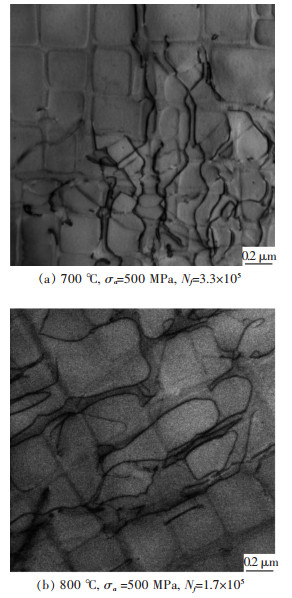
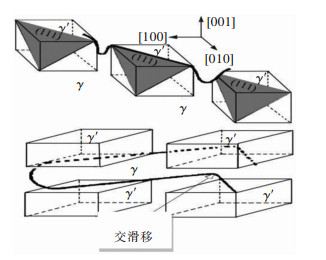
High cycle fatigue properties of a single crystal superalloy at different temperatures
-
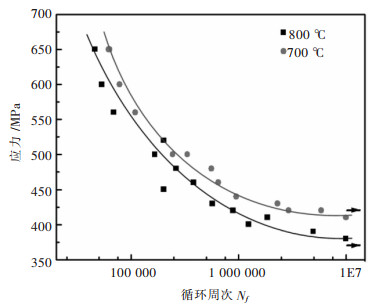
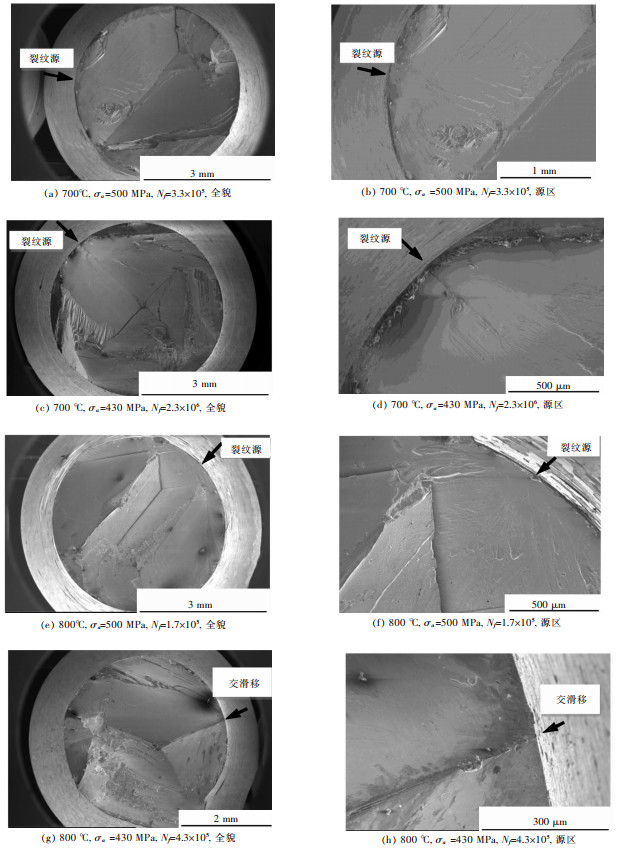
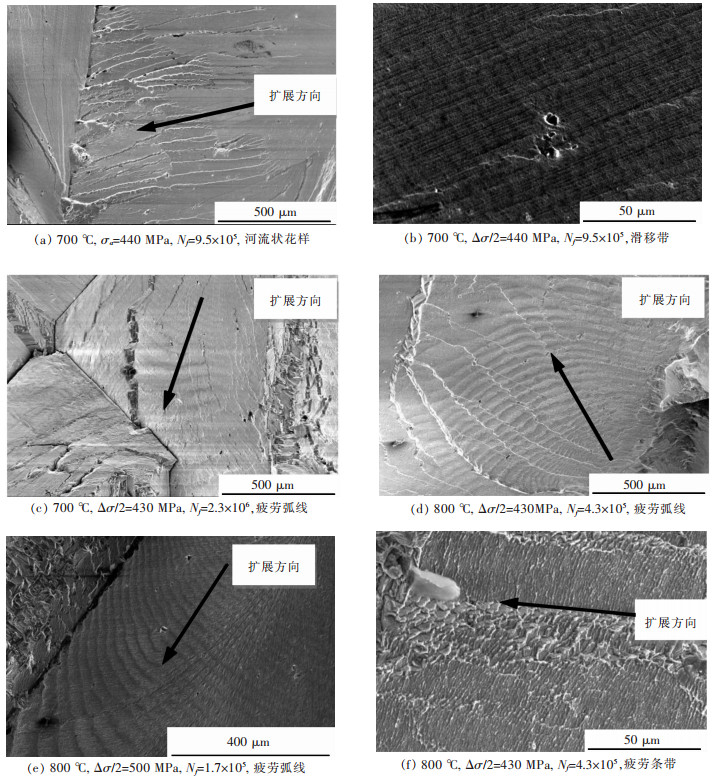
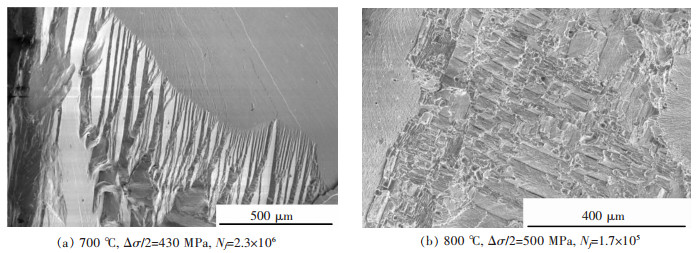
摘要: 研究了一种单晶高温合金700 ℃和800 ℃的高周疲劳性能,采用扫描电镜和透射电镜分析了断口和断裂机制.结果表明,随着温度升高,合金的疲劳强度系数降低,Basquin系数增加,高周疲劳极限降低.合金700 ℃与800 ℃具有相同的高周疲劳断口,都有几个{111}面平面组成,为类解理断裂机制.疲劳断口由裂纹源区、扩展区和瞬断区3部分组成.裂纹起源于试样的表面或亚表面,并沿{111}面扩展.扩展区可见河流状花样、滑移带、疲劳弧线和疲劳条带特征.瞬断区可见解理台阶和撕裂棱.断裂后γ′相仍保持立方形状,位错不均匀分布在γ基体通道中.Abstract: The high cycle fatigue properties of a single crystal superalloy were investigated at 700 ℃ and 800 ℃. SEM and TEM were used to study the fracture surface and fracture mechanism. The results showed that the fatigue strength coefficient dropped, Basquin exponent rose and the fatigue limit decreased with the increasing test temperature. The fracture surfaces were the same at the above temperatures, each consisting of several {111} planes. The fracture mechanism was all quasi-cleavage fracture. Fatigue source zone, crack propagation zone and transient fracture zone could be seen on the fracture surface. The fatigue crack initiated at or near the surface and propagated along {111} planes. The river pattern, slip band, fatigue arc and fatigue striation could be seen in the crack propagation zone. The cleavage step and tear ridge could be seen in the transient fracture zone. The γ′ phase morphology still maintained cubic after fracture. Dislocations were unevenly distributed in the γ matrix of the alloy.
-
0 引言
随着电子信息高新技术的迅速发展,对电子材料的需求日益增大,由于我国的电子行业起步较晚,大量的材料仍需进口。KFC引线框架材料是在铜中加入少量的铁、磷等元素的低铁铜合金,以其优良的导电率,较好的强度和耐热性能而广泛的用于三极管、半导体及IC引线框架。研究KFC材料的组织与性能,对于提高我国生产KFC材料的生产技术,提高产品的质量,具有十分重要的意义。
1 试验方法
选用国外生产的两种规格的KFC引线框架材料,用Spectro LAB直读光谱仪进行化学成分分析;用CMT5105电子万能试验机进行抗拉强度的测定;用HXD-1000-TMB维式硬度计测试材料在室温、经250、350、400、450、520℃分别加热5min后的硬度;用ZEISS金相显微镜观察组织形貌,浸蚀剂为Fe(NO)3酒精溶液。
2 试验结果与讨论
2.1 试验结果
2.1.1 材料的化学成分
两种规格材料的化学成分见表 1。
表 1 两种材料的化学成分 %
从整体上,1号试样中Fe、P含量比2号试样多。1号试样中Fe、P原子比为1.73:1,2号试样中Fe、P原子比为2.45:1,1号试样中P的加入比例相对较高。
2.1.2 材料的力学性能
两种规格材料的室温力学性能见表 2。
表 2 材料的力学性能
1号试样的抗拉强度、硬度较大,2号试样的抗拉强度相对较小、硬度较小。室温性能1号样优于2号样。
2.1.3 材料的金相组织
1号试样内部有细小的沉淀颗粒,同时也有分布不均匀的粗大颗粒。2号试样内部为细小且分布均匀的第二相沉淀颗粒。
2.1.4 材料在不同温度加热后的硬度
将两试样在不同的温度加热,测定加热后材料硬度的变化。硬度的不同变化反映材料不同的耐热性能。见图 3。
1号试样在450℃以前,硬度值略有下降,450℃以后材料的硬度才有大幅度的下降。2号试样从室温到520℃时,硬度值一直没有大幅度的下降。一般将材料加热后硬度降为原硬度的80%的温度定义为材料的耐热温度。经作图,1号试样的耐热温度为475℃,2号试样的耐热温度大于520℃。2号试样的耐热性能性能优于1号试样。
2.2 试验结果分析
KFC合金是在铜中加入Fe、Zn、P等低固溶度元素,是典型的析出强化型合金。由Cu-Fe相图可知,Fe在铜中的固溶度随温度有重大变化,1094℃时有最大的固溶度4.0%,而室温下,Fe几乎不溶入Cu中,以α-Fe形式输出,如果有磷存在,可以生成细小的FemP金属化合物,该化合物的析出导致合金的强度增加[1]。加入的合金元素的作用分别如下。
(1)Fe的作用:细化晶粒;延长再结晶过程,提高材料的强度和硬度;降低材料的导电率[2]。
(2)P的作用:可以脱氧,固溶在铜中,防止氢脆;与合金中的Fe、Mg、Co等元素作用,形成第二相而使材料强化;降低材料的导电导热性能[3]。
(3)Zn的作用:增加材料的强度;防止在金属基体与渡层中间出现脆性第二相Cu3Sn、Cu6Sn6[3],改善长期工作后合金与焊料的结合情况,提高集成电路焊点的可靠性乃至器件的可靠性[4]。
材料中适量的元素的加入,对改善材料的性能有好处,但一定要控制在一定的范围之内,铁和磷的加入量以铁磷原子2:1~3:1的比例为宜[1]。
1号试样中,Fe、P原子比为1.73:1,P的含量相对较高,过量的P与Fe形成FemP金属化合物。当形成的化合物颗粒分布不均,生产工艺没控制好时,易在材料中形成粗大的Fe3P沉淀颗粒。由金相图可以看出,1号试样中有大的析出颗粒,2号试样中析出颗粒的尺寸较小。
KFC合金经固溶、时效处理,材料内析出的第二相沉淀颗粒使材料的强度增加,合金的强化理论mott-nabarro理论认为[5]:沉淀颗粒引起材料的强度的增加值为:

式中:μ——沉淀颗粒的切变模量;
r——沉淀颗粒的半径;
φ——沉淀颗粒的体积分数;
ε——错配函数;
b——柏氏矢量。
由两试样化学成分分析比较可知,1号试样中,Fe、P含量比2号试样多。两试样的金相组织可以看出,1号试样内部细小沉淀颗粒的体积分数φ1大于2号试样内部沉淀颗粒的体积分数φ2,1号试样内部细小沉淀颗粒的半径r1大于2号试样内部沉淀颗粒的半径r2,同时1号样的晶粒内还有粗大的、较硬的沉淀颗粒,对材料的强度、硬度也有增加。因此1号试样整体上室温强度、硬度值大于2号试样。
材料内部析出的第二相沉淀颗粒对位错的运动起阻碍作用,位错与沉淀颗粒的交互作用遵循Qrowan机制[6]:

式中:Δτ——位错绕过析出颗粒时临界分切应力的增值;
r——析出颗粒半径;
L——析出颗粒之间间距。
沉淀颗粒的半径越大,颗粒之间的距离越小,临界分切应力增值越大,材料抗拉强度越大。
材料内部析出的沉淀颗粒的分布及大小,同样影响材料的使用性能。作为引线框架材料的KFC, 要求在400~500℃时,有较好的耐热性能[7],即在此温度时,材料在3min左右,硬度不应有明显的下降。两试样的试验结果表明,2号试样在500℃左右有较好的耐热性能。2号试样的使用性能较好。
两试样的金相图片的比较可以看出,1号试样的晶粒内部,第二相沉淀颗粒较多(有细小的沉淀相,也有大颗粒的沉淀相)。材料在加热时,第二相沉淀颗粒聚居、长大,在温度较高时,粗大的第二相沉淀颗粒将会异常长大,使材料中起强化作用的第二相沉淀颗粒的体积分数迅速降低,材料出现软化现象。2号试样中第二相沉淀颗粒的大小及分布均匀,材料在加热过程中,第二相均匀长大,彼此相互制约,同时细小均匀分布的第二相沉淀颗粒对位错及晶界起钉扎作用,有效地阻止了晶界和位错的移动,使得材料在较高温度下有较好地耐热性能。
1号试样的室温力学性能优于2号试样,但2号试样的耐热性能优于1号试样,从整体上没法说那种试样较好,要根据实际产品的使用要求来评判。但归根结底要通过控制产品的化学成分和产品的内部组织结构,从而控制产品的性能。
3 结论
(1)KFC合金中,Fe、Zn、P等低固溶度元素的加入量,以及加入比例,影响产品的最终性能,探索合理的加入量以及加入比例,对保证产品的性能有很大的意义。
(2)合金内部第二相的分布及大小,影响产品的力学性能及耐热性能。生产中,应根据成品的性能要求,合理控制生产工艺参数,从而控制材料内部第二相沉淀颗粒的大小及分布。
-
表 1 合金成分/(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of alloy/(mass fraction %)

表 2 合金不同温度的疲劳性能参数
Table 2 Fatigue property parameters of the alloy at different temperature

-
[1] CARON P, KHAN T. Evolution of Ni-based superalloys for single crystal gas turbine blade applications [J]. Aerospace Science Technology, 1999(3): 513-523. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4da7da944907065a3961e2e5c96ac759&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] 刘世忠, 史振学, 熊继春, 等.一种单晶高温合金的组织和持久性能[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2017, 8(1): 118-121. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/darticle.aspx?type=view&id=201701020 [3] 史振学, 杨万鹏, 刘世忠, 等.长期时效温度对一种单晶高温合金的组织和拉伸性能的影响[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2018, 9(4): 35-39. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/darticle.aspx?type=view&id=201804006 [4] 史振学, 赵金乾, 刘世忠, 等.表面缺陷对单晶高温合金高周疲劳性能的影响[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2018, 9(6): 21-25. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/darticle.aspx?type=view&id=201806008 [5] 谢洪吉, 李嘉荣, 韩梅, 等.超温对DD6单晶高温合金组织及高周疲劳性能影响[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2018, 47(8): 2483-2488. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xyjsclygc201808033 [6] MÜLLER S, RÖSLER J, SOMMER C, HARTNAGEL W. The influence of load ratio, temperature, orientation and hold time on fatigue crack growth of CMSX-4[C]//Superalloys 2000, Warrendale, TMS, 2000: 347-355.
[7] 谢洪吉. DD6单晶高温合金疲劳性能研究[D].北京: 北京航空材料研究院, 2018: 38-39. [8] SHI Z X, WANG X G, LIU S Z, et al. Low cycle fatigue properties and microstructure evolution at 760℃ of a single crystal superalloy [J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2015, 25(1): 78-82. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2015.01.009
[9] 张志华, 于慧臣, 李影, 等.单晶镍基高温合金在600~760 ℃下的低循环疲劳行为[J].航空材料学报, 2018, 38(3): 58-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hkclxb201803009 [10] WRIGHT P K, JAIN M, CAMERON D. High cycle fatigue in a single crystal superalloy: time dependence at elevated temperature [C]//Superalloys 2004. Pennsylvania, PA: TMS, 2004: 657-666.
[11] LUKAS P, KUNZ L, SVOBODA M. High cycle fatigue of superalloy single crystals at high mean stress [J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2004, 387/389: 505-510. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.01.093
[12] 韩国明, 张振兴, 李金国, 等. DD98M镍基单晶高温合金900 ℃高周疲劳行为[J].金属学报, 2012, 48(2): 170-175. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsxb201202007 [13] ASTM. Annual book of ASTM standard, ASTM standard E606, vol.03.01, ASTM[M]. Philadelphia, PA, 1996.
[14] CHU Z K, YU J J, SUN X F, et al. High cycle fatigue behavior of a directionally solidified Ni-base superalloy DZ951 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008(496): 355-361. doi: 10.1016-j.msea.2007.11.045/
[15] WAN J S, YUE Z F. A low-cycle fatigue life model of nickel-based single crystal superalloys under multiaxial stress state[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 392: 145-149. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.09.069
[16] WASSON A J, FUCHS G E. The effect of carbide morphologies on elevated temperature tensile and fatigue behavior of a modified single crystal Ni-base superalloy [C]// Superalloys. Pennsylvania, PA: TMS, 2008: 489-497.
[17] SHI Z X, LI J R, LIU S Z, et al. High cycle fatigue behavior of the second generation single crystal superalloy DD6 [J]. Transaction Nonferrous Metal Society of China, 2011, 21(5): 998-1003. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60812-1
[18] 史振学, 李嘉荣, 刘世忠, 等.第二代单晶高温合金DD6的低周疲劳行为[J].材料热处理学报, 2011, 32(5): 41-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6432738 [19] LIU Y, YU J J, XU Y, et al. High cycle fatigue behavior of a single crystal superalloy at elevated temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 454/455: 357-366. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.11.045
[20] 史振学, 王效光, 刘世忠, 等. DD9单晶高温合金在800℃的高周旋弯疲劳性能[J].机械工程材料, 2016, 40(1): 16-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jxgccl201601004 [21] 黄志伟, 袁福河, 王中光, 等.铸造镍基高温合金M963的高温低周疲劳行为[J].金属学报, 2007, 43(7) : 678 -682. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2007.07.002 [22] ZHANG J X, MURAKUMO T, HARADA H. Creep deformation mechanisms in some modern single crystal superalloys[C]//Superalloys 2004. Pennsylvania, PA: TMS, 2004: 189-195.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孟令琪,迟庆新,李艳明,董自超. CoAl渗层对DD5合金低周疲劳性能的影响研究. 兵器材料科学与工程. 2023(05): 106-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 水丽. 应变幅对一种新型镍基单晶高温合金高温低周疲劳性能的影响. 机械工程材料. 2022(06): 31-35+43 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蒋立武,杨宇,武美伶,蔡敏. 一种Ni_3Al基单晶高温合金在1100℃/137 MPa蠕变行为的各向异性研究. 稀有金属. 2021(09): 1025-1033 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: