Synthesis and characterization of core-shell like Ag2CO3@AgBr composite photocatalyst and its high visible light photocatalytic performance
-
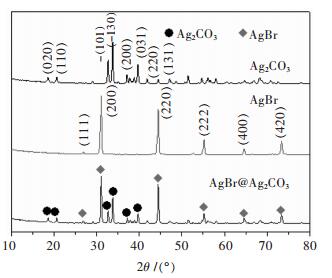
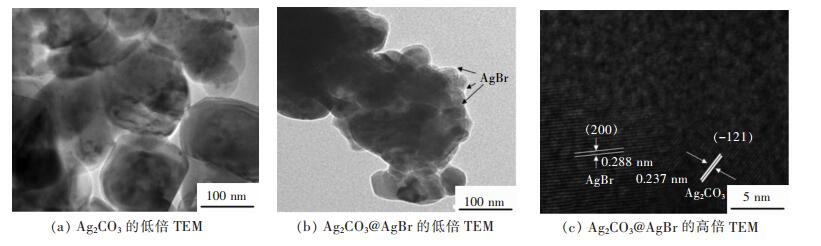
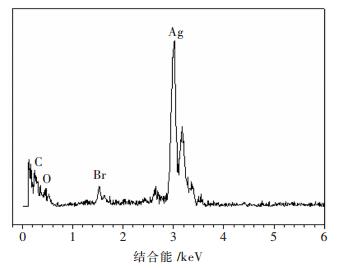
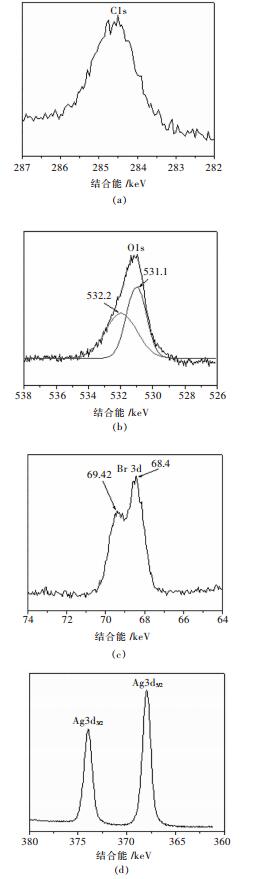
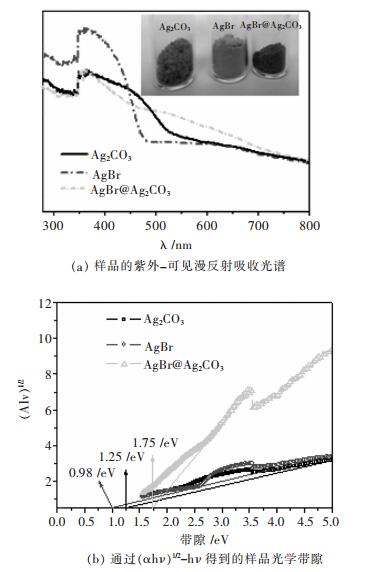
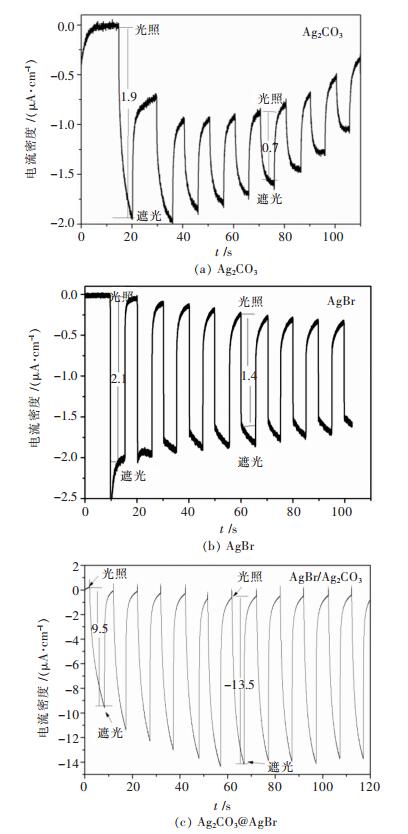
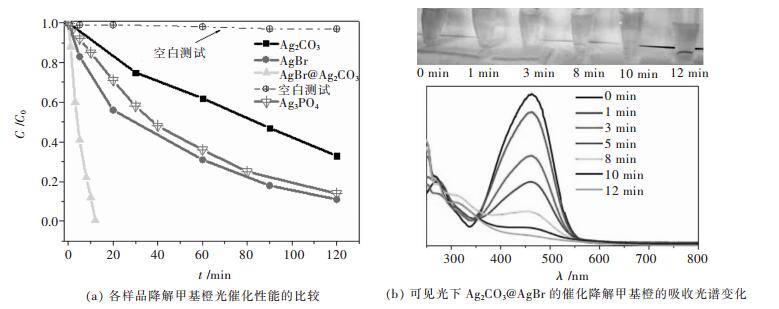
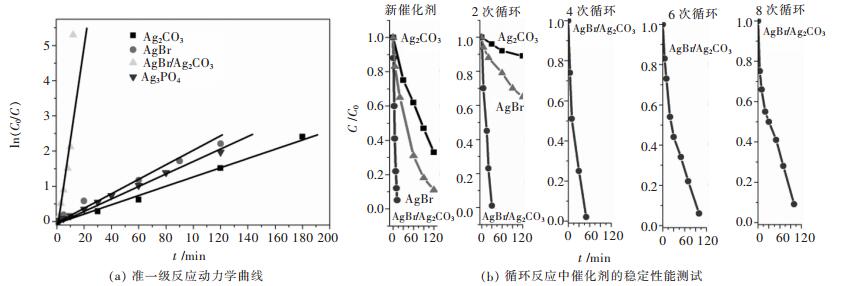
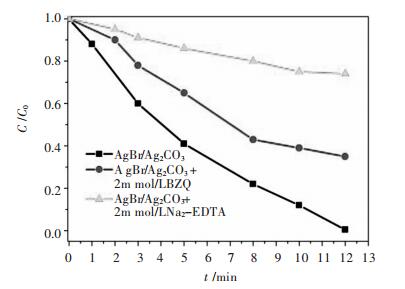
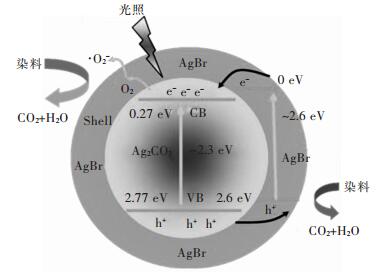
摘要: 采用连续沉淀法合成了类似核/壳结构的Ag2CO3@AgBr复合光催化剂.利用氮气物理吸附、X射线粉末衍射、扫描电镜、透射电镜、光电子能谱、紫外-可见漫反射和光电流等测试手段对所制备的AgBr、Ag2CO3和Ag2CO3@AgBr进行了系列表征,考察了AgBr壳对Ag2CO3的组织结构、光吸收、光电流响应性能和光催化性能的影响.结果表明,在Ag2CO3晶体表面的复合AgBr纳米颗粒,能显著增强催化剂在可见光区的吸光性能、增大催化剂的比表面积和增强光电流响应强度.在可见光下(400 nm<λ<660 nm),催化降解甲基橙测试表明,Ag2CO3@AgBr表现出优异的光催化性能,其降解速率常数分别是纯Ag2CO3和AgBr的11倍和10倍,同时其稳定性也得到大幅度提高.在核/壳界面中,形成了具有能级匹配的Ag2CO3@AgBr异质相结,这种异质相结提高了光生电子和空穴的分离效率,同时壳层AgBr可以阻止主体光催化剂Ag2CO3在水溶液中的溶解,提高其稳定性.Abstract: Core-shell like Ag2CO3@AgBr composite photocatalyst was fabricated by the successive precipitation method. The obtained AgBr, Ag2CO3, Ag2CO3@AgBr samples were well characterized by N2 physical adsorption, powder X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra, and photocurrent test. The effects of AgBr shell on the texture, light absorption, photocurrent response and photocatalytic performance for main Ag2CO3 photocatalyst were investigated. The results showed that Ag2CO3@AgBr composite displayed much stronger and broader visible light absorption than pure AgBr and Ag2CO3. A distinct increase in both surface area and photocurrent density for Ag2CO3@AgBr was observed. Under visible light (400 nm < λ < 660 nm) irradiation, the photocatalytic activity test in degradation of methyl orange (MO) dye showed that Ag2CO3@AgBr showed excellent photocatalytic activity and the degradation rate constant over Ag2CO3@AgBr (0.209 min-1) was 14 times higher than that of Ag2CO3 (0.0136 min-1), 10 times faster than that of AgBr (0.0180 min-1). Moreover, in recycling photoactivity tests, AgBr and Ag2CO3 fast lost the activity, but high stabilty was obtained over Ag2CO3@AgBr. Between the AgBr shell and Ag2CO3 core, the produced intimate Ag2CO3/AgBr interface with matched band-gap structure largely promoted the transfer of photogenerated electrons and holes. Moreover, the AgBr shell could effectively inhibit the dissolution of Ag2CO3 in aqueous solution, resulting in extremely high stability.
-
Keywords:
- Ag2CO3 /
- AgBr /
- Heterostructure /
- Photocatalytic activity and stability /
- Visible light
-
质量轻且具有良好密封性的铝箔,广泛应用于电子、仪表、食品、包装、建筑等领域,成为工业生产和日常生活中不可缺少的材料,实际应用对铝箔的力学性能和表面等质量提出了更高的要求,希望性能更好、质量更高、成品率更高[1-4]。应用在电子、建筑等领域的铝箔,大多是99.0%~99.5%的工业纯铝;应用在铝电容器的铝箔,则是纯度超过99.9%的高纯铝,所以在市场上直接采购到的铝箔,无法直接应用于电容器中,需要采用合适的方法来制备高纯铝。目前尽管我国在全球铝电容器制造中占据重要地位,但是专用于电容器的铝箔材料质量却较为一般,无论是微观组织结构、力学性能,还是其表面质量,与国际先进生产制备技术仍有较大差距。在实际工业生产制备中,多是采用向纯铝中添加部分化学元素,通过改变合金成分,提高纯铝铝箔性能,从而提高纯铝铝箔生产质量。为进一步提升铝箔的质量特别是综合力学性能,多通过增加合金元素例如Cu来提升铝箔坯料性能[5-10]。为进一步明确Cu对电容器用铝箔坯料的影响,推动我国铝箔生产质量的提高,将Cu熔入纯铝中,重点探讨不同的添加量对铝箔坯料组织影响,并分析对力学性能影响,最终总结经验指导生产和研究。
1 试验材料与试验方法
试验所用的原始材料为1A99工业纯铝,对应美国标准(AA)牌号为1 199 Aluminum[11],具体的化学成分如表 1所列。
表 1 1A99工业纯铝的化学成分Table 1. Chemical compositions of 1A99 commercially pure aluminium
因为少量元素与微量元素总体占比较低,并不会对试验结果产生明显影响,可以正常试验。
将试验材料通过感应加热机,加热到720 ℃高温使其充分熔化,保温30 min处理后,分别向熔化金属中加入Al总用量分别为0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%(质量分数)的纯Cu,充分搅拌后,维持在720 ℃温度保温10 min,精炼处理后,将析出熔渣去除,将熔化合金注入磨具内。静置一段时间,使金属冷却到室温,每组分浇注5份样品,并以机械将其轧制成厚度为6 mm的铝箔坯料,然后轧制成2.5 mm厚的铝箔坯料,接着轧制成1.25 mm,最后将铝箔(坯料)轧制成0.6 mm厚度。分别将制成的铝箔坯料放置于370 ℃环境中,保温6 h后,随炉冷却,退火操作后获得最终产物,为了探究退火温度对其组织性能的影响,增加一组加热温度325 ℃,保温6 h,随炉冷却的样。
为充分检测在纯铝中加入Cu元素制成的铝箔组织变化与力学性能,采用由日立集团提供TM4000PlusII台式显微镜,对铝箔坯料观察其退火前后显微组织。力学性能则是由苏州检卓仪器提供的SHK-A101材料试验机,针对铝箔坯料在退火处理前后变化完成性能测试。
其操作流程为:先通过铝箔剪切器对铝箔进行剪切,保证切口光滑,以长170 mm、宽15 mm的试样为准,将材料试验机对铝箔样品进行夹紧,以1 mm/min的速度进行匀速拉伸,在位移时记录样品的载荷变化,在样品被彻底拉断后停止记录。同时,应用CHANNEL 5.0,对本试验测得信息进行数据分析,提升数据研究质量。因为本试验仅是添加微量的Cu,所以没有特殊情况,仅以“添加”与“未添加”进行描述。
2 试验结果分析
2.1 纯铝铝箔坯料组织观察
通过光学显微镜对退火处理后未添加与添加不同Cu含量的铝箔坯料显微组织进行观察,并进行对比,研究具体组织变化。图 1是未添加Cu的铝箔坯料显微组织照片,对于未加入Cu元素的工业纯铝,退火后,工业纯铝组织中晶粒比较粗大,平均晶粒大小在50 μm以上,同时晶粒大小分布不均匀。
图 2所示为不同Cu添加量铝箔坯料显微组织照片。从图 2(a)到图 2(e),随着铜添加量增加,轧制铝箔坯料组织中晶粒有变小和均匀化趋势,且观察到第二相粒子均匀分布于晶界及其附近区域[12-15],将纯铜添加至工业纯铝内,在高温作用下,Cu会与α-Al固溶体充分结合,产生铜铝合金。而剩余Cu则会在高温下,与Al进一步反应,产生第二相化合物CuAl2从Al基体中析出。观察已加入Cu元素的铝箔坯料组织,强化相晶粒规格较小,并以等轴方式均匀,使纯铝铝箔坯料具有均匀的组织,稳定提升纯铝显微组织综合性能。
对比图 2(e)与图 2(f),添加0.5%和0.6%纯Cu的铝箔坯料组织中平均晶粒大小都约为10 μm,添加的纯Cu增加0.1%,但铝箔坯料组织中晶粒细化不明显,晶粒的均匀性也没有明显均匀化趋势,所以,轧制纯铝铝箔坯料中选择添加0.5%的纯Cu获得更理想的显微组织。
2.2 Cu对再结晶晶粒影响
对于0.6 mm厚度的铝箔坯料,在退火处理时,除原本的370 ℃外,增设1组325 ℃作为对照组,如图 3所示,未添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板,其晶粒并没有过于明显的边界波动特征,但是添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板,其晶粒则可以观察到明显的波动特征,尤其是边部周围,波动特征会更为明显。这可能由于在温度的影响下,纯铝冷轧板会获得更高的变形率,添加Cu后,会使加工硬化率得到进一步提升。在325 ℃条件下,进行6 h退火处理,未添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板并没有完全完成再结晶过程,应用显微镜仍可以观察到部分区域存在纤维组织, 而其表面位置则具有最多的纤维组织。
但是,在相同的条件下,添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板则完成了再结晶化,形成细小的等轴状晶粒, 晶粒中可以明显看到第二相的细小弥散。在结束370 ℃×6 h退火处理后,未添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板,应用显微镜可以观察到,其平均晶粒规格约在51.2 μm, 而且晶粒也不是完全转化成等轴晶,长轴与短轴之比约为1.87,晶粒规格并不均匀,其数量保持正态分布,即晶粒规格在40~50 μm数量最多,其他规格的晶粒数量相对较少。添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板的平均晶粒规格约为30.4 μm,而且晶粒基本为等轴晶,长轴与短轴之比约为1.33,晶粒规格同样保持正态分布,但是不同规格的晶粒数量分布相对集中,规格在20~30 μm的数量最多。在退火之后,再次结晶化的晶粒规格明显下降,有可能是添加Cu的纯铝冷轧板的冷轧晶粒规格偏小,存在一定的晶界波动,这导致原本较小的晶界面积获得显著提升,使晶界周边存在较多的位错塞积,造成晶格畸变概率明显提升,形核区域也有所增加,在这种条件下,形核率得到有效提升,再结晶速度加快,晶粒规格也随之降低。
2.3 Cu对纯铝铝箔晶粒与组织影响分析
通过光学显微镜对退火处理前后的铝箔显微组织以0.8 μm进行细致观察,并将两者进行对比,研究具体晶粒与组织影响。对于未加入Cu元素的工业纯铝,在退火操作处理后,具有较大规格的晶粒,其数量较多,平均晶粒规格在3.07 m左右,同时晶粒大小并不均匀,这种材料应用于铝电容器的阳极铝箔的制备环节,难以保证拥有良好成品质量,所以需要对其展开进一步的研究[5-6]。将Al总用量的0.5%纯铜添加至工业纯铝内,在700 ℃的高温作用下,Cu会和固溶体充分结合,产生铜铝合金,使纯铝的性能得到稳定提升;而剩余Cu则在高温影响下,与Al进一步发生反应,产生第二相化合物,从Al基体中析出,保证Al的纯度不受影响。观察已加入Cu元素的工业纯铝,强化相晶粒规格明显下降,大多数的晶粒规格较小,其平均晶粒规格在2.65 m左右,并以等轴方式均匀分布,这种变化使纯铝拥有均匀的组织结构, 稳定提升纯铝显微组织的多方面能力,从而提高纯铝的综合性能。而且,向纯铝加入Cu,强化相生成速度加快,在相同处理条件下,添加Cu的纯铝比未添加Cu的纯铝拥有更多强化相。大量强化相有效提高材料应用强度,提高纯铝铝箔实用性。从Al基体中获得的,其拥有可溶性,可以溶在合金中,让纯铝拥有一定量的合金,从而达到强化性能的效果,可以稳定提升合金抗拉性能,提高材料应用质量。所以,将Al总用量的0.5%纯铜作为添加物,加入工业纯铝中,可以使纯铝内部拥有较多、较大规格的晶粒数量有效缩减,以较小规格的晶粒维持纯铝组织结构稳定性,并有效提高组织均匀性,更符合工业生产需求,这也是我国在工业制备纯铝的主要研究方向。
2.4 Cu对纯铝铝箔力学性能影响
2.4.1 退火前抗拉强度与伸长率分析
图 4所示为不同Cu添加量的铝箔坯料抗拉强度曲线图,本试验将6.0 mm厚度铝箔坯料轧制成0.6 mm厚度铝箔,经过4道次轧制工序,组织内部晶粒在轧制力影响下充分破碎,大尺寸晶粒变为小晶粒,一定程度上提升了铝箔抗拉性能。对铝箔坯料展开力学性能方面测试,将数据收集并整理后,分析得出,铝箔在没有添加纯铜且未进行退火处理前,其抗拉强度为145.7 MPa,伸长率为4.3%;在纯铝中加入纯铜制成合金后,产生强化相,稳定提升铝箔力学性能,随着纯铜添加量的增加,铝箔坯料的抗拉强度增加,纯铜添加量为0.5%时,抗拉强度提升到219.3 MPa,上升幅度为50.5%,Cu元素会使Al晶粒组织细化,并保持良好均匀性,稳定提高铝箔抗拉性能。与此同时,随着含Cu添加量的增加,铝箔坯料的塑性却明显下降,纯铜添加量为0.5%的铝箔坯料伸长率缩减至1.8%,下降了54.3%。
2.4.2 退火后抗拉强度与伸长率分析
退火前,铝箔坯料经过了多道工序反复处理,铝箔坯料组织晶粒充分破碎,从而使晶粒进一步缩小,晶粒均匀性增加;退火处理后,晶粒均匀性进一步改善。与此同时,铝箔坯料的内应力增加、塑性降低,如图 5所示,塑性降低会影响铝箔后续轧制的进行。为使后续轧制道次顺利进行,提高铝箔的成品率和质量,需要对铝箔进行退火处理,使铝箔内部晶粒实现再结晶,消除加工硬化,降低内应力,恢复铝箔的塑性。作为处理代价,此时会使铝箔的抗拉性能降低。退火处理后,铝箔坯料抗拉性能大幅度降低,含Cu量0.5%的铝箔坯料的抗拉强度为100.2 MPa,比退火前下降54.3%;伸长率大幅度提升至17.4%,比退火前上升667%。
向纯铝中加入纯铜,Cu元素会于位错周边大量聚集,使位错产生钉扎效应,让原本活跃的晶界迁移行为产生阻滞反应,并有效阻碍晶粒再结晶,限制其进一步长大。Cu在高温作用下,会与Al产生CuAl2合金相,有序分散至合金组织内[16-20]。弥散对于合金有强化作用,从而提高铝箔的抗拉性能,Cu添加量为0.5%的铝箔坯料退火后的抗拉强度为100.2 MPa,未加入Cu的铝箔坯料退火后的抗拉强度为53.1 MPa,上升幅度为88.8%。Cu添加量0.5%的铝箔坯料的伸长率为17.4%,未加Cu的铝箔坯料退火后的伸长率为28.4%,下降幅度降为38.7%。
3 结论
1)在纯铝中加入Cu,可以使组织细化,缩减晶粒规格,有效提升组织均匀性。
2)向纯铝加入Cu,使强化相生成速度加快,大量强化相可有效提高材料应用强度,提高纯铝铝箔实用性。从Al基体中获得CuAl2,其拥有可溶性,在合金中拥有强化效果,可以稳定提升合金抗拉性能。
3)经过退火处理,CuAl2依然起到加强弥散强化效果,可以大幅度提升铝箔抗拉性能,同时获得良好的塑性。
4)将0.5%纯铜作为添加物,加入工业纯铝中,可以使纯铝内部较大规格的晶粒有效缩减,并有效提高组织均匀性,更符合工业生产需求。
在实际纯铝铝箔生产中,可以适当添加Cu,用于提升铝箔组织均匀度与抗拉性能。
-
-
[1] YU C L, BAI Y, HE H B, et al. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic performance of rod-shaped Pt/PbWO4 composite microcrystals[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36:2178-2185. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)61009-9
[2] YU C L, LI G, KUMAR S, et al. Stable Au25(SR)18/TiO2 composite nanostructure with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 17(4): 2847-2852.
[3] 薛霜霜, 何洪波, 吴榛, 等.研磨-焙烧法制备BiOI/BiOBr异质结光催化剂及其光催化性能[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2017, 8(1):86-93. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201701015 [4] LI J D, YU C L, FANG W, et al. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic performance of heterostructured AgCl/Bi2WO6 microspheres[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36: 987-993. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)60849-X
[5] YU C L, ZHOU W Q, ZHU L H, et al. Integrating plasmonic Au nanorods with dendritic like α-Bi2O3/Bi2O2CO3 heterostructures for superior visible-light-driven photocatalysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 184: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.026
[6] 魏龙福, 余长林, 陈建钗, 等.水热法合成Ag2CO3/ZnO异质结复合光催化剂及其光催化性能[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2014, 5(1): 47-53. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201310021 [7] YU C L, ZHOU W Q, LIU H, et al. Design and fabrication of microsphere photocatalysts for environmental purification and energy conversion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 287: 117-129. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.112
[8] 何洪波, 薛霜霜, 余长林.钨基半导体光催化剂研究进展[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2015, 6(5): 32-39. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201505007 [9] ASAHI R, MORIKAWA T, OHWAKI T, et al. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5528): 269-271. doi: 10.1126/science.1061051
[10] YU C L, FAN C, MENG X J, et al. A novel Ag/BiOBr nanoplate catalyst with high photocatalytic activity in the decomposition of dyes[J]. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 2011, 103(1): 141-151. doi: 10.1007/s11144-011-0291-6
[11] ISHIKAWA A, TAKATA T, KONDO J N, et al. Oxysulfide Sm2Ti2S2O5 as a stable photocatalyst for water oxidation and reduction under visible light irradiation (λ≤650 nm)[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(45): 13547-13553. doi: 10.1021/ja0269643
[12] ZOU Z G, YE J H, SAYAMA K, et al. Direct splitting of water under visible light irradiation with an oxide semiconductor photocatalyst[J]. Nature, 2001, 414(6864): 625-627. doi: 10.1038/414625a
[13] TSUJI I, KATO H, KUDO A. Visible-light-induced H2 evolution from an aqueous solution containing sulfide and sulfite over a ZnS-CuInS2-AgInS2 solid-solution photocatalyst[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2005, 117(23): 3631-3634. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3757
[14] WANG X C, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(1): 76-80. doi: 10.1038/nmat2317
[15] XIANG Q, YU J J. Graphene-based photocatalysts for hydrogen generation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4(5): 753-759. doi: 10.1021/jz302048d
[16] ONG W J, GUI M M, CHAI S P, et al. Direct growth of carbon nanotubes on Ni/TiO2 as next generation catalysts for photoreduction of CO2 to methane by water under visible light irradiation[J]. Rsc Advances, 2013, 14(3): 4505-4509. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48009-1_9
[17] TANG J T, GONG W, CAI T J, et al. Novel visible light responsive Ag@(Ag2S/Ag3PO4) photocatalysts: synergistic effect between Ag and Ag2S for their enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(8): 2543-2547. doi: 10.1039/c2ra22245k
[18] YI Z G, YE J H, KIKUGAWA N, et al. An orthophosphate semiconductor with photooxidation properties under visible-light irradiation[J]. Nature Materials, 2010, 9(7): 559-564. doi: 10.1038/nmat2780
[19] BI Y P, OUYANG S X, UMEZAW A N, et al. Facet effect of single-crystalline Ag3PO4 sub-microcrystals on photocatalytic properties[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(17): 6490-6492. doi: 10.1021/ja2002132
[20] BI Y P, OUYANG S X, CAOJ Y, et al. Facile synthesis of rhombic dodecahedral AgX/Ag3PO4 (X=Cl, Br, I) heterocrystals with enhanced photocatalytic properties and stabilities[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011, 13(21): 10071-10075. doi: 10.1039/c1cp20488b
[21] YANG X F, CUI H Y, LI Y, et al. Fabrication of Ag3PO4-graphene composites with highly efficient and stable visible light photocatalytic performance[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(3): 363-369. doi: 10.1021/cs3008126
[22] TANG J T, LIU Y H, LI H Z, et al. A Novel Ag3AsO4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(48): 5498-5500. doi: 10.1039/c3cc41090k
[23] LI J D, FANG W, YU C L, et al. Ag-based semiconductor photocatalysts in environmental purification[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 358: 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.139
[24] YANG J H, WANG D, HAN H X, et al. Roles of cocatalysts in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(8): 1900-1909. doi: 10.1021/ar300227e
[25] WANG W S, DU H, WANG R X, et al. Heterostructured Ag3PO4/AgBr/Ag plasmonic photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under visible light[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(8): 3315-3321. doi: 10.1039/c3nr00191a
[26] YU C L, LI G, KUMAR S, et al. Phase transformation synthesis of novel Ag2O/Ag2CO3 heterostructures with high visible light efficiency in photocatalytic degradation of pollutants[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(6): 892-898. doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.6
[27] LI J D, WEI L F, YU C L, et al. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/Ag2CO3 photocatalyst and its visible light photocatalytic activity[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 358: 168-174. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.007
[28] YU C L, WEI L F, ZHOU W Q, et al. Enhancement of the visible light activity and stability of Ag2CO3 by formation of AgI/Ag2CO3 heterojunction[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 319: 312-318. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.05.158
[29] SONG S Q, CHENG B, WU N S, et al. Structure effect of graphene on the photocatalytic performance of plasmonic Ag/Ag2CO3-rGO for photocatalytic elimination of pollutants[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 181: 71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.034
[30] CAMPBELL C T, PAFFETT M T. The interactions of O2, CO and CO2 with Ag (110)[J]. Surface science, 1984, 143(2): 517-535. http://www.nature.com/subjects/theoretical-chemistry/research.atom
[31] BIGELOW R W. An XPS study of air corona discharge-induced corrosion products at Cu, Ag and Au ground planes[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1988, 32(1): 122-140. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238140768_Corona_Corrosion_of_Aluminum_in_Air
[32] XU C W, LIU Y Y, HUANG B B, et al. Preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic properties of silver carbonate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(20): 8732-8736. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.05.060
[33] YU C L, YANG K, SHU Q, et al. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic performance of Mo-Doped ZnO photocatalysts[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2012, 55(9): 1802-1810. doi: 10.1007/s11426-012-4721-8
[34] WANG P, HUANG B B, QIN X Y, et al. Ag@AgCl: A highly efficient and stable photocatalyst active under visible light[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(41): 7931-7933. doi: 10.1002/anie.v47:41
[35] YIN L, WANG Z, LU L, et al. Universal degradation performance of a high-efficiency AgBr/Ag2CO3 photocatalyst under visible light and an insight into the reaction mechanism[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 39(6): 4891-4900. doi: 10.1039/C5NJ00385G



 下载:
下载: