Process of removing phosphorus and molybdenum from complex scheelite concentrates with high phosphorus and molybdenum
-
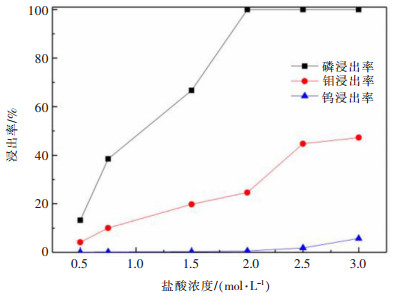
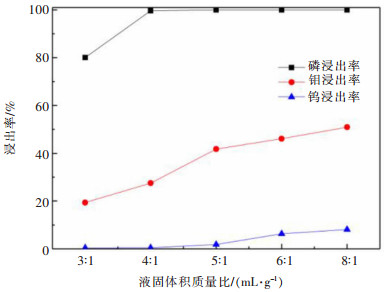
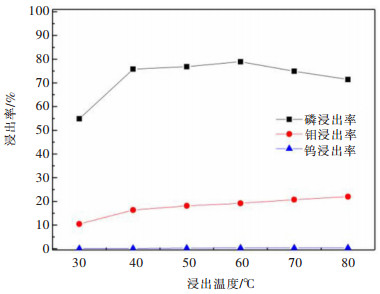
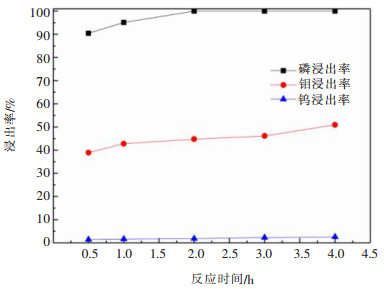
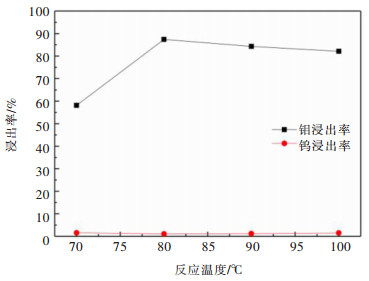
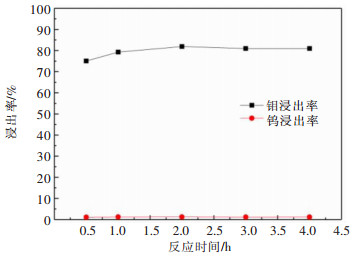
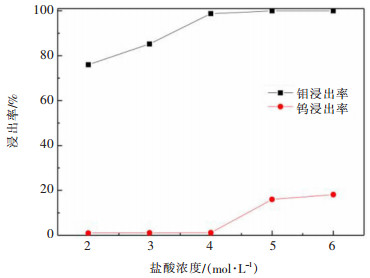
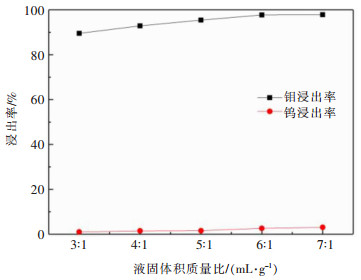
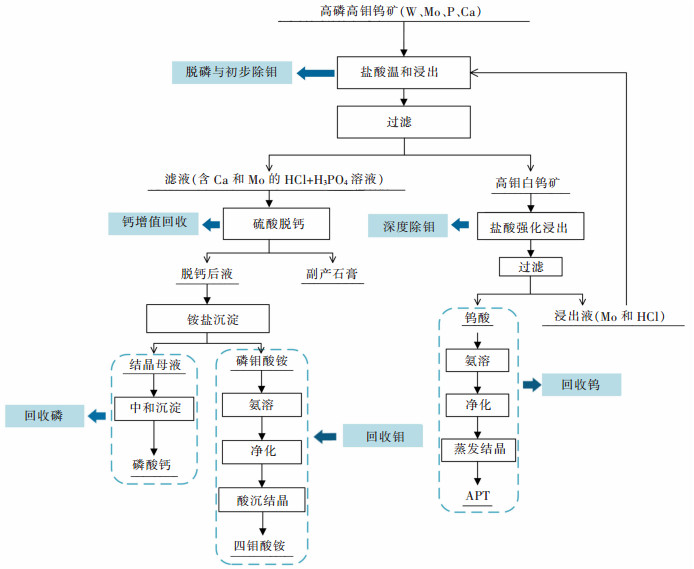
摘要: 利用磷灰石、钼酸钙和钨酸钙等含钙矿物与盐酸反应的差异性规律,首先在温和的盐酸浸出条件下预处理高磷高钼复杂白钨矿,即反应温度为50 ℃,盐酸浓度2.5 mol/L,反应时间2 h,液固比(指液体体积与固体质量之比,单位为L/kg,下同)5:1的条件下实现杂质磷的高效选择性浸出,磷的浸出率达到99%以上,同时实现钨钼的初步分离,钼浸出率为44.76%,钨浸出率仅为1.84%。然后,再利用钨酸和钼酸在盐酸体系中溶解度的性质差异,进一步提高盐酸浓度和反应温度强化浸出,在盐酸浓度4 mol/L,反应温度80 ℃,反应时间2 h,液固比5:1的条件下,钼的浸出率达到95%,而钨以钨酸的形式留在固相,此步骤的钨浸出率只有1.55%,实现了钼的深度分离和钨矿的转型。Abstract: Considering the differences of hydrochloric acid leaching fluorapatite, calcium molybdate and scheelite concentrate, the scheelite concentrates which contain high phosphorus and molybdenum were first treated by hydrochloric acid, under the conditions such as hydrochloric acid concentration 2.5 mol/L, reaction temperature 50 ℃, reaction time 2 h, liquid-solid ratio of 5:1. The results showed that over 99% of phosphorus was leached, molybdenum leaching rate was 44.76%, and the tungsten loss rate was only 1.84%. After that, based on the different solubility of tungstic acid and molybdic acid in hydrochloric acid, the scheelite concentrates were leached by hydrochloric acid. Under the conditions of hydrochloric acid concentration 4 mol/L, reaction temperature 80 ℃, reaction time 2 h and liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, the leaching rate of molybdenum reached 95%, and tungsten was leached in the form of tungstate in solid phase. Hence the loss rate of tungsten was only 1.55%, which realized the deep separation of molybdenum and tungsten.
-
高纯度金属钴因具有特殊结构和性能在功能薄膜、集成电路导线、磁传感、磁记录溅射靶材,高纯试剂及标样配置等多领域有广泛应用[1-4](图 1).其通常是在高浓度、高纯钴盐电解质水溶液中电解或电精炼制得.钴盐电解质水溶液的除杂、提纯是重要环节.随着该研究领域多年发展,除杂、提纯方法形成了以离子交换法、萃取色层法、膜分离法和溶剂萃取法等[5]为主体的技术.由于钴、镍原子半径、外层电子结构和物理化学性质相近,两者的有效分离、提纯是上述方法的核心任务.
目前,电解质水溶液中钴、镍分离研究主要集中在分离、提纯方法采用的分离材料的研发、改性、组合和分离提取工艺的改进方面,应用对象多集中在含高镍低钴的硫酸盐电解质水溶液.
1 电解质水溶液中钴、镍分离提纯方法研究进展
1.1 离子交换法研究进展
离子交换法也称树脂交换法,是利用离子交换树脂的功能基团和溶液中钴、镍离子交换反应能力差异实现钴、镍分离、提纯的方法.离子交换树脂起到媒介的作用,其在高pH值条件下吸附电解质水溶液中特定金属离子发生离子交换反应,在低pH值条件下再将吸附的金属离子脱附,自身实现再生.其反应方程式为:
离子吸附反应:nR-H+Men+ →nR-Me+nH+
离子脱附反应:nR-Me+nH+→nR-H+Men+
(其中R-H表示阳离子交换树脂,Men+表示金属离子)
应用于钴镍分离、提纯的离子交换树脂主要有以下几类:阴离子交换树脂[6]、阳离子交换树脂[7-10]、无机离子交换树脂[11, 12]、螯合树脂[13-18]等,研究主要集中在设计不同功能基团的离子交换树脂以及相应深度分离工艺方面.例如,王允什等[6]利用阴离子交换树脂D370对高镍、低钴(镍钴质量比为7:4)的氯化物盐电解质水溶液中钴、镍分离进行了研究.在酸性条件下,钴离子与该树脂功能基团能形成络阴离子并易在低pH值溶液中脱附实现树脂再生,而镍离子却不进行这种反应.该树脂深度分离的实验表明高纯度的镍盐水溶液中镍钴浓度比提高到了6 000:1. VAUGHAN等[10]对一种新型阳离子交换树脂TP272的主要性能,包括钴、镍负载作为pH的函数,钴负载平衡等温线进行了研究,并确定了回收钴的理想条件. LI等[16]使用多胺型螯合树脂NDC-984从含有镍杂质的氯化钴溶液中分离出镍,得到纯度高达99.999 %的高纯钴盐水溶液. ZAINOL等[17]则是利用亚胺基二乙酸螯合树脂吸附多元硫酸溶液中的镍钴,镍、钴的吸附选择性分别高达58 000和16 800,实现了钴与镍的高效分离.
综上可以发现,离子交换法在进行钴、镍离子深度分离的过程中具有高分离级数,除杂效果好,腐蚀性小,且环境污染较小等优点,但交换效率不高,操作周期较长则是树脂离子交换法的缺点,导致该法很难实现大规模工业化生产应用.
1.2 萃取色层法研究进展
为了充分利用离子交换分离工艺分离级数高以及萃取剂的高选择性的优点,萃取色层法得到了广泛研究.萃取色层法是将大孔径树脂吸附萃取剂制成色层柱.电解质水溶液淋洗经过色层柱时,不同的金属离子在水相和萃取剂之间分配,实现有价金属与部分杂质的分离.溶液中特性离子(钴离子)选择性的被提取进入到萃取剂中,并在树脂表面再进一步进行选择性吸附.吸附后的色层柱经溶剂淋洗除杂后再经反萃和脱附形成高纯盐水溶液.该法能实现离子的深度分离.萃取色层法的研究主要集中在选择不同树脂作为萃取剂的优良载体,以提高分离体系的稳定性,减少萃取剂的流失[19-22];同时对相应分离工艺条件进行探索以改善萃取效率[23-26].例如,汪菊香等[22]采用HZ818苯乙烯二乙烯基苯大孔树脂吸附P507和Cyanex272萃取剂制成色层柱对钴镍离子进行研究,得到的硫酸钴溶液纯度达到99.27 %.陈松等[23]用HPD-100苯乙烯—二乙烯基苯大孔吸附树脂和P507萃取剂制备的萃淋树脂净化硫酸钴溶液,通过研究确定萃淋树脂的萃取容量以及萃取pH值、淋洗pH值、流出体积等条件,得到的高纯氯化钴溶液中钴镍浓度比大于80 000.周移等[25]利用萃取色层法研究了硫酸盐电解质水溶液体系中的钴、镍分离.研究发现P507萃取剂经MgSO4改性后萃取Co2+的能力得到了很大提高,实现了Co2+、Ni2+完全分离.
相比较而言,萃取色层法结合了萃取剂的高选择性和离子交换分离工艺的分离级数高的优点,在分离性质相近的元素上有着优良的性能,但萃取色层法存在色层柱萃取容量低,萃取剂容易流失,工作寿命相对短等缺点.提高色层柱的萃取容量,克服萃取剂流失,开发选择性更好的萃取剂是该方法迫切需要解决的问题.
1.3 膜分离法研究进展
膜分离法是一种利用疏水多孔膜材料作支撑体吸附含有萃取剂的有机溶液制成液态膜,液膜两侧分别进行萃取和反萃反应.通过一侧高pH值水溶液中的特性粒子与萃取剂络合进入液态膜中,并在膜的另一侧低pH值的水溶液中解络(反萃)实现分离.分离过程中萃取剂同时实现再生.膜分离法兼容了萃取和膜渗透2项技术的特点,是一种快速高效和节能的新型离子分离技术,其反应过程可表示为:
液膜(萃取)/水溶液界面:nR-H+Men+→ nR-Me+nH+
液膜(反萃)/水溶液界面:nR-Me+nH+ → nR-H+ Men+
(其中R-H表示有机萃取剂,Men+表示金属离子)
膜分离法研究主要集中在液膜制备方面的尝试,主要包括支撑液膜[27, 28]与微乳液膜(混合液膜)[29-32]2大类.支撑液膜的主要尝试在于通过向不同的膜材料中加入适用于钴镍分离的萃取剂、提高液膜稳定性,并优化分离条件,如JERZY等[27]对利用疏水性聚丙烯多孔膜吸附含有机磷酸萃取剂的有机溶液制成液膜对硫酸盐水溶液体系中的钴、镍分离进行研究.讨论了水溶液pH值、离子浓度和膜中萃取剂浓度对分离效果的影响. PARHI等[28]以Celgard 2400(一种微孔聚丙烯)吸附LIX 841,TOPS-99和Cyanex-272形成支撑液膜分离硫酸铵溶液中的铜、锌、钴和镍,先用LIX 841分离出铜,再用TOPS-99分离出锌,最后使用Cyanex-272分离钴,实现了铜、锌、钴和镍的分离,得到的溶液中镍钴的摩尔浓度比高达1 180.而微乳液膜则是在通过控制成膜的成分以及含量达到最优的钴镍分离效果的方面进行着尝试,如李英等[29]研究了P507+煤油+NaOH的微乳液膜对硫酸盐电解质水溶液中钴、镍分离,研究表明:当P507体积浓度为20 %(溶剂为煤油),NaOH浓度为3 mol/L,相比(VO/VA)为1:1,水相的pH值为5时,萃取10 min,钴萃取率可达到90 %,镍萃取率为10 %,钴、镍离子分离系数达到68.刘汉星等[30]对曲拉通X-100+正丁醇+正庚烷+水+P204+NaOH组成的微乳液膜体系萃取分离钴和镍进行了研究,在较优分离条件下含钴50 mg/L、镍30 mg/L的电解质水溶液钴的萃取率为87.4 %,镍为10.87 %,钴镍的分离系数达到57.
综上,膜分离法具有较高的选择性、传质推动力大、速率快、试剂使用量大大减小、分离级数少、萃取与反萃取可以同时进行等优点,但液膜的稳定性差限制了它的应用范围,目前还处于中试阶段.
1.4 溶剂萃取法研究进展
溶剂萃取法具有选择性好、直收率高、流程简单、处理量大、操作连续和易于实现自动化控制等特点,是目前钴、镍分离研究最多的方法.利用钴、镍离子在有机相和水相之间的分配比不同来实现深度分离,达到提纯溶液的目的.研究多集中在萃取剂和含高镍低钴的硫酸盐电解质水溶液萃取分离工艺等方面.
1.4.1 溶剂萃取法分离钴、镍萃取剂的研究进展
萃取剂是溶剂萃取法的核心材料.经过多年发展,应用于溶剂萃取法分离钴、镍的萃取剂主要可分为以下几大类:酸性磷(膦)类萃取剂,如P204、P507、Cyanex272等;有机酸类萃取剂,如VersaticTM10;螯合类萃取剂,如LIX-84;胺类萃取剂,如N235、N263等.在萃取工艺中,通常采用单一萃取剂进行2种离子或多种离子的分离萃取过程,但随着协同效应被普遍研究,有时也会出现2类萃取剂混合进行协同萃取的情况[33, 34].
由于钴、镍盐电解质水溶液大多是由矿物经过酸浸出得到,水溶液呈酸性,所以目前广泛应用的钴、镍分离萃取剂主要是酸性磷(膦)类萃取剂,如P204、P507、Cyanex272以及与它们成分大致相同衍生的阳离子交换萃取剂.其中P204萃取剂分离钴、镍离子所需要的条件比较苛刻,而且钴、镍离子的分离系数比较低,二者的分离效果并不理想,但P204分离除去钙、铁、铜等杂质元素的性能非常好,被广泛用于钴、镍离子深度分离之前的除杂工序.
P507是一种对钴离子有选择性反应的有机磷萃取剂,学名为2-乙基己基膦酸单2-乙基己基酯,也称PC-88A、HEHEHP. P507由于钴、镍的分离系数高,毒性低,化学稳定性好、价格便宜,被广泛应用于镍钴萃取分离.针对P507的研究首先是对其适用的体系进行讨论[35-37],袁承业等[35]在合成P507之后,实验证明P507是一种高效的钴、镍分离萃取剂,适用于硫酸盐、硝酸盐和氯化物电解质水溶液体系中的钴、镍离子分离.同样,陈耀宗等[36]研究发现P507对低浓度钴、镍氯盐体系中萃取分离钴镍仍有效果,研究还发现氯离子浓度对钴、镍离子分离的影响十分显著.关于P507分离效率并进行流程优化的研究也随即展开[38-44].邬建辉等[40]的研究表明P507对铜、锌、钴的萃取效率均大于98 %,而反萃率超过了99 %.何广廖[41]采用皂化率为70 %,体积浓度为20 %的P507对含钴8~24 g/L,含镍大于100 g/L的氯盐电解质水溶液进行钴镍分离研究.通过7级萃取→2级洗涤→4级反萃分离工艺得到了钴镍质量浓度比达到2 100的电解质水溶液.诸多研究说明,P507是钴、镍离子分离的优良萃取剂,适用于镍、钴质量浓度或摩尔浓度比变化范围大的各种硫酸盐、氯化物溶液.
Cyanex272也是一种对钴有选择性反应的新型萃取剂,其主要成分是二(2,4,4一三甲基戊基)膦酸,是专门针对钴、镍离子分离而设计出来的萃取剂.针对Cyanex272的研究一方面是利用萃取剂的高选择性配合以合适的工艺条件实现钴镍高效分离[45, 46],如刘大星等[45]通过实验证明无论在高钴或低钴的硫酸盐溶液中Cyanex272都具有优良的钴、镍离子分离能力,钴、镍离子浓度比约为1:5的水溶液经过9级分馏萃取可以得到Ni/Co(质量浓度比)>104的硫酸镍溶液以及Co/Ni(质量浓度比)> l03的氯化钴反萃液.关于Cyanex272的另一方面研究在于与其他萃取剂组成协萃体系的探索,以提高萃取容量与体系稳定性的尝试[47-50].田君等[47]通过实验说明Cyanex272的协萃体系,可大大改善钴、镍离子萃取分离的热力学与动力学性能. SARANGI等[49]通过对比实验确定0.005M Na-PC88A与0.025M Na-Cyanex272混合,钴镍分离系数最大达39 266.
在高氯离子浓度的环境下,利用镍不形成氯配离子的性质,叔胺类或季铵盐萃取剂也可以实现钴镍的有效分离.周学玺等[51, 52]则对季铵萃取剂萃取分离钴、镍离子进行了研究.研究发现:较低的氯离子浓度下(4~5 mol/L)该萃取剂可有效的分离钴、镍,萃取且分相速度较快,负载有机相可用水实现反萃制得高纯度氯化钴溶液,反萃后的有机相不需再生即可重复使用,适合处理低钴高镍的溶液.含镍18 g/L、含钴8 g/L的氯盐电解质水溶液,经8级萃取,3级洗涤,5级反萃后,两相出口镍、钴的回收率分别达到96.58 %和97.79 %,萃余液中镍钴浓度比大于500,反萃液中钴镍浓度比大于300,均满足生产工业氯化钴、氯化镍要求.反萃后的萃取剂不必用酸再生,略加澄清可循环使用.当然胺类萃取剂存在萃取需要较高的氯离子浓度,甚至需要预先用盐酸处理,并且黏度大的缺点.上述原因限制了胺类萃取剂的应用.
由于钴、镍金属离子可以与氨形成稳定的配合物而溶解在氨-铵盐溶液中,利用形成氨配合物稳定常数的差异,使用螯合类萃取剂就可以实现二者的分离.汪胜东等[53]使用LIX84从多金属结核氨浸液中进行萃取分离镍、钴、铜的研究.原料液先使用LIX84共萃取铜镍实现与钴的分离,负载有机相经洗涤除氨后,选择性反萃镍,实现镍与铜的分离.以较优实验条件进行联动和连续实验,得到的硫酸镍溶液钴镍质量浓度比达859 000,满足镍电积的要求.限制该萃取分离工艺使用的主要问题是从有机相中存在共萃的氨,会进入反萃段,生成镍-铵复盐沉淀,影响产品质量.
1.4.2 溶剂萃取法钴、镍分离工艺研究进展
溶剂萃取分离工艺过程一般分为3个阶段:萃取、洗涤和反萃.萃取过程主要流程如图 2.目前,溶剂萃取分离钴、镍研究多集中在对高镍低钴的硫酸盐电解质水溶液体系,针对氯盐电解质水溶液体系和含高钴、低镍盐的电解质水溶液体系研究偏少.
对于硫酸盐电解质水溶液体系中钴镍分离的研究对象多是含有多种金属杂质的溶液,研究内容主要集中在探索较优的实验条件以及合理安排工艺步骤促进钴镍收率及分离效果这方面.由于钴镍都为稀缺资源,一部分研究就是围绕着高效回收钴镍这一目标而展开的[42, 54-57].董存武等[42]通过对2种不同的萃取工艺对比,确定了较优操作工艺,镍离子的回收率可达99.69 %,钴离子的回收率可达98.19 %.何展伟等[54]采用化学沉降与溶剂萃取相结合的工艺步骤处理以含镍、钴、铜的混合废料,超过98 %的钴得到了回收.随着材料高纯化的需求越来越大,在追求高效回收的同时,钴、镍有效分离的研究也引起了科研人员的重视[38, 58-61].桑雅丽等[58]利用P507作萃取剂对镍钴离子摩尔比为3:1的硫酸盐溶液分离工艺进行研究.当平衡水相pH值为4.2,P507的体积分数为20 %时,钴的萃取率最高为99.95 %,钴、镍的分离系数最大为128.王靖坤等[59]对镍基高温合金废料硫酸浸出溶液进行回收,采用6级萃取钴→6级洗涤→4级反萃的连续萃取工艺,制得了镍钴浓度比达8 000的富镍电解质和钴镍浓度比达12 576的富钴电解质.范艳青等[61]利用胺类萃取剂对大洋富钴结壳经硫酸活化浸出除杂后的硫酸盐电解质水溶液体系进行萃取分离工艺研究.在较优萃取工艺条件下,钴萃取率达99.99 %,反萃率达99.81 %,反萃液中钴、镍浓度比达106,萃取分离后得到的氯化钴和氯化镍溶液纯度高,满足电解沉积金属的要求,还可用于生产高纯化工产品.
尽管溶剂萃取分离研究大多是围绕硫酸盐电解质水溶液体系展开,但随着硫元素在冶金中暴露出的不良影响[62, 63],以及资源合理利用的要求,氯盐电解质水溶液萃取分离钴、镍的工艺研究越发受到关注[50, 64-66]. COLL等[64]采用将萃取剂Primene JMT与Cyanex272混合在氯盐电解质中进行协同萃取分离钴、镍. Primene JMT起到维持pH值平衡的作用,VJMT:VCyanex272:VD100 = 10 %:10 %:80 %的协同萃取剂对钴、镍离子分离效果较好;钴、镍浓度均为1 g/L的溶液,经4级逆流萃取(VO/VA),超过99 %的钴和11 %的镍被萃取进入有机相,89 %的镍和0.3 %的钴留在了水相中. LUO等[65]以PC88A为萃取剂,对含钴56.78 g/L,含镍140.78 mg/L的氯盐电解质水溶液体系中钴、镍离子萃取分离工艺进行研究.在较优工艺条件(平衡pH值为4.48,温度为35 ℃,萃取剂体积浓度为20 %,相比(VO/VA)为1:1.5)下,钴、镍离子分离系数达到350. SHEN等[66]利用VN235:VTBP:V煤油 =30 %:20 %:50 %的有机相,对钴镍合金盐酸浸出含钴23.96 g/L,含镍12.63 g/L的氯盐电解质水溶液的钴镍分离工艺进行研究.研究发现经过7级萃取(VO/VA=2:1)→3级洗涤(VO/VA=10:1)→3级反萃(VO/VA=5:1)后,钴的萃取率高达99.9 %,镍的回收率大于99.7 %,萃取余液中镍钴质量浓度比达到6 000,反萃得到的氯化钴溶液中钴镍质量浓度比为9 000,取得很好的钴镍分离效果.
2 展望
目前钴、镍盐电解质水溶液体系中钴、镍分离方法主要还是针对高镍、低钴的体系展开.而实际上,电解或电解精炼制备高纯钴的钴盐电解质水溶液是以高钴、低镍盐的状态存在.对高钴、低镍盐电解质水溶液中钴、镍分离的研究明显不足.但另一方面,人们对高纯乃至超高纯金属钴需求在逐渐提高,对高钴、低镍盐电解质水溶液中钴、镍分离进行研究的要求越来越强烈.对高钴、低镍盐电解质水溶液体系中钴、镍分离的研究势在必行,需要在以下几个方面加强:
1)目前分离钴、镍的萃取剂和吸附材料主要是针对高镍中的钴提取,而针对高钴中镍提取的萃取剂和吸附材料研究需要加强;
2)现有萃取剂和吸附材料对钴的萃取容量和吸附容量小,提高钴的容量研究需要加强;
3)现有分离工艺忽略了萃取剂及其溶剂、吸附材料等在分离、提纯过程中低pH值条件下对处理对象造成的污染,溶解在水溶液中的有机杂质的去除研究需要加强;
4)避免有机物残留带来的污染,不溶解的无机物选择性吸附剂开发需要加强.
-
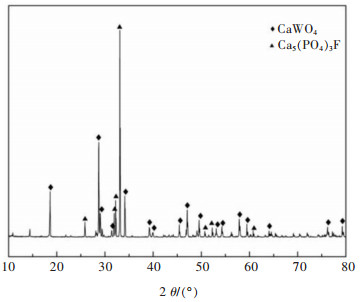
表 1 实验所用白钨矿中主要成分含量
Table 1 Content of main components in scheelite ore used in the experiment

表 2 第1段盐酸浸出渣的主要成分含量
Table 2 The content of main components of the first stage hydrochloric acid leaching residue

表 3 盐酸中钨酸和钼酸的溶解度[22]
Table 3 Solubility of tungstate and molybdate in hydrochloric acid

-
[1] 谢小豪, 王云, 汪艳亮, 等.废旧硬质合金回收方法及其研究进展[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2020, 11(2): 64-70. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=202002009 [2] 赵中伟, 孙丰龙, 杨金洪, 等.我国钨资源、技术和产业发展现状与展望[J].中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(9): 1902-1916. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgysjsxb201909007 [3] 高玉德.我国钨矿资源特点及选矿工艺研究进展[J].中国钨业, 2016, 31(5): 35-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgwy201605007 [4] 黎继永, 谢贤, 童雄, 等.低品位白钨矿选矿技术的研究发展[J].矿产综合利用, 2015(4): 1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kczhly201504001 [5] 赵中伟, 李江涛, 陈星宇, 等.我国白钨矿钨冶炼技术现状与发展[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2013, 4(5): 11-14. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=2013050003 [6] 中国钨业协会.中国钨工业发展规划(2016-2020年)[J].中国钨业, 2016, 32(1): 9-15. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgwy201701003 [7] 王夏.河南省栾川县扎子沟钨钼矿床特征及找矿标志[J].河南科技, 2017(5): 85-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hnkj201705035 [8] 廖宇龙.高钼白钨中矿酸性化学选矿浸出液的钨钼萃取研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2011: 35-37. [9] 陈升, 戴林明, 熊庆, 等.浅析白钨分解的理论与工艺[J].价值工程, 2019, 38(26): 148-150. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzgc201926062 [10] 肖连生.中国钨提取冶金技术的进步与展望[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2013, 4(5): 6-10. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=2013050002 [11] 吴金玲, 李江涛, 刘旭恒, 等.碳酸钠选择性浸出钨钼混合矿的热力学[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2013, 4(5): 33-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxysjs201305009 [12] 赵中伟.钨冶炼的理论与应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2013. [13] 李停停, 钟祥熙, 张威, 等.白钨矿浸出工艺现状及发展趋势[J].金属矿山, 2017(10): 128-134. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsks201710026 [14] MARTINS J P. Kinetics of soda ash leaching of low-grade scheelite concentrates[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1996, 42(2): 221-236. doi: 10.1016/0304-386X(95)00099-3
[15] 万林生, 邓登飞, 赵立夫.钨绿色冶炼工艺研究方向和技术进展[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2013, 4(5): 15-18. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=2013050004 [16] GAUR R S. Modern hydrometallurgical production methods for tungsten[J]. JOM, 2006, 5(9): 45-49. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3b4e2301293fb2cab6d3672fbfbfd393
[17] 何利华, 赵中伟, 杨金洪.新一代绿色钨冶金工艺-白钨硫磷混酸协同分解技术[J].中国钨业. 2017, 32(3):49-53. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90381X/201703/672646500.html [18] 谭震波.白钨精矿重选-酸浸脱磷[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 1982 (6):58-59. [19] 李青刚, 张贵清, 张斌, 等.一种从磷中矿中回收钨、钼的方法[P].中国专利, CN101348868A, 2009-01-21. [20] ZHANG W J, YANG J H, ZHAO Z W, et al. Coordination leaching of tungsten from scheelite concentrate with phosphorus in nitric acid[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(6): 1312-1317. doi: 10.1007/s11771-016-3181-2
[21] BRADLEY J S, VINCENT A. PATRIC K. Quantitative of aqueous dodecatungstophosphoric acid speciation by nmr spectroscopy[J]. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 2004, 57: 261-268. doi: 10.1071/CH02037
[22] 李洪桂.羊建高.李昆, 等.钨冶金学[M].长沙:中南大学出版社, 2010. -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王崇国,金小容,刘广龙,陈艳丽,苏军德,汪晓文. 钴锍氯化浸出工艺试验研究. 中国有色冶金. 2024(04): 48-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王嘉萱,刘志慧,戴梦秋,张彩霞. 红土镍矿浸出液萃取分离钴镍的研究. 当代化工研究. 2022(08): 159-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邹冰,张越强. 集成电路芯片湿法去层技术研究. 微处理机. 2021(03): 6-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郁建成,马保中,马玉天,赵健,王成彦. 钴资源氨法回收研究进展. 有色金属科学与工程. 2021(03): 20-28 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王轩,陈胜利. 镍钴湿法冶金中萃取剂的研究与应用. 世界有色金属. 2021(22): 23-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李强,杨皓迪,李奇勇,黄舒宁,邢丹霞. 湿法炼锌净化钴渣酸浸液萃取除杂试验研究. 湿法冶金. 2020(02): 151-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 彭文博,李腾飞,白祖国,陈道康,恽建军. 膜技术在含钴浓盐水资源化中应用. 无机盐工业. 2020(05): 65-67+74 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘丹,贺昕,滕海涛. 螯合树脂TP207深度去除氯化钴溶液中的镍. 有色金属工程. 2020(06): 49-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张兴勋. 从某萃余液除杂后液中回收钴的试验研究. 矿产综合利用. 2020(02): 151-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 于凯,艾峥嵘,谢宏伟,刘吉利,宁志强. 用P507从高浓度氯化钴溶液中萃取分离钴镍试验研究. 湿法冶金. 2020(06): 502-506 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: