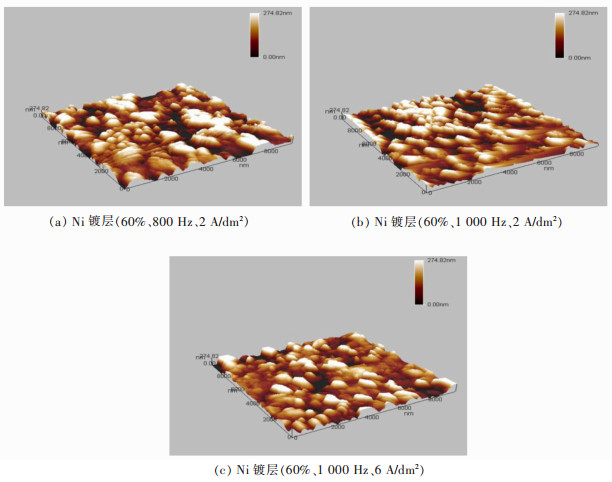
Parameter influence and corrosion resistance mechanism of Ni coatings under pulse electroplating
-
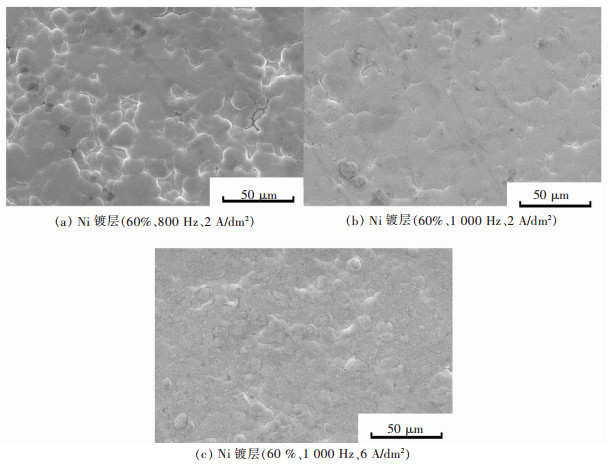
摘要: 用脉冲电流在钕铁硼磁体表面制备Ni镀层;并通过单因素试验依次对脉冲参数进行优化。实验发现当占空比为60%、频率为1 000 Hz、电流密度为6 A/dm2时,Ni镀层的耐腐蚀倾向和腐蚀速率最小,Ni镀层耐电化学腐蚀性能较优。观察镀层表面的微观结构发现镀层表面Ni颗粒尺寸更加均匀,镀层表面平整度更高,因此镀层的综合质量更高,改善了镀层的耐腐蚀性能。对相同静态腐蚀条件下Ni镀层腐蚀形貌观察发现,占空比和频率优化后的Ni镀层表面均生成团聚状的腐蚀产物,出现应力腐蚀现象,腐蚀较为严重。调控电镀过程中的电流密度能够减少镀层的残余应力,避免出现应力腐蚀现象,从而提升镍镀层的耐腐蚀性能。Abstract: The Ni plating was prepared on the surface of the NdFeB magnet under a pulse current, and the pulse parameters were optimized by one-variate test in turn. The results showed that the Ni plating was of the least corrosion resistance tendency and corrosion rate, and the optimal electrochemical corrosion resistance at the duty ratio of 60%, frequency of 1 000 Hz and current density of 6 A/dm2. It was found that in the microstructure of the plating that the Ni particles were of more uniform size and the plating of smoothing surface so that the overall quality of Ni plating was promoted, and the corrosion resistance was improved as well. Under the same static corrosion condition, it was also found that aggregated corrosion products were generated on the surface of Ni plating when duty ratio and frequency were optimized, which showed rather serious stress corrosion. Regulating the current density in the process of plating could reduce the residual stress of the plating and avoid stress corrosion, and accordingly improve the corrosion resistance of Ni plating.
-
Keywords:
- pulse current /
- Ni plating /
- NdFeB /
- corrosion resistance
-
目前的锂离子电池正极材料主要集中在镍钴锰系,但这些正极材料都有着各自的缺陷. 商品化的LiCoO2正极材料由于钴资源稀有,价格昂贵并且LiCoO2的实际容量不高,高温条件下的热稳定性和安全性能差及钴离子的环境污染等问题阻碍了其进一步发展[1]. LiNiO2理论比容量为274 mAh/g,实际容量可达190~210 mAh/g,在容量和价格上比LiCoO2有优势,但是LiNiO2存在诸多缺点,如合成困难[2-3]、在充放电过程中因Jahn-Teller效应导致循环性能差[4]、首次充放电库仑效率较低、存在安全问题[5]等. 尖晶石型LiMn2O4的主要缺点在于Mn3+的溶解、Jahn-Teller效应和电解液分解引起的循环容量下降,高温条件下尤为明显[6-7]. 1999年,Liu等[8]最早用混合氧氧化物法制备LiNi1-x-yOxMnyO2三元系列材料,这种材料充分综合LiNiO2的高比容量、LiCoO2良好的倍率性能,以及LiMnO2的高安全稳定性和低成本等优点,综合性能优于单组分化合物. 王海燕等[9]采用碳酸盐共沉淀法制备LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2正极材料,在2.8~4.3 V,1 C下,放电比容量为137.8 mAh/g,前40 次循环容量保持率为96 %. 马全新等[10]采用液相共沉淀法制备LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2,正极材料,在20 mA/g电流密度,2.5~4.3 V下,首次放电比容量为175 mAh/g,首次库伦效率在89 %~90 %之间,30次循环未见容量衰减. Li等[11-12]采用固相法,制备LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2,在40 mA/g电流密度,3.0~4.6 V下,首次放电比容量达到172 mAh/g,25次循环后,容量保持率为85 %. 钟盛文等[13]采用共沉淀法制备LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2,并研究掺杂Al(OH)3对材料循环性能的影响,在2.75~4.2 V,1 C下,首次放电比容量达到157.2 mAh/g,循环50次容量保持率为94.8 %.少量Al(OH)3的掺杂对材料结晶性有所提高,但是放电比容量有所下降,前100次循环掺杂对材料循环性能无明显效果. 袁超群等[14]采用高温固相反应合成了LiNi0.75-xCoxMn0.25O2(x=0.05,0.1,0.15,0.2,0.25),结果表明:当x=0.2时,材料性能最好,在50 mA/g电流密度,3~4.3 V下,首次放电比容量为172.5 mAh/g,放电效率为90.9 %. 中南大学Li等[15]采用快速共沉淀法制备LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2纳米材料. 在18 mA/g电流密度下,2.7~4.3 V,首次放电比容量达192.4 mAh/g,40次循环后容量保持率达91.56 %. Cho等[16]用AlPO4对LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2进行表面包覆. 结果表明:包覆后,材料的容量几乎没有减少,首次放电比容量达188 mAh/g,热稳定性和循环稳定性都得到改善. 杨驰[17]通过溶胶-凝胶法制备出LiNi0.92Co0.04Mn0.04O2正极材料,在2.8~4.3 V,0.5 C下,首次放电比容量为211.3 mAh/g,50次循环后仍有174.5 mAh/g,容量保持率为82.6 %. 通过对文献的参阅研究发现,国内外对镍基尤其是镍基三元正极材料的研究时间不长,相关方面的研究也不是很多. 用资源丰富的Ni、Mn取代昂贵且是战略资源的Co,融合了3种元素的优势,因此制备出容量高并且循环稳定的镍基三元正极材料显得尤为重要. 而LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2作为一种很有潜力的三元镍基正极材料,文中将采用共沉淀法合成镍钴锰氢氧化物前驱体,使其和LiOH·H2O混合均匀后,经高温焙烧合成正极材料LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2,并研究不同焙烧温度和锂配量对材料综合性能的影响,以期制备出高容量和稳定的LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2正极材料.
1 实 验
1.1 LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2材料的合成
以NiSO4·6H2O、MnSO4·H2O、CoSO4·H2O为原料,按照6∶3∶1的摩尔比混合均匀,配制成2 mol/L的金属盐溶液,另称取一定量的NaOH配制成4 mol/L的碱溶液,通过恒流泵将混合盐溶液和碱溶液同时均匀的滴加到有N2保护的反应釜中,控制反应釜中的温度为55 ℃,反应pH值控制在11.35附近,保持共沉淀反应在20 h左右,保证制得形貌规则的类球形前驱体Ni0.6Co0.1Mn0.3(OH)2,反应完成后,将前驱体进行洗涤,过滤,干燥24 h后与LiOH·H2O按化学一定的计量比混合,放于石英管式炉中,在不同的温度和锂配量下进行焙烧,制得正极材料LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2.
1.2 LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2材料形貌及结构表征
实验采用日本理学公司生产的Miniflex X射线衍射仪(XRD)进行结构分析,测试条件为:铜阳极CuKα射线(波长Å=0.154 18 nm),电压为45 kV,电流为40 mA,扫描速度为5°/min,扫描步长为0.02°,扫描范围为10°~80°.采用荷兰飞利浦XL30W/TMP型扫描电镜对材料进行形貌分析.
1.3 LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2材料的电化学性能测试
将称量好的聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)溶于N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)中,待PVDF完全溶解后,按照正极材料∶PVDF∶导电剂=90∶6∶4的配制,搅拌调成糊状料浆,将料浆均匀涂覆于铝箔上,放于120 ℃的恒温鼓风干燥箱中干燥,待干燥完全后,在双辊轧膜机上对辊,通过手动冲片机冲片制得极片,放于60 ℃的恒温干燥箱中干燥12 h. 选用的负极材料为锂片,以1 mol/L的LiPF6/DMC+EMC+EC(体积比为 1∶1∶1)为电解液,隔膜采用 Celgard2400,在充满氩气的手套箱中装配成2032型纽扣电池.采用NEWARE BTS型电池测试系统对电池进行电性能测试,充放电电压范围为2.75~4.2 V,测试温度为25 ℃.
2 结果分析与讨论
2.1 iNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2材料的电化学性能
图 1所示为不同焙烧温度的材料在25 ℃,电压范围为2.75~4.2 V,1 C倍率下,50次循环后的循环曲线. 表 1为不同焙烧温度,材料在1 C倍率下50次循环后的放电比容量.
表 1 不同温度下LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2 放电比容量表Table 1. Discharge specific capacity of LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2 at different temperature温度/℃ 首次放电容量
/(mAh·g原员)第50 次放电容量
/(mAh·g-1)效率/% 750 120.3 108.4 90.10 800 133.2 121.0 90.84 850 137.1 121.2 88.40 900 146.0 130.9 89.66 结合图 1和表 1分析可知:焙烧温度对材料的电化学性能有较大的影响,在一定温度范围内,随着焙烧温度的提高,合成材料的循环放电比容量随着温度的升高而增大.这是因为焙烧温度的提高,材料的固相反应更加完全,晶体生长的更加完整,材料的结构完整性更好,在后期电池循环过程中,材料晶体的完整有利于锂离子的顺利脱嵌,保证了材料具有一个比较高的放电比容量以及循环稳定性,综上可知:900 ℃时材料性能较好,在2.75~4.2 V,1 C倍率下,首次放电比容量为146.0 mAh/g,经过50次循环后仍有130.9 mAh/g,容量保持率为89.66 %.
通过前期对正极材料焙烧温度的探讨,得到较好焙烧温度900 ℃,实验中发现在相同的焙烧温度下,不同的锂配量对正极材料的电化学性能有较大影响,后期将对材料的锂配量进行探讨,实验中选择在最佳焙烧温度900 ℃下,对正极材料的锂配量进行探讨. 图 2所示为900 ℃下,不同锂配量的材料在25 ℃,2.75~4.2 V,1 C倍率下的循环曲线. 表 2为不同锂配量下LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2在50次循环后的放电比容量.
表 2 在不同锂配量下LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2 的放电比容量表Table 2. Discharge specific capacity of LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2 at different Li/M(Ni, Co, Mn)锂配量 首次放电容量
/(mAh·g-1)第50 次放电容量
/(mAh·g-1)效率/% 1.01 122.8 104.8 85.9 1.03 133.4 124.2 93.1 1.05 146.0 130.9 89.6 1.07 139.7 131.2 93.9 1.09 143.7 141.3 98.3 1.10 138.8 99.7 71.8 根据图 2和表 2分析可以得到:在最佳焙烧温度900 ℃下,正极材料的电化学性能随着锂配量的增加,放电比容量呈现先增大后减小的趋势,且当锂配量不足或过多时,正极材料的循环稳定性会受到较大的影响.在焙烧过程中,锂元素会挥发,导致正极材料出现缺锂现象,Ni2+占据Li+位置,使Li+和Ni2+混排严重,锂配量过多又会导致Li+析出吸附在正极材料表面,阻碍Li+的脱嵌,使材料性能下降,所以锂的适当过量将弥补烧结过程中锂的挥发,让材料的晶体生长完整,结构更加稳定以及良好的循环性能. 综上可知,当锂配量为1.09时,在2.75~4.2 V,1 C倍率下,正极材料的首次放电比容量为143.7 mAh/g,50次循环后仍有141.3 mAh/g,容量保持率为98.3 %,所以锂配量为1.09下正极材料的电化学性能最好.
2.2 iNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2材料的晶体结构
通过对材料焙烧温度和锂配量的探讨,确定了较佳烧结温度和最佳锂配量,XRD测试中选取最佳条件下制备的正极材料进行结构分析,图 3所示为最佳条件下合成LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2的XRD图谱.
由图 3分析可知,最佳条件下合成的材料在2θ为(003)、(101)、(006)、(102)(104)、(108)、(110)等特征晶面附近处都出现LiNiO2特征峰,表明材料具有典型的α-NaFeO2型层状结构,尤其在(006)和(102)以及(108)和(110)晶面处出现明显的层状LiNiO2的特征峰,并且两组特征峰分裂明显,强度相近,表明材料中合成了层状结构较好的正极材料,由此我们可以知道,在较佳温度900 ℃和较佳锂配量1.09下焙烧出的正极材料其固相反应完全,材料晶体发育完整,阳离子混排程度较小,二维层状有序度高,因此其电化学性能更好.
2.3 LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2材料的表面形貌
SEM测试过程中同样选取较佳温度900 ℃和最佳锂配量1.09下烧制出的正极材料进行形貌分析,图 4所示为最佳条件下合成LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2的扫描电镜图.
从图 4中可以看到,合成的正极材料颗粒均是由多个亚微米级的一次颗粒堆积形成的二次颗粒,一般在10 μm左右,且颗粒之间存在较多的空隙,颗粒表面光滑,球形度好,比表面积较大,有利于活性物质与电解液的充分接触,降低材料的内阻以及在充放电过程在层通道中的传递,从而提升了材料的电化学性能.
3 结 论
实验采用共沉淀法合成Ni0.6Co0.1Mn0.3(OH)2前驱体,采用高温固相法,在空气氛下,合成LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2正极材料. 通过实验探究其合成的工艺条件,结果表明,相同条件下,900 ℃时材料的性能较优. 在25 ℃,2.75~4.2 V,1 C倍率下,材料的首次放电比容量为146.0 mAh/g,50次循环后放电比容量为130.9 mAh/g,容量保持率为89.66 %.较佳的焙烧温度900 ℃下,通过锂配量的优化对比得出,锂配量为1.09时放电比容量最好,在25 ℃,2.75~4.2 V,在1 C倍率循环下,其首次放电比容量为143.7 mAh/g,50次循环后放电比容量仍有141.3 mAh/g,容量保持率为98.3 %,由此可以看出制备出的LiNi0.6Co0.1Mn0.3O2正极材料具有较高的比容量并且循环性能优异,是一种很有潜力的锂离子电池正极材料.
-
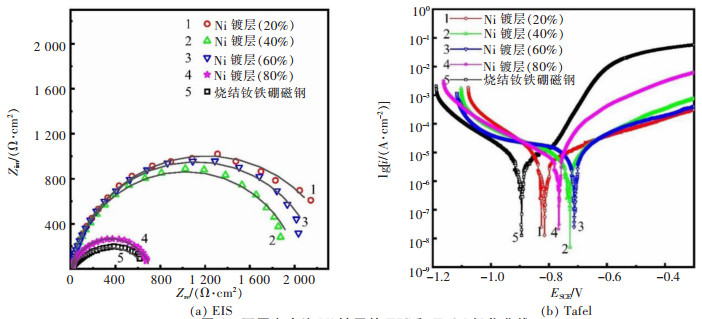
表 1 不同占空比下Ni镀层的Tafel拟合结果
Table 1 The tafel fitting results of Ni coatings with different duty ratio

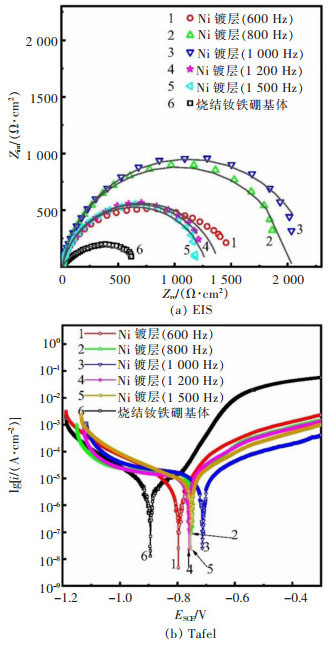
表 2 不同频率下Ni镀层的Tafel拟合结果
Table 2 The tafel fitting results of Ni coatings with different frequency

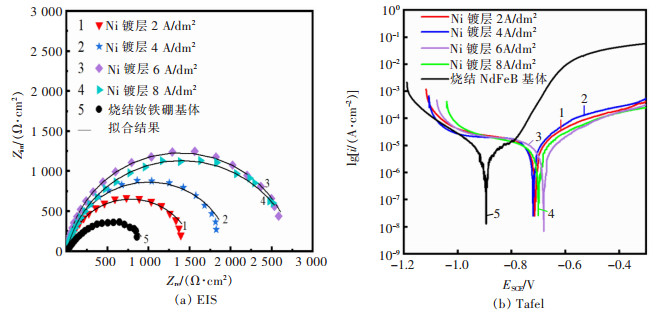
表 3 不同电流密度下Ni镀层的Tafel拟合结果
Table 3 The tafel fitting results of Ni coatings with different current density

-
[1] 刘卫强, 查善顺, 岳明, 等. 高矫顽力烧结钕铁硼永磁研究进展[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2017, 43(10): 1569-1579. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2017010002 [2] SAGAWA M, FUJIMURA S, TOGAWA N, et al. New material for permanent magnets on a base of Nd and Fe (invited)[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1984, 55(6): 2083-2087. doi: 10.1063/1.333572
[3] 李家节, 郭诚君, 钟明龙, 等. NdFeB磁体耐盐雾腐蚀行为研究[J]. 稀土, 2015, 36(5): 49-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201505009.htm [4] YANG L J, BI M X, JIANG J, et al. Effect of cerium on the corrosion behavior of sintered (Nd, Ce)FeB magnet[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2017, 432: 181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.01.094
[5] XU J L, XIAO Q F, MEI D D, et al. Microstructure, corrosion resistance and formation mechanism of alumina micro-arc oxidation coatings on sintered NdFeB permanent magnets[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 309: 621-627. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.12.023
[6] 王勇, 张祖军. NdFeB磁性材料表面化学镀Ni-W-P合金研究[J]. 机械工程与自动化, 2020, 3(1): 90-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCKG201102014.htm [7] ZHANG P, LIANG L, JIN J, et al. Magnetic properties and corrosion resistance of Nd-Fe-B magnets with Nd64Co36 intergranular addition[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 616: 345-349. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.07.085
[8] 黎翻, 曾阳庆, 甘家毅, 等. 钕铁硼永磁材料腐蚀机理及表面防护技术现状[J]. 湖南有色金属, 2018, 34(1): 46-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2018.01.014 [9] 黄涛, 王向东, 石晓宁, 等, 钕铁硼稀土永磁材料腐蚀防护技术的研究进展[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2018, 36(4): 394-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB201804002.htm [10] 徐超, 周建波, 崔小莹, 等. 电沉积制备镍-铁-钨合金析氢电极的工艺研究[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 2020, 39(9): 527-531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDTL202009002.htm [11] YUAN X T, WANGY, SUN D B, et al. Influence of pulse parameters on the microstructure and microhardness of nickel electrodeposits[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2008, 202 (9): 1895-1903. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2007.08.023
[12] MOHAJERI S, DOLATI A, GHORBANI M. The influence of pulse plating parameters on the electrodeposition of Ni-TiO2 nanocomposite single layer and multilayer structures on copper substrates[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2015, 262: 173-183. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.12.042
[13] WANG P. Effect of pulse reverse electrodeposition parameters on the microstructure of the Ni/NiO composite coating[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2020, 15: 241-51.
[14] 卢帅, 郭昭, 齐海东, 等. 占空比对脉冲电镀Zn-Ni-Mn合金镀层的影响[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2017, 37(11): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3849.2017.11.001 [15] WANG X, SHEN L D, QIU M B, et al. Effect of friction on preparation of ndFeB Nickel coating by jet electrodeposition[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2018, 13: 7706-7717.
[16] GYFTOU P, PAVLATOU EA, SPYRELLIS N. Effect of pulse electrodeposition parameters on the properties of Ni/nano-SiC composites[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(11): 5910-5916.
[17] NASIRPOURI F, SANAEIAN MR, SAMARDAK AS, et al. An investigation on the effect of surface morphology and crystalline texture on corrosion behavior, structural and magnetic properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel films[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 292: 795-805. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.053
[18] 赵品, 谢辅洲, 孙振国, 等. 材料科学基础教程[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2016. [19] 房博文, 贺春林, 霍嘉翔, 等. 电流密度对电镀铜-镍合金微观结构和耐蚀性[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 2020, 39(7): 377-382. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDTL202007001.htm [20] 高远, 程先华. 高效电镀电流密度与腐蚀裂纹研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2003, 11(4): 438-440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0299.2003.04.029 [21] 谭俊, 郭文才, 徐滨士, 等. 脉冲换向电刷镀镍基纳米SiO2复合镀层的耐腐蚀性能研究[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2006(4): 193-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGFF200604000.htm [22] 曾祥德. 影响亮镍镀层应力腐蚀因素分析[J]. 五金科技, 1993(1): 28-31.




 下载:
下载: