热处理后其力学性能普遍有所提高。
3 结论
1) SLM成形的Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金组织呈现各向异性。其合金建造面组织为大尺寸柱状晶, 而扫描面组织为小尺寸柱状晶和等轴晶。各向异性组织的形成与SLM过程产生的温度梯度有关。由于建造面温度梯度高, 使合金在(oz)方向形成[111]择优生长取向。
2) SLM成形的Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金中存在大量冶金缺陷, 且受打印参数影响较大。激光能量密度过高或过低都会均导致合金形成大量孔隙、裂纹缺陷。激光能量密度较高时会导致合金中Mg及Zn元素蒸发, 从而降低合金的硬度。
3) 热处理可提高SLM成形Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的力学性能。经过热处理后, 合金的维氏硬度可由91.70提升至144.27, 抗拉强度由183.71 MPa提升至257.53 MPa。
-
表 1 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金粉末化学成分
Table 1 The chemical composition of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy powder

表 2 Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的热处理工艺
Table 2 The heat treatment processes for Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy

表 3 热处理前后Al-Zn-Mg-Sc合金的拉伸性能
Table 3 The tensile properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy before and after heat treatment

-
[1] WANG P, ECKERT J, PRASHANTH K G, et al. A review of particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(8): 2001-2034. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65357-2
[2] 魏娟娟, 米国发, 许磊, 等. 激光增材制造铝合金及其复合材料研究进展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019, 48(8): 27-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201908008.htm [3] LI N, HUANG S, ZHANG G D, et al. Progress in additive manufacturing on new materials: a review[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35(2): 242-269.
[4] 耿遥祥, 樊世敏, 简江林, 等. 选区激光熔化专用AlSiMg合金成分设计及力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2020, 56(6): 821-830. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB202006002.htm [5] RESCHETNIK W, BRüGGEMANN J P, AYDINöZ M E, et al. Fatigue crack growth behavior and mechanical properties of additively processed EN AW-7075 aluminium alloy[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2016, 2: 3040-3048. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2016.06.380
[6] BRüGGEMANN J P, RISSE L, KULLMER G, et al. Optimization of the fracture mechanical properties of additively manufactured EN AW-7075[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2018, 13: 311-316. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2018.12.052
[7] ZHOU S Y, SU Y, WANG H, et al. Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of 7xxx series Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy: Cracking elimination by co-incorporation of Si and TiB2[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 36: 101458. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2020.101458
[8] 徐国富, 彭小燕, 段雨露, 等. 新型Al-Mg-Sc-Zr和Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(8): 1577-1587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201608001.htm [9] TAN Q Y, LIU Y G, FAN Z Q, et al. Effect of processing parameters on the densification of an additively manufactured 2024 Al alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2020, 58: 34-45.
[10] ABOULKHAIR N T, EVERITT N M, ASHCROFT I, et al. Reducing porosity in AlSi10Mg parts processed by selective laser melting[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2014(1/2/3/4): 77-86.
[11] GALY C, LEGUEN E, LACOSTE E, et al. Main defects observed in aluminum alloy parts produced by SLM: from causes to consequences[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 22: 165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2018.05.005
[12] WANG Y F, YU C F, XING L L, et al. Grain structure and texture of the SLM single track[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 281: 116591. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116591
[13] LIU J W, KOU S. Crack susceptibility of binary aluminum alloys during solidification[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 110: 84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.03.030
[14] KOU S A. Criterion for cracking during solidification[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 88: 366-374. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.01.034
[15] SONAWANE A, ROUX G, BLANDIN J J, et al. Cracking mechanism and its sensitivity to processing conditions during laser powder bed fusion of a structural aluminum alloy[J]. Materialia, 2021, 15: 100976. doi: 10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100976
[16] 阎昱, 易海佳, 王海波. 增材制造工艺对316L不锈钢板材力学性能的影响[J]. 北方工业大学学报, 2020, 32(5): 124-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFGY202005020.htm [17] LEI Z L, BI J, CHEN Y B, et al. Effect of energy density on formability, microstructure and micro-hardness of selective laser melted Sc-and Zr-modified 7075 aluminum alloy[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 356: 594-606. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.08.082
[18] QI T, ZHU H H, ZHANG H, et al. Selective laser melting of Al7050 powder: melting mode transition and comparison of the characteristics between the keyhole and conduction mode[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 135: 257-266.
[19] 邹田春, 欧尧, 祝贺, 等. 热处理对激光选区熔化AlSi7Mg合金微观组织和拉伸性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019, 48(20): 154-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201920039.htm [20] KHAN M A, WANG Y W, ANJUM M J, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the precipitate behaviour, corrosion resistance and high temperature tensile properties of 7055 aluminum alloy synthesis by novel spray deposited followed by hot extrusion[J]. Vacuum, 2020, 174: 109185. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109185
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 刘冉,党鲜婷,彭雅婷,吴韬,韩飞. 激光熔覆CoCrNi/WC复合涂层的组织及性能研究. 稀有金属. 2025(01): 68-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 潘文瀚,许明三,韦铁平,叶建华,朱峰立,杨林沂. 选区激光熔化拱形点阵力学性能影响及优化. 有色金属科学与工程. 2025(01): 43-53 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 侯少杰,李春燕,李春玲,张强,陈佳欣,程志强. 大尺寸非晶合金的成分设计和新制备方法研究进展. 稀有金属. 2024(02): 240-253 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张莹莹,王学兵,熊宁,柳学全,赵虹淳. 丝电爆法制备球形W-25%Re合金粉末的组织和性能研究. 稀有金属. 2024(10): 1367-1377 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郭鑫涛,杨亚琴,蔺温杰,郑建民,张博宇,张幸悦,苗芳,刘斌. 难熔金属材料增材制造工艺研究进展. 铜业工程. 2023(06): 1-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: