Recovery of copper from copper manganese residue by acid leaching and selective sulfide precipitation
-
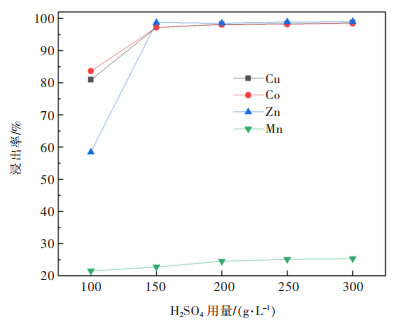
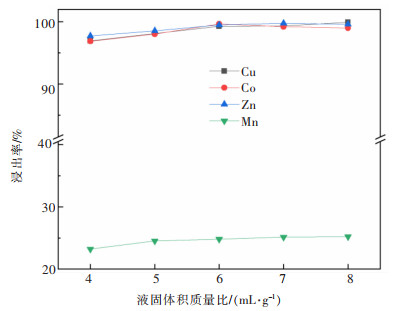
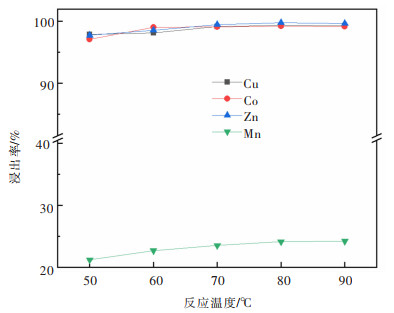
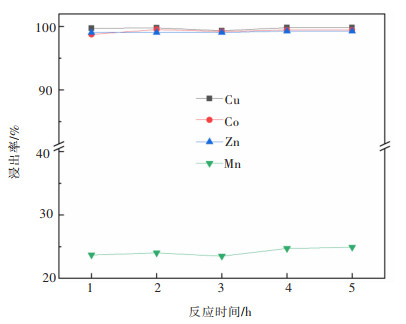
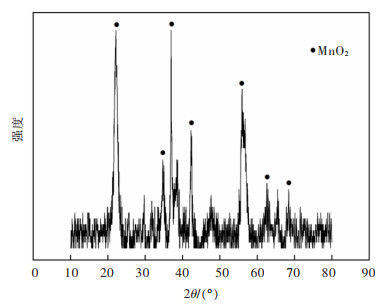
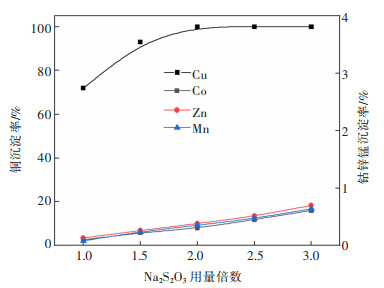
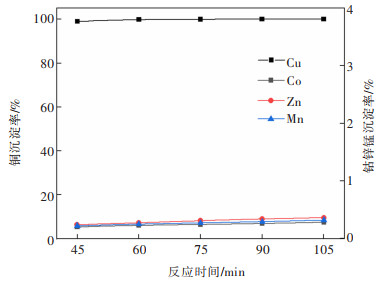
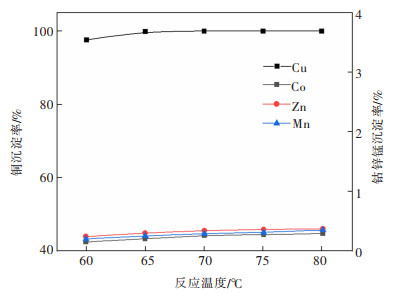
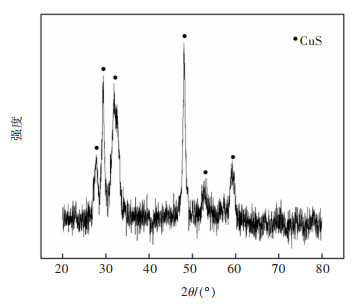
摘要: 系统开展了铜锰渣的H2SO4浸出及酸浸液Na2S2O3选择性沉铜研究,通过单因素实验,分别探究了2个工艺过程的影响因素。实验结果表明:铜锰渣酸浸的较优条件为:H2SO4用量200 g/L,液固体积质量比(mL/g)7∶1,反应温度80 ℃,反应时间2 h,该条件下铜、钴、锌、锰的浸出率分别为99.81%,99.54%,99.07%,24.10%,浸出渣主要物相为MnO2。酸浸液选择性硫化沉铜的较优条件为Na2S2O3用量倍数2.0,反应时间90 min,反应温度70 ℃,该条件下铜、钴、锌、锰的沉淀率分别为99.99%,0.26%,0.34%,0.29%,沉铜渣主要物相为CuS。经过上述工艺过程,铜的回收率达到99.80%,浸出渣和沉铜渣可直接用于工业生产,沉铜后液可继续分离锌、钴等金属元素。Abstract: In this paper, a systematic study of H2SO4 leaching of copper manganese slag and Na2S2O3 selective copper precipitation in acid leaching solution was conducted. The influencing factors of these two processes were explored by single factor experiment. The results showed that the optimal conditions for sulfuric acid leaching of copper manganese slag were H2SO4 dosage of 200 g/L, liquid to solid of (mL/g) 7∶1, reaction temperature of 80 ℃ and reaction time of 2 h. Under these conditions, the leaching rates of copper, cobalt, zinc and manganese were 99.81%, 99.54%, 99.07% and 24.10% respectively, and the main phase of leaching residue was MnO2. The optimal conditions for selective copper precipitation in acid leaching solution were Na2S2O3 dosage multiple of 2.0 and reaction time of 90 min, reaction temperature of 70 ℃. The results indicated that the precipitation rates of copper, cobalt, zinc and manganese were 99.99%, 0.26%, 0.34% and 0.29% respectively, and the main phase of copper slag was CuS. After the above process, the recovery efficiency of copper could reach 99.80%. The leaching residue and copper precipitation residue could be directly used in industrial production, and the liquid after copper precipitation could continue to separate zinc, cobalt and other metal elements.
-
Keywords:
- copper manganese slag /
- leaching /
- sulfide precipitation /
- selective precipitation /
- sulphuric acid /
- sodium thiosulfate /
- copper
-
2022年,我国粗钢产量为10.13亿吨[1],钢铁工业从烧结到轧钢的过程中易产生一种大量的固体废弃物——除尘灰[2-3]。酒泉钢铁集团公司(以下简称“酒钢”)拥有工艺配套完整,碳钢、不锈钢并举的钢铁产业链,整个生产链中产生性质各异的除尘灰,如烧结除尘灰、炼铁除尘灰、碳钢除尘灰等[4]。目前这些除尘灰大多采用堆存或不加任何处理直接返回烧结的方式处理,堆存会占用大量土地资源,返回烧结将使有害元素(如Zn、Pb、K、Na等)在高炉中富集,造成高炉炉壁结瘤,给高炉冶炼及设备使用寿命均带来不利影响[5]。
对除尘灰的处理,目前主要采用回转窑或转底炉工艺使锌铁分离回收铁粉的模式。赵海涛等[6]对窑尾除尘灰进行焙烧-磁选,得到铁品位为57%以上、铁回收率约为90%的铁精矿;张志荣等[7]利用高炉除尘灰在1 200 ℃条件下与铁矿石直接还原-磁选,获得铁品位为93.45%、铁总回收率为87.14%的还原铁粉;刘琳等[8]利用某钢铁厂3种除尘灰按质量百分比为1∶1∶1比例混合焙烧,得到铁品位为91.30%、铁回收率为82.37%的磁选铁精矿,焙烧脱锌率达到99.05%。但上述试验大多仍为单一除尘灰焙烧-磁选回收铁模式,多种除尘灰复配直接还原-磁选试验研究却很少报道。
据统计,酒钢润源环境科技有限公司堆存的各类除尘灰总量已达36.2万吨,对周边生态环境造成严重污染。为解决该问题,本试验对酒钢6种除尘灰进行系统研究,提出对除尘灰进行分类处理后再进行返烧结利用的初步方案,现参照回转窑原理对酒钢6种除尘灰复配进行直接还原实验,验证火法工艺处理复配除尘灰的可行性及有害元素脱除效率,并对窑渣后续磁选铁精粉进行深入探究,实现了除尘灰资源的有效利用,对钢铁企业的绿色发展具有一定的现实意义[9-10]。
1 实验部分
1.1 实验原料
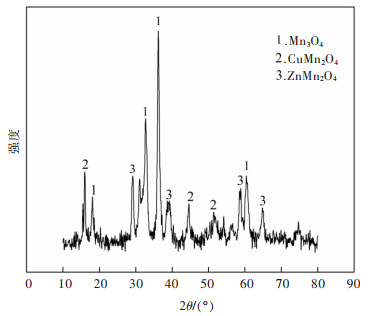
对实验所用高炉重力除尘灰(BFGDA)、高炉布袋灰(BFBD)、混合除尘灰(MDA)、炼钢OG泥(OG)、炼钢二次除尘灰(SSDA)、堆存高炉布袋灰(SBFBA)进行XRD物相分析(结果见图1)。由图1可知,6种除尘灰主要存在α-Fe2O3相和Fe3O4相。
6种除尘灰的化学成分如表1所列,各除尘灰铁含量均较高,这为后续的铁粉磁选工作提供了必要的前提条件。
表 1 6种除尘灰的化学成分Table 1. Chemical compositions of six types of dust removal ashes除尘灰名称 TFe CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 K2O Na2O ZnO PbO Cl S TiO2 BFGDA 47.71 3.31 5.80 0.81 2.87 0.61 0.11 1.69 0.62 8.12 0.11 0.28 BFBD 36.70 4.65 4.97 1.70 2.37 0.48 0.64 3.25 1.03 6.38 1.07 0.18 MDA 38.46 6.05 6.74 1.56 2.35 0.50 0.24 4.68 1.96 4.59 0.57 0.22 OG 52.20 14.56 2.63 5.43 2.34 0.65 0.36 7.80 0.33 8.03 0.10 0.71 SSDA 35.57 9.22 5.62 1.38 2.56 1.52 0.47 9.85 0.45 4.13 1.36 0.35 SBFBA 26.62 5.61 7.06 1.74 2.79 2.68 0.88 6.55 0.41 5.44 0.43 0.08 还原剂为74 μm(200目)AR炭粉(含C量≥99%),购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 实验设备与分析方法
电子天平(JH-C10002),密封式粉碎制样机(GJ-50),电热鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9000),马弗炉(BLMJ-XAF-16-12),Ф50磁选管(XCGS-Ф50),X 射线衍射仪(D8ADVANCE),X 射线荧光光谱分析仪(ARL Advant-X Intellipower™ 3600)。
全Fe含量即铁品位采用三氯化钛还原重铬酸钾滴定法测定[11],金属Fe含量采用电磁振荡三氯化铁法测定[12]。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 球团复配设计
由表1可知各除尘灰锌铁含量差异较大,SSDA、MDA和OG铁含量较高,BFBD、MDA和BFGDA锌含量较低。为有效脱除其有害元素并回收铁,根据各类除尘灰堆存量及酒钢润源环境科技有限公司的年处理能力,按照分类处理原则,基于6种除尘灰复配5种球团,其中BFBD∶SSDA=3.8,保持铁含量为50%左右,各原料按照配比要求,分别为S1 ~ S5(见表2)。
表 2 5种球团复配设计表Table 2. Compound design of five kinds of pellets配料组 BFBD SSDA SBFBA MDA BFGDA OG S1 42.50% 11.25% 46.25% — — — S2 34.00% 9.00% 15.00% 8.00% — 34.00% S3 34.00% 9.00% 15.00% 8.00% 34.00% — S4 34.00% 9.00% 32.50% 8.00% — 16.50% S5 28.50% 7.50% 15.50% 6.50% 28.50% 13.50% 注: “—”为空白值。1.3.2 复配球团直接还原实验
按照表2比例复配除尘灰得到球团混合料,由表3所列的XRF分析可知,复配后的球团配料成分主要为Fe2O3、SiO2、CaO、ZnO等,铁含量基本为50%左右。设定焙烧温度分别为900、1 000、1 100、1 200、1 300 ℃,配碳量为10%、20%、30%、40%、50%,焙烧时间取30、60、90 min,进行实验。
表 3 各球团主要成分分析结果Table 3. Analysis results of the main components of each pellet配料组 Fe2O3 SiO2 CaO ZnO Al2O3 K2O Na2O S TiO2 PbO S1 52.76 10.93 7.74 5.33 4.73 4.25 3.25 1.30 0.53 0.38 S2 49.56 9.66 16.75 3.80 3.58 2.73 2.07 0.98 0.40 0.26 S3 53.44 10.31 9.61 4.92 4.56 3.69 3.29 1.22 0.56 0.32 S4 48.53 9.12 10.15 5.60 4.18 3.97 5.13 0.99 0.47 0.37 S5 52.65 9.95 10.24 4.82 4.28 3.78 2.75 1.07 0.52 0.34 1.3.3 窑渣金属磁选实验
对焙烧产物窑渣进行水封,防止物料二次氧化。随后对窑渣进行细磨3 min,在150 mT下磁选5 min,得到窑渣铁精粉。球团烧损率、脱锌率、脱钾率、脱钠率及铁回收率计算公式如下。
1)烧损率
% (1) 式(1)中:θ 为烧损率的数值,单位%;m0为还原前球团质量的数值,单位g;m为还原后球团质量的数值,单位g。
2)脱锌率
(2) 式(2)中:η 为脱锌率的数值,单位%;Z为焙烧后球团中锌的质量分数的数值,单位%;Z0为焙烧前球团中锌的质量分数的数值,单位%。
脱钾率和脱钠率公式与式(2)类似。
3)Fe回收率
(3) 式(3)中:R 为Fe回收率的数值,单位%;m1为磁选后球团质量的数值,单位g;ω1为磁选后铁精粉的全Fe质量分数的数值,单位%;ω0为焙烧还原铁粉所含的全Fe质量分数的数值,单位%;k为磁选产率的数值,单位%。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 铁氧化物和ZnO的还原热力学
复配球团在还原气氛中焙烧,炭粉与氧气的不充分燃烧产物引发布多尔反应,其产生的CO维持还原反应的持续进行[13-14]。在焙烧过程中,Fe2O3与CO发生反应还原为单质铁,见式(4)。铁氧化物还原是逐级进行的,由于反应初始CO含量不够充足,Fe2O3先初步还原为Fe3O4,当T < 843 K时,Fe3O4直接被还原为Fe;当T > 843 K时,Fe3O4先生成FeO,再进一步被还原成Fe。反应中后期,在充足的CO及高温气氛下,Fe2O3则被直接还原为Fe,这说明Fe3O4和FeO是Fe2O3还原为Fe的中间过渡相[8]。
(4) Zn在除尘灰中主要以ZnO的形式存在,且ZnO的熔点(2 248 K)和沸点(2 633 K)均远高于实验焙烧温度,故ZnO的还原以气固反应为主,见式(5)。ZnO的还原反应是吸热反应,焙烧温度越高ZnO越易被还原。随着温度不断升高,碳逐渐被消耗,CO浓度也逐渐增大,有害金属锌得到充分的自还原反应,以蒸气态进入烟气(Zn的沸点为1 180 K),从而被脱除[15-16]。
(5) 2.2 K和Na元素的脱除机理
除尘灰中K和Na主要以氯化物和氧化物形式存在[17-18]。除尘灰球团中NaCl熔沸点分别为1 074 K和1 686 K,KCl的熔沸点分别为1 043 K和1 693 K,虽然NaCl和KCl的沸点超过了实验模拟温度范围(900~1 300 ℃),但在1 200 ℃时,KCl和NaCl的蒸气压分别达到了18 kPa和11 kPa;而当焙烧温度为1 300 ℃时,两者的蒸气压已分别高达43 kPa和28 kPa,温度越高,KCl、NaCl蒸气压越大,越易被挥发。因此,随着温度的升高,由于KCl和NaCl的高饱和蒸气压,两者在高温下被气化为二次烟道气,随烟尘排出[19-20]。
2.3 球团直接还原实验
为验证火法工艺处理复配除尘灰的可行性及有害元素脱除效率,对焙烧时间、焙烧温度及配碳量的影响进行研究。
2.3.1 焙烧时间的影响
图2所示为在焙烧温度为1 100 ℃、碳配比为30%的条件下,不同焙烧时间对球团烧损率及有害元素脱除效率影响的实验结果。随着焙烧时间的延长,各项指标逐渐增大并趋于稳定,当焙烧时间由30 min延长至60 min时,S5的烧损率由29.81%增大到36.62%,脱锌率、脱钾率和脱钠率分别由49.12%、51.68%、59.30%迅速增大到67.86%、75.56%、72.41%。当焙烧时间延长到90 min时,锌气压降低,还原气氛减弱,使得球团烧损率及有害元素脱除率均无太大变化,甚至略有降低[21],说明适宜焙烧时间为60 min时,除尘灰中各有害元素即可被有效去除。
2.3.2 焙烧温度的影响
在焙烧时间为60 min,碳配比为30%的条件下,焙烧温度对球团烧损率及有害元素脱除效率的影响见图3。当焙烧温度由900 ℃升至1 100 ℃时,各球团的各项指标均缓慢变化;当焙烧温度从1 100 ℃升至1 300 ℃时,各项指标增幅最大,其中S2的烧损率由30.66%迅速提高到54.44%,S4和S5的脱锌率却先降低后再升高,而各球团的脱钾率和脱钠率均稳步提升,S4的脱钾率、脱钠率基本保持在70%和80%以上的较高水平。虽然焙烧温度越高,有害元素脱除效率也越高,但是不可避免的,复配球团液相析出现象也极为严重,实践表明,复配球团在过高的温度下焙烧,烧结固相反应会促进低熔点化合物硅酸盐、铁酸盐的形成,导致析出液相与容器内壁紧密黏连,不易清理,同时,液相的出现也会恶化Zn、K、Na的脱除与回收[22]。另外,当焙烧温度超过1 100 ℃后,物料中FeO和SiO2较易生成硅酸铁(2FeO·SiO2),使得铁回收率降低,影响回收铁质量[23]。故焙烧温度宜控制在1 100 ℃左右。
2.3.3 配碳量的影响
在1 100 ℃下焙烧60 min,观察配碳量对球团烧损率及有害元素脱除效率的影响,结果见图4。S4和S5相比其他配料,其有害元素脱除效率均保持着较高水平,尤其是S4的脱钠率和S5的脱钾率,无论碳配比如何,脱钠率和脱钾率基本保持在80%和74%以上。各球团脱锌率均随着碳配比的增大而逐渐增大,其中S5的脱锌率从含碳量10%的56.86%提升到含碳量50%的80.33%。配碳量的增加,使得还原剂增多,促进有害元素的脱除,但过多碳含量会恶化传质条件,导致金属化率降低[10]。故配碳量为30%时可有效控制生产成本,经济效益提升最为明显。
2.4 最终产品条件分析
将5种不同条件下(900 ℃、50% C,1 100 ℃、30% C,1 200 ℃、10% C,1300 ℃、10% C,1 300 ℃、30% C,焙烧时间60 min)各球团的指标对比分析,由图5可知,各球团在1 300 ℃、30% C条件下焙烧60 min,虽脱锌率、脱钾率、脱钠率表现优良,但在高温段形成的低熔点化合物易产生较多的液相,不断黏结在容器内壁表面,导致窑渣很难再次得到充分有效地回收与利用[24]。且在1 100 ℃、30% C,1 200 ℃、10% C 2个条件下,各球团的各项指标差异均无太大区别,故从降低能耗比和减少成本的实际角度出发,1 100 ℃、30%C是较适宜的焙烧条件。
2.5 金属磁选实验
2.5.1 优选配料
由图6可看出,1300 ℃、10%C的各球团配料铁品位最高,特别是S4直接还原后的铁品位可高达37.65%。前期的直接还原实验中已证实在1 300 ℃下焙烧复配球团液相析出严重,不利于后续的磁选流程,而1 100 ℃、30% C和1 200 ℃、10% C的铁品位不仅相近且较高,故1 100 ℃、30% C更加符合要求。
2.5.2 磁选结果
选取1 100 ℃、30% C条件下焙烧60 min的5种球团,每次称取30 g焙烧窑渣,磁场强度150 mT,磁选时间5 min,焙烧窑渣磁选结果如图7所示。
由图7可知,S5窑渣磁选后铁品位为80.84%,铁回收率为81.44%。直接还原铁粉和磁选铁精粉的组分分析见表4,直接还原铁粉铁品位30.77%,磁选铁精粉残锌量小于0.5%,有害元素含量相比直接还原铁粉进一步降低,说明磁选过程也可对有害元素进行有效脱除。该磁选铁精粉可作为钢铁生产原料,在冶炼过程中与其他原料一起加入炉中进行熔炼,提高含铁量,提升炉渣的熔化性和钢液的纯净度。
表 4 1 100 ℃,30%C S5焙烧60 min直接还原铁粉及磁选铁精粉组分Table 4. Components of direct reduction of iron powder and magnetic separation iron concentrate powder under 1 100 ℃, 30%C S5 roasted 60 min种类 TFe SiO2 CaO Al2O3 ZnO K2O Na2O MgO MnO 直接还原铁粉 30.77 22.04 10.22 8.18 2.51 1.40 1.18 2.82 1.17 磁选铁精粉 80.84 2.01 1.38 0.98 0.46 0.32 0.20 0.63 0.18 3 结 论
通过对酒钢6种除尘灰复配设计直接还原—磁选试验研究,得出如下结论:
1)S4和S5在1 100 ℃、30%C和1 200 ℃、10%C条件下焙烧60 min,有害元素脱除效果优良,但从降低能耗比、减少工业固废量及后续磁选铁回收率要求来看,S5为优选产品。
2)在焙烧温度1 100 ℃、碳配比30%、焙烧时间60 min的条件下,S5的烧损率、脱锌率、脱钾率、脱钠率分别为36.62%、67.86%、75.56%、72.41%,得到铁品位为30.77%的焙烧物料。在磁场强度150 mT,磁选时间5 min的条件下,得到铁品位为80.84%、铁回收率为81.44%的磁选铁精粉。
3)将6种除尘灰按S5复配混料,符合大宗工业固废减量化要求,充分证实了火法工艺对后续除尘灰处理的可行性,可有效提升经济效益。
-
表 1 铜锰渣元素成分分析结果
Table 1 Analysis results of element composition of copper manganese slag

表 3 较优条件实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of optimal conditions

表 4 较优条件实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of optimal conditions

表 5 2号沉铜渣元素成分分析结果
Table 5 Analysis results of element composition of No.2 copper slag

-
[1] 刘超, 陈甲斌. 全球钴资源供需形势分析[J]. 国土资源情报, 2020(10): 27-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3709.2020.10.005 [2] 卢宜冠, 郝波, 孙凯, 等. 钴金属资源概况与资源利用情况分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(1): 72-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.01.008 [3] 王静静, 周康根, 岳楠, 等. 氨法从氯化铜锰锌钴废液中选择性分离锰[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2015, 6(4): 16-20. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201504004 [4] 罗能荣, 王鹃. 从氯化铜锰液中回收有价金属的生产实践[J]. 有色冶金节能, 2017, 33(2): 51-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJJN201702015.htm [5] 兰州金川新材料科技股份有限公司. 一种从碳酸铜锰钴钙锌混合物中分离铜钴锰的方法: CN201510635739.4[P]. 2016-01-27. [6] 苏轶娜. 我国重要矿产资源供需形势研究[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2019, 32(7): 46-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDKJ201907009.htm [7] 郭学益, 田庆华, 刘咏, 等. 有色金属资源循环研究应用进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(9): 1859-1901. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201909006.htm [8] 赖丹, 杨华, 罗翔. 经济政策不确定性对经营效率的影响——以有色金属行业上市公司为例[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2020, 11(4): 98-105. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=202004015 [9] 樊有琪, 蔡兵, 杜春云. 铜烟尘提取铜和锌的湿法工艺探索[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2016, 45(2): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2016.02.015 [10] 吴莹, 方登志, 于艳杰, 等. 烟道灰中铜锌锰的分离与回收[J]. 中国锰业, 2017, 35(2): 123-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201702010.htm [11] 黄涛, 陈丽杰, 张喆秋, 等. 离子交换法从氧化铜钴矿加压氨浸液中分离铜钴的研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2018(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2018.04.001 [12] 彭宇, 肖发新, 孙树臣, 等. 高碱性脉石低品位氧化铜矿提铜研究进展[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2020, 11(5): 69-74. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=2020050010 [13] 谢晓峰, 李磊, 王飞, 等. 铜渣氯化烟尘中铜的湿法回收[J]. 过程工程学报, 2015, 15(3): 424-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ201503011.htm [14] 张彩霞, 舒庆, 刘若琳, 等. 新型铜萃取剂对十二烷基苯基羧基甲酮肟的合成及其萃铜性能[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2017, 8(6): 36-42. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=2017060006 [15] 陈炎, 程洁红. 醛肟萃取剂萃取分离废锂离子电池中的铜[J]. 过程工程学报, 2017, 17(6): 1170-1175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ201706009.htm [16] 宫文宇. 化学沉淀法处理含铜污水工艺分析[J]. 炼油与化工, 2020, 31(2): 71-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4962.2020.02.026 [17] 黄万抚, 胡昌顺, 曹明帅, 等. 难处理含铜废水处理技术研究[J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47(10): 2248-2253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.10.047 [18] LUNA I Z, HILARY L N, CHOWDHURY A M S, et al. Preparation and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized via chemical precipitation method[J]. Open Access Library Journal, 2015, 2(3): 1-8. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/276499509_Preparation_and_Characterization_of_Copper_Oxide_Nanoparticles_Synthesized_via_Chemical_Precipitation_Method
[19] TOKUDA H, KUCHAR D, MIHARA N, et al. Study on reaction kinetics and selective precipitation of Cu, Zn, Ni and Sn with H2S in single-metal and multi-metal systems[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(9): 1448-1452. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.073
[20] 柴立元, 王海棠, 尤翔宇, 等. M(Ⅱ)-S-H2O体系的热力学平衡[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2012, 3(5): 8-13. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201205002 [21] 李琛, 韩俊伟, 刘维, 等. 硫化沉淀法回收锌浸出液中的铜[J]. 矿冶工程, 2019, 39(1): 102-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC201901028.htm [22] 李志仁, 许万祥, 朱军, 等. 从高酸湿法炼锌渣浸出液中分离铁及回收铜、锌实验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2013, 32(5): 326-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ201305023.htm [23] 郝冬冬, 蒋开喜, 王玉芳, 等. 白烟灰浸出液中铜的综合回收[J]. 矿冶, 2019, 28(4): 126-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2019.04.023 [24] 武汉大学, 吉林大学. 无机化学(上册)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1994.




 下载:
下载: