Effects of thickness of absorption layer and buffer layer on the performance of Cu3BiS3 solar cell
-
摘要: 三元硫化物半导体Cu3BiS3的组成元素在地壳中含量丰富、无毒,且具有优异的光电性能,被认为是一种极具潜力的太阳能电池吸收层材料。目前关于Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件的研究报道还非常少,在器件结构设计与制作工艺方面有一系列亟待解决的关键科学问题。文章分别通过溶液旋涂的层数及化学浴沉积时间来调控Cu3BiS3吸收层与CdS缓冲层薄膜厚度,详细分析了吸收层及缓冲层厚度对太阳能电池器件的影响规律及机制。结果表明,吸收层厚度的增加能够使光的吸收增强,使短路电流密度JSC增大,进而提高光电转换效率;然而吸收层厚度过高,会造成器件效率的下降。缓冲层厚度的增加,有利于提高器件的开路电压VOC;缓冲层过厚,同样造成器件短路电流密度的减小以及效率的下降。实验中器件的较优光电转换效率为0.288%,对应的开路电压、短路电流密度、填充因子分别为0.215 V,2.292 mA/cm2,48.049%。Abstract: Ternary chalcogenide semiconductor Cu3BiS3 has been perceived as a potential candidate of solar absorber materials in recent years, due to the low-toxic and earth-abundant component elements, and excellent optoelectronic properties. Nonetheless, sporadic investigations on Cu3BiS3 solar cell devices have been reported. There are lots of key scientific problems in structure design and manufacture process of photovoltaic device urgently need to be solved. In this paper, we adjusted the thickness of absorption layer and buffer layer through the spin-coating cycle and deposition time of chemical bath, respectively. Then, the effects of thickness of absorption and buffer layer on the performance of Cu3BiS3 solar cell were systematically analyzed. The results show that, increasing the thickness of absorption layer will enhance the light absorption and short-circuit current density (JSC), consequently improve the conversion efficiency. However, too thick film will cause the decline of device efficiency. Increasing the thickness of buffer layer is beneficial to the open-circuit voltage (VOC). Similarly, too thick film will bring about the decrease of JSC and device efficiency. The best device efficiency of 0.288% was obtained in our experiments. The corresponding VOC, JSC and fill factor (FF) values are 215 mV, 2.292 mA/cm2 and 48.049%, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- Cu3BiS3 /
- CdS /
- thin film solar cells
-
Cu3BiS3的组成元素在地壳中含量丰富、无毒,其直接光学带隙在1.5 eV左右,接近太阳能高效转换的最佳值,具有高光吸收系数(α > 104 cm-1),能够在较薄的吸收层内实现充分的光吸收,而且材料形成温度低(200~300 ℃),是一种极具潜力的太阳能电池的吸收层材料[1-3]。然而,目前关于Cu3BiS3材料的研究报道主要集中在材料制备与表征方面[4-14],Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件的相关报道非常少[15-17]。2018年,我们课题组采用一步溶液法制备了纯相的Cu3BiS3薄膜,并首次组装薄膜太阳能电池器件,得到了0.17%的光电转换效率[18-19]。迄今为止,Cu3BiS3太阳能电池的最高转换效率报道也仅为1.7%[17],远低于其他类型的太阳能电池。
目前关于Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件的研究尚处于初始阶段,器件结构基本参照CIGS[20]、CZTS[21]薄膜太阳能电池,包括Mo基底、Cu3BiS3吸收层、CdS缓冲层、ZnO/ITO(氧化铟锡)及Al顶电极几部分。其中,Cu3BiS3与CdS薄膜构建的P-N异质结是器件的核心结构,对器件的性能起到关键性的作用。因此,本文分别通过旋涂层数及化学浴沉积时间来调控Cu3BiS3及CdS薄膜厚度,深入探讨Cu3BiS3与CdS薄膜厚度对器件性能的影响机制及规律,为制备高效率Cu3BiS3薄膜太阳能电池器件奠定基础。
1 实验
1.1 Cu3BiS3薄膜的制备
氯化铋(BiCl3)、氯化亚铜(CuCl)、硫脲(CH4N2S)与二甲基亚砜(C2H6OS,DMSO)均为分析纯试剂,购于阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。将2.28 g CH4N2S加入到10 mL DMSO中,搅拌30 min,然后再分别加入1.05 g BiCl3及0.99 g CuCl,搅拌12 h,即得到前驱体溶液。
在氮气氛围的手套箱中,将配制的前驱体溶液旋涂在预先清洗干净的钠钙玻璃及钼玻璃基底上。转速为500 r/min,旋涂为5 s;转速为3 000 r/min,旋涂为20 s;然后在280 ℃的加热台上退火2 min,最后冷却。根据厚度需求重复上述操作多次,即得到Cu3BiS3薄膜。
1.2 CdS薄膜的制备
CdS缓冲层的沉积采用化学浴方法[22]。具体流程如下:将0.17 g CdSO4·8/3H2O加入到317 mL去离子水中,搅拌至完全溶解,然后置于65 ℃水浴锅中。在75 mL去离子水中加入2.5 g CH4N2S,搅拌至完全溶解备用。将59 mL NH3·H2O加入CdSO4·8/3H2O溶液中,搅拌5 min,然后将样品放入该溶液中预处理15 min。将CH4N2S溶液加入到NH3·H2O与CdSO4·8/3H2O的溶液中,沉积到所需时间后取出样品,用去离子水冲洗,最后用氮气吹干。
1.3 薄膜的表征
薄膜的X射线衍射(XRD)数据由丹东通达TD3700 X射线衍射仪测得;薄膜的形貌使用Phenom Pro扫描电子显微镜(SEM)进行分析;薄膜的载流子浓度及迁移率由Ecopia HMS3000霍尔效应测试系统进行表征;薄膜的吸收光谱使用Shimadzu UV-2600紫外-可见分光光度计进行测试。
1.4 太阳能电池器件的制备及测试
采用射频磁控溅射在Mo/Cu3BiS3/CdS样品表面沉积ZnO窗口层,溅射功率为100 W,工作气压为0.2 Pa,溅射时间为5 min。紧接着,采用直流磁控溅射沉积ITO透明导电层,溅射功率为100 W,工作气压为0.12 Pa,溅射时间为10 min。最后,使用热蒸镀方法沉积Al栅格电极,即得到Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件。
器件的J-V特性曲线使用Newport Oriel Sol 3A级太阳光模拟器与Keithley 4200 SCS半导体特性分析系统进行表征。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 吸收层厚度对器件性能的影响规律
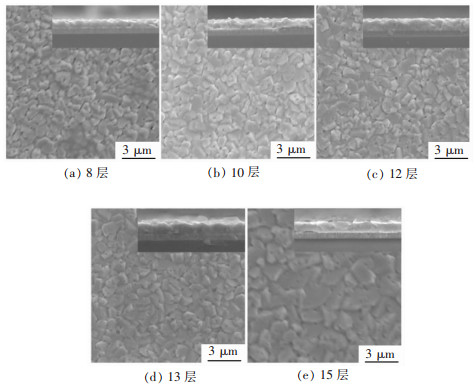
光的吸收层厚度对器件的性能具有重要的影响,本文通过调整旋涂层数来获得不同厚度的Cu3BiS3薄膜。图 1给出了旋涂不同层数的Cu3BiS3薄膜SEM图片。由薄膜的截面SEM图片(图 1中插图)可以测量出,旋涂8,10,12,13,15层的薄膜厚度分别约为0.67,0.87,0.95,1.04,1.20 μm。从图 1薄膜表面的电镜照片中可以发现,旋涂不同层数均得到了致密的薄膜。然而,随着旋涂层数的增加,不仅薄膜的厚度增大,薄膜的晶粒尺寸也呈现出增大的趋势。
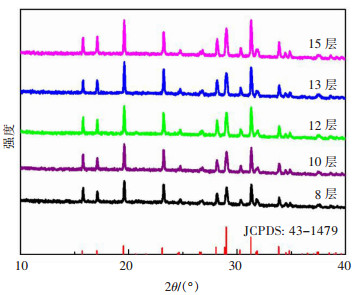
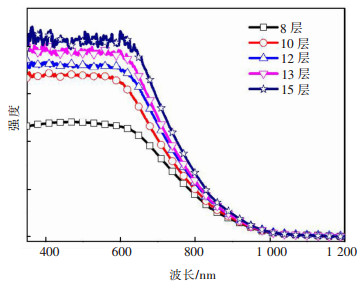
图 2给出了不同旋涂层数薄膜的X射线衍射图谱。不同厚度样品的衍射峰均与正交晶相Cu3BiS3(JCPDS: 43-1479)的衍射峰位置吻合。随薄膜厚度的增加SEM图片中衍射峰的强度呈现增大的趋势,结晶性更优,这与电镜形貌像中观察到的厚膜中晶粒尺寸较大相符。图 3给出了不同厚度薄膜的紫外-可见吸收光谱。可以看出,在可见光区域,Cu3BiS3薄膜具有较强的吸收。随着厚度的增加,薄膜对可见光的吸收增强。
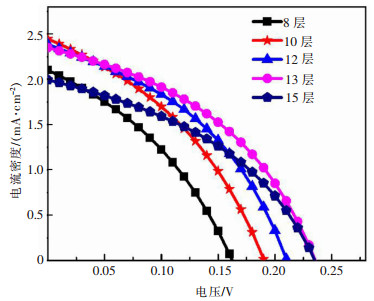
将不同厚度的Cu3BiS3薄膜组装成太阳能电池后,进行J-V测试,结果如图 4及表 1所示。器件的开路电压VOC随着吸收层厚度的增加而增大,旋涂到13层后,VOC基本保持不变。这可能是由于随着旋涂层数的增加,增大的晶粒尺寸降低了晶界密度,由此引起的载流子复合受到一定程度的抑制;薄膜厚度增加后致密性增强,漏电缺陷减少,并联电阻亦显著增大。器件的短路电流密度JSC随着吸收层厚度的增加,呈现先增大后减小的趋势。出现这种变化规律的原因可能是由于随着厚度的增加,薄膜对太阳光的吸收增强,进而使得JSC增大;然而继续增加薄膜的厚度,远离耗尽层区域产生的载流子寿命过短,无法扩散至内建电场区域,因此对光生载流子的产生及收集贡献不大,但是会影响载流子的有效传输,使JSC减小,也会增大器件的串联电阻。器件的填充因子FF与光电转换效率随着吸收层厚度的增加,也对应地呈先增大后减小的趋势。综合比较,可以发现旋涂13层为较优的吸收层制备条件,此时薄膜的厚度约为1 μm。
表 1 不同旋涂层数制备的Cu3BiS3电池器件参数Table 1. Photovoltaic parameters of solar cells fabricated with different Cu3BiS3 layers
2.2 缓冲层厚度对器件性能的影响规律
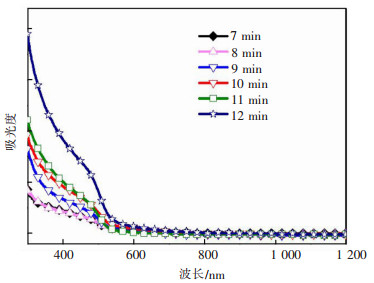
缓冲层处于窗口层和吸收层之间,与吸收层形成P-N异质结,具有优化吸收层和窗口层的晶格与能带匹配、在溅射沉积窗口层时保护吸收层、有效降低漏电流等作用,是薄膜太阳能电池结构中的重要一环[23-26]。本文以CdS作为缓冲层,采用经典的化学浴方法沉积,通过反应时间调控缓冲层的厚度。随着沉积时间的延长,CdS/Cu3BiS3复合薄膜的颜色先由棕黄色变为紫色,之后由紫色向青蓝色转变。这是由于厚度的增加,CdS薄膜对光的吸收的增强而导致的。图 5给出了钠钙玻璃上不同沉积时间CdS的紫外-可见吸收光谱。从图 5中可以看出,CdS缓冲层的吸光范围主要在500 nm以下,而且吸收的强度随着沉积时间的延长而增强。
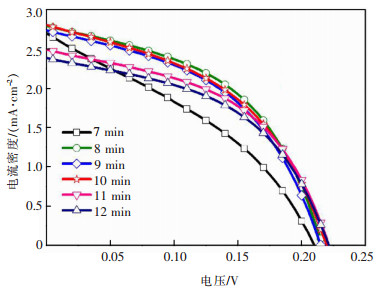
图 6给出了对应不同缓冲层厚度的Cu3BiS3电池器件J-V曲线,具体的器件参数见表 2。可以看出,随着CdS沉积时间的增加,开路电压VOC呈现微弱的增大的趋势。这是由于随着沉积时间延长,缓冲层厚度增加,薄膜致密度提高,抑制了漏电,使得VOC增大,填充因子FF改善。当沉积时间大于8 min后,延长沉积时间使得CdS薄膜增厚,缓冲层吸收更多的光,而这部分被吸收的光对光电流几乎没有贡献,造成短路电流密度JSC的减小。因此,CdS沉积时间为8 min时,Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件整体表现出较好的性能。此时,开路电压VOC为0.215 V,短路电流密度JSC为2.292 mA/cm2,填充因子FF为48.049,光电转换效率为0.288%。
表 2 基于不同CdS沉积时间的Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件参数Table 2. Photovoltaic parameters of Cu3BiS3 solar cells fabricated with different CdS deposition time
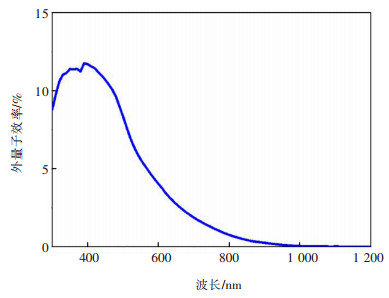
虽然本文对吸收层及缓冲层厚度进行了优化,但是Cu3BiS3太阳能电池的转化效率仍然非常低。为此,我们对较优工艺条件下所制备的Cu3BiS3电池器件进行了光谱响应分析。图 7给出了电池器件的外量子效率曲线。从图 7中可以看出,在整个太阳光谱范围内器件的外量子效率都非常低。而且,主要的光吸收范围位于600 nm以下,光生载流子的贡献很可能仅限于异质结界面处。然而,从前述的紫外-可见吸收光谱(图 3)中可以看出,Cu3BiS3薄膜在可见光范围内具有很强的吸收能力。由此判断,器件效率低的原因可能是由于Cu3BiS3/CdS异质结能级的不匹配以及界面扩散导致没能形成有效的内建电场,因此器件表现出较差的光生载流子收集能力。因此,下一步需要更深入的揭示Cu3BiS3材料的基本物理性质,然后设计与材料性质相匹配的器件结构,这样才能从根本上提升器件性能。
3 结论
详细探讨了吸收层及缓冲层薄膜厚度对Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件的影响规律及机制。研究表明,随着Cu3BiS3吸光层厚度的增加,薄膜致密性增强,漏电缺陷减少,并联电阻增大,使得VOC增大。同时,适当的厚度增加会使薄膜对太阳光的吸收增强,进而使得JSC提高。然而薄膜过厚,对光生载流子的产生及收集贡献不大,一定程度上会影响载流子的有效传输,增大器件的串联电阻。1 μm左右是电池器件中Cu3BiS3吸光层的合适厚度。随着CdS缓冲层厚度的增加,薄膜致密度提高,漏电流降低,VOC呈现出微弱的增大趋势。沉积时间超过8 min会造成CdS薄膜吸收过多的光,而这部分被吸收的光对光电流几乎没有贡献,造成JSC的减小。CdS沉积时间为8 min时,Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件表现出较好的性能。此时,太阳能电池器件的VOC为0.215 V,JSC为2.292 mA/cm2,FF为48.049%,光电转换效率为0.288%。
-
表 1 不同旋涂层数制备的Cu3BiS3电池器件参数
Table 1 Photovoltaic parameters of solar cells fabricated with different Cu3BiS3 layers

表 2 基于不同CdS沉积时间的Cu3BiS3太阳能电池器件参数
Table 2 Photovoltaic parameters of Cu3BiS3 solar cells fabricated with different CdS deposition time

-
[1] WHITTLES T J, VEAL T D, SAVORY C N, et al. Band alignments, band gap, core levels, and valence band states in Cu3BiS3 for photovoltaics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(30): 27033-27047.
[2] MESA F, DUSSAN A, GORDILLO G. Study of the growth process and optoelectrical properties of nanocrystalline Cu3BiS3 thin films[J]. Physica Status Solidi C, 2010, 7(3/4): 917-920.
[3] LI J, HAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. Facile preparation of Cu3BiS3 nanorods film through a solution dip-coating process[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(23): 17772-17777. doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-7716-6
[4] DESHMUKH S G, PANCHAL A K, KHERAJ V. Development of Cu3BiS3 thin films by chemical bath deposition route[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(26): 11926-11933.
[5] CHAKRABORTY M, THANGAVEL R, KOMNINOU P, et al. Nanospheres and nanoflowers of copper bismuth sulphide (Cu3BiS3): Colloidal synthesis, structural, optical and electrical characterization[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 776: 142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.151
[6] DESHMUKH S G, KHERAJ V, KARANDE K J, et al. Hierarchical flower-like Cu3BiS3 thin film synthesis with non-vacuum chemical bath deposition technique[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(8): 084013. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab283f
[7] HUSSAIN A, LUO J T, FAN P, et al. P-type Cu3BiS3 thin films for solar cell absorber layer via one stage thermal evaporation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 505: 144597.
[8] GEREIN N J, HABER J A. Synthesis of Cu3BiS3 thin films by heating metal and metal sulfide precursor films under hydrogen sulfide[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(26): 6289-6296. doi: 10.1021/cm061452z
[9] YAKUSHEV M V, MAIELLO P, RAADIK T, et al. Electronic and structural characterisation of Cu3BiS3 thin films for the absorber layer of sustainable photovoltaics[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 562: 195-199. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2014.04.057
[10] NGOEN K A, DUMRONGROJTHANATH P, THONGTEM T, et al. Effect of medium solvents on crystalline degree and specific surface area of Cu3BiS3 nanoparticles synthesised by biomolecule-assisted hydrothermal and solvothermal methods[J]. International Journal of Nanotechnology, 2017, 14(1/2/3/4/5/6): 22-30. doi: 10.1504/IJNT.2017.082439
[11] MANIMOZHI T, ARCHANA J, RAMAMURTHI K. Shape controlled synthesis of Cu3BiS3 nano-and microstructures by PEG assisted solvothermal method and functional properties[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(13): 15385-15392. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.190
[12] PAI N, LU J, SENEVIRATHNA D, et al. Spray deposition of AgBiS2 and Cu3BiS3 thin films for photovoltaic applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018(6): 2483-2494.
[13] DESHMUKH S G, PANCHAL A K, KHERAJ V. Development of Cu3BiS3 thin films by chemical bath deposition route[J]. Journal of Materials: Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28: 11926-11933. doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-7002-7
[14] ZHANG L, JIN X, YUAN C, et al. The effect of the sulfur concentration on the phase transformation from the mixed CuO-Bi2O3 system to Cu3BiS3 during the sulfurization process[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 389: 858-864. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.08.003
[15] YIN J, JIA J. Synthesis of Cu3BiS3 nanosheet films on TiO2 nanorod arrays by a solvothermal route and their photoelectrochemical characteristics[J]. Cryst Eng Comm, 2014, 16(13): 2795-2801. doi: 10.1039/c3ce41958d
[16] HERNÁ DEZ-MOTA J, ESPÍNDOLA-RODR?GUEZ M, SÁ NCHEZ Y. Thin film photovoltaic devices prepared with Cu3BiS3 ternary compound[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2018, 87: 37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2018.07.008
[17] YANG Y, XIONG X, YIN H, et al. Study of copper bismuth sulfide thin films for the photovoltaic application[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(2): 1832-1837. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-0455-5
[18] LI J, HAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. One-step synthesis of Cu3BiS3 thin films by a dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-based solution coating process for solar cell application[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018, 174: 593-598. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.09.050
[19] 李佳佳. Cu3BiS3的制备及光电性能研究[D]. 兰州: 中国科学院兰州化学物理研究所, 2018. [20] BALLABIO M, MARRON D F, BARREAU N, et al. Composition-Dependent Passivation Efficiency at the CdS/CuIn1-xGaxSe2 Interface[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(9): 1907763. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907763
[21] ZHAO Y, HAN X, CHANG L, et al. Effects of selenization conditions on microstructure evolution in solution processed Cu2ZnSn(S, Se)4 solar cells[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019, 195: 274-279. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.03.024
[22] RAMANATHAN K, CONTRERAS M A, PERKINS C L, et al. Properties of 19.2% efficiency ZnO/CdS/CuInGaSe2 thin-film solar cells[J]. Progress in Photovoltaics, 2003, 11(4): 225-230. doi: 10.1002/pip.494
[23] 陆熠磊, 王书荣, 李志山, 等. 不同镉源制备铜锌锡硫电池缓冲层的研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2016, 45(9): 2341-2346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.09.031 [24] 阎森飚, 徐键. CZTS薄膜太阳能电池无镉缓冲层材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(7): 7045-7052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB202007008.htm [25] 范玉, 李晓东, 林舒平, 等. 溅射制备Zn(O, S)薄膜及其在CIGS电池中的应用[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2017, 46(6): 996-1001. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2017.06.007 [26] 屈飞, 李辉, 古宏伟, 等. CIGS太阳能电池用CBD-CdS/Zn(S, O)复合缓冲层的研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2018, 42(11): 1172-1177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXJS201811008.htm -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 唐华著,肖清泉,付莎莎,谢泉. 以Spiro-OMeTAD作为空穴传输层的ZnS/SnS太阳能电池模拟研究. 人工晶体学报. 2024(08): 1394-1408 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张红,张国成,宁宇. TiO_2缓冲层在SnS薄膜太阳能电池中的数值仿真研究. 固体电子学研究与进展. 2022(04): 299-305 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: