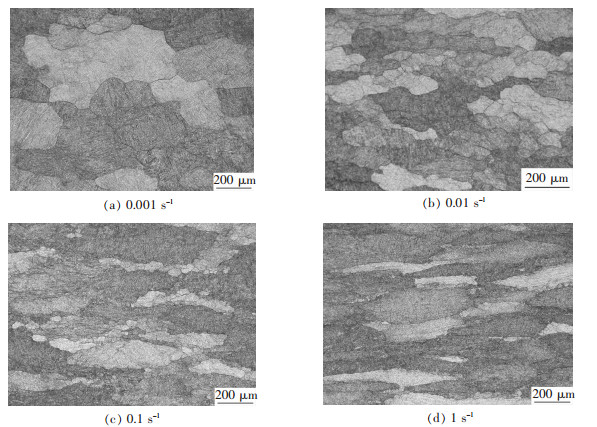
High temperature deformation behavior of BT25 titanium alloy
-
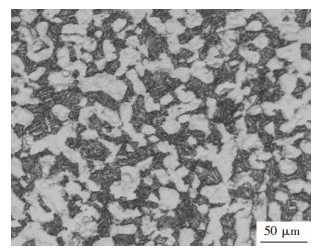
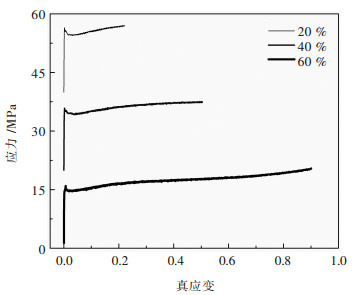
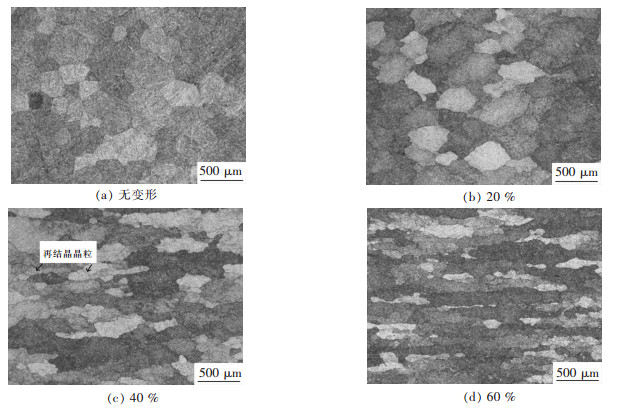
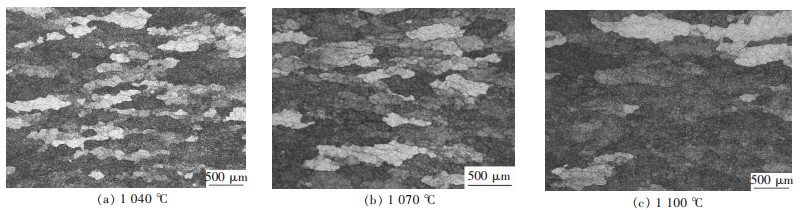
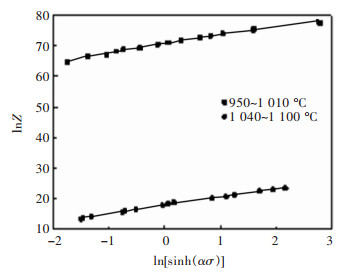
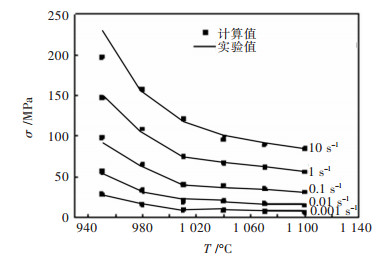
摘要: 对BT25钛合金在温度为950~1 100 ℃,应变速率为0.001~10 s-1条件下的高温变形行为进行了研究,分析了热力学参数对流变应力和微观组织的影响,并以Arrhenius方程为基础,构建了本构方程,最后进行了验证.结果表明:BT25合金在相同温度和应变速率下变形,变形量越大,动态再结晶越充分并细化了晶粒.相同变形量,变形温度越低,应变速率越高,动态再结晶晶粒尺寸越细小;流变应力随应变速率的增加而增加,随变形温度的升高而减小;BT25合金在α+β两相区(950~1 010 ℃)Q=763.51 kJ/mol,β相区(1 040~1 100 ℃)Q=231.36 kJ/mol.Abstract: The high temperature behavior of BT25 titanium alloy was investigated from 950 ℃ to 1 100 ℃ and strain rate range 0.001 s-1 to 10 s-1. The effects of thermodynamic parameters on flow stress and microstructure were analyzed. Based on the arrhenius equation, the constitutive equation was constructed and validated. The results show that at the same temperature and strain rate, the larger the deformation, the more the dynamic recrystallization is. At the same deformation degree, the lower the deformation temperature and higher the strain rate, thefiner the dynamic recrystallization grain size is. The flow stress increases with the increase of strain rate, and decreases with the rising deformation temperature. The deformation activation energy of BT25 titanium alloy is 763.51 kJ/mol in α+β phase region(950~1 010 ℃) and 231.36 kJ/mol in β phase region(1 040~1 100 ℃).
-
Keywords:
- BT25 titanium alloy /
- deformation parameter /
- dynamic recrystallization /
- flow stress
-
0 前言
近年来随着越来越多的微细粒嵌布矿石被开发和利用, 以及钨、锡、钽铌等脆性易过粉碎矿物在处理过程中产生的大量微细物料, 研究表面性质对细粒重选的影响已引起人们极大的关注。从理论上说, 作用在粒径为d的矿粒的质量力Fm∝d3, 而作用在矿粒上界面力Fs∝d2, 也就是说Fs/Fm∝1/d, 可见粒度减小, 界面力的作用将急剧显现出来。因而, 在微细粒矿物重选中, 利用表面性质来强化微细物料的分选已成为一个重要的研究方向。
有关这方面的研究, 国内外许多学者都作了一些工作, 取得了一些进展, 但也还存在许多问题有待进一步完善。例如, 有关pH值、金属离子和分散剂对分选的影响, 不同的研究者曾得出不同的结论。又如关于表面电性的影响机理, 有强调矿粒同分选床面界面力作用的, 有强调矿粒间界面力作用的, 还有综合两种作用力的等等〔1〕。笔者借用前人得出的一些指导性原则, 重点从床面材质入手, 大胆进行工业试验, 并取得了较好的效果。
1 试验条件
1.1 矿石性质
宜春钽铌矿属钠长石化-锂云母化花岗岩型含钽、铌、锂、铷、铯等多种有用金属的大型矿床, 钽、铌矿物主要为富锰铌钽铁矿、细晶石、含钽锡石, 脉石矿物主要为长石、石英、锂云母。钽铌矿物硬度5.5~6, 密度5.5~6.4g/cm3, 性脆, 磨矿过程中易过粉碎。长石密度为2.65 g/cm3, 锂云母密度为2.87g/cm3, 属韧性矿物, 难磨。且锂云母矿物含量达20%以上。钽铌矿物在0.4mm开始出现单体, 至0.1mm时单体达95%左右。由于钽铌矿物与锂云母矿物的可磨性差异, 导致磨矿过程中新生大量-0.038mm粒级微细矿粒, 造成选矿经济技术指标难以提高。
试验选用两段球磨排矿与Ø1.0m螺旋分级机溢流合并为原矿, 经Ø1.2m螺旋溜槽处理, 得出的中矿为试验摇床的给矿, 属不脱泥直接处理工艺。现场生产局部工艺流程见图 1。
1.2 试验设备
试验采用现场生产中使用的6-S型摇床。其工艺参数为:冲程16mm, 冲次310 r/min。
床面采用自制的新型材料床面, 床面结构为单波纹形床面。
床面是由无机化工原料制造而成, 制造工艺简单、费用很低, 每台床面造价为300元。
床面制作过程为:①废旧床面处理。②制床面压模具。③在处理过的旧床面上, 利用压模具生产新床面。④新床面表面处理。
2 试验结果及分析
2.1 试验现象及观察
这种新型床面在现场生产中投入使用以来, 运行正常, 各项机械性能与普通玻璃钢床面没有什么差异, 正常运转已达3个月。观察床面精矿输送情况发现, 该新型床面比普通床面, 其钽铌精矿的输送速度明显加快, 精矿的输送能力加强。
其次, 原摇床正常情况下几乎看不到较高品位精矿, 采用新型床面后, 试验中能产出部分较高品位精矿。精矿端, 各级密度差较大的矿物分带明显, 有利于最终精矿及复选精矿的接取。
2.2 试验数据及分析
现场测定选别指标详见表 1。从表 1结果可以推算出-0.038mm粒级钽铌精矿粒级回收率为61.75%。
表 1 试验测定指标 %
试验表明:当处理试验矿样-0.038mm粒级钽铌品位为0.0384%时, 可获得尾矿-0.038mm粒级钽铌品位0.0150%, 钽铌精矿-0.038mm粒级回收率61.75%的较好指标。
3 选别机理初探
新型床面选别钽铌矿物的分选机理, 与普通床面的选别机理相比, 在床面运动特性、操作参数的影响等方面是相同的; 它们的差异主要体现在床面材质不同而引起的床面表面电性的差异而产生的选别差异〔2〕。
3.1 新型床面对钽铌矿物的静电吸附作用
试验过程中, 可发现在床面覆盖矿浆部分, 有薄薄一层黑色的表面沉积物, 将这种沉积物进行化学分析, 其主要成分:(TaNb)2O53.21%、Fe2O390.20%。由于新采用的床面没有磁性, 成分物质不具磁性, 可以得出:新型床面对微细粒钽铌矿物存在着很强的表面静电吸附。
3.2 新型床面对脉石矿物的静电排斥作用
在新型床面的制造材料中加入了大量的经选别钽铌精矿的尾矿(主要为长石、石英、锂云母等脉石矿物), 使得床面具有更强的同性静电排斥作用, 即对微细粒脉石矿物床面具有更强的静电排斥作用。
3.3 表面吸附沉积物的归队分选
床面上的吸附沉积物在粗粒脉石矿物的摩擦作用下, 重新归队分选, 提高了微细粒钽铌矿物的回收效果。
被吸附沉积下来的钽铌矿物, 被吸附前粒度是很微细的, 被吸附沉积后, 整体性较好; 在粗粒脉石的摩擦作用下脱离床面, 重新进入床面分选。
相对较易磨损的床面特性, 对吸附沉积下来的钽铌矿物重新入选提供了有利条件。
4 结语
(1) 新型床面由于采用了新型材质, 使其表面对钽铌矿物具有较强的静电吸附作用的同时又具有对脉石矿物较强的静电排斥作用, 因而强化了微细粒钽铌矿物的分选效果。
(2) 在生产现场试验中, 证实了这种新型床面选别钽铌矿物的优势, 取得了钽铌精矿-0.038mm粒级回收率达61.75%的选别指标。
(3) 试验在现场进行的不脱泥直接处理钽铌分选工艺, 具有一定的发展前景, 对微细粒钽铌的回收提供了很好的实例。
-
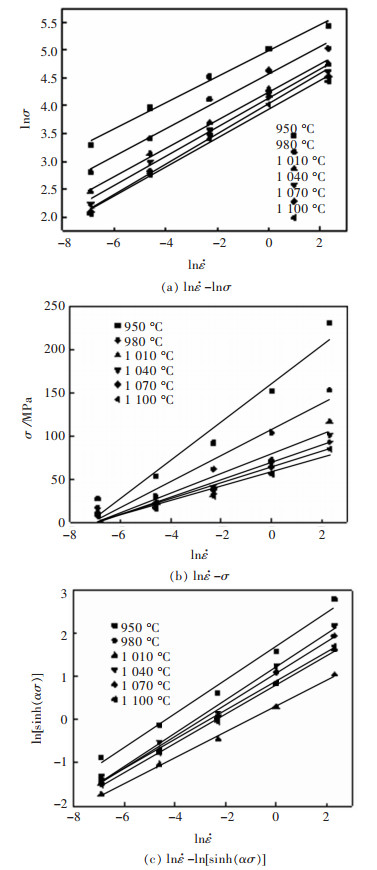
图 6 ${\rm{ln}}\dot \varepsilon - {\rm{ln}}{\rm{ \mathsf{ σ} }} $、${\rm{ln}}\dot \varepsilon - {\rm{ \mathsf{ σ} }} $和${\rm{ln}}\dot \varepsilon - {\rm{ln}}\left[{{\rm{sinh}}\left( {\alpha {\rm{ \mathsf{ σ} }} } \right)} \right]$关系曲线
Fig 6. ${\rm{ln}}\dot \varepsilon - {\rm{ln}}{\rm{ \mathsf{ σ} }} $、${\rm{ln}}\dot \varepsilon - {\rm{ \mathsf{ σ} }} $和${\rm{ln}} - {\rm{ln}}\dot \varepsilon \left[{{\rm{sinh}}\left( {\alpha {\rm{ \mathsf{ σ} }} } \right)} \right]$ relationship lines
表 1 BT25合金的化学成分/(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of BT25 titanium alloy /(mass fraction, %)
元素 Al Zr Sn Mo W Si Cr Cu Fe C O N H Ti 含量 6.81 2.25 2.00 2.10 0.94 0.20 0.01 0.02 0.05 0.02 0.15 0.15 0.001 余量 表 2 BT25钛合金在不同变形条件下的修正稳态流变应力/MPa
Table 2 Corrected saturation stress of BT25 alloy under different deformation conditions
${\dot \varepsilon }$/s-1 T/℃ 950 980 1 010 1 040 1 070 1 100 0.001 26.79 16.54 11.60 9.32 8.03 7.76 0.01 52.56 30.31 23.07 19.95 16.75 15.94 0.1 91.71 61.29 39.97 35.23 32.58 29.86 1 151.54 103.21 73.09 69.01 63.96 55.71 10 229.91 152.80 116.55 100.56 92.58 84.51 表 3 m,β,α,n常数值
Table 3 m, β, α, n constant values
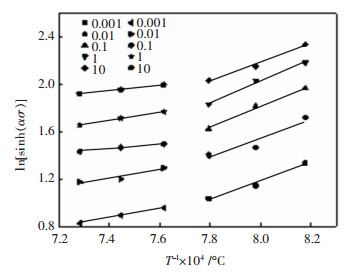
T/℃ m β α=β/m n 950~1 010 0.066 942 4.116 382 9 0.016 262 2 2.984 068 1 040~1 100 0.108 344 4 3.785 128 47 0.028 623 7 2.727 527 表 4 c,Q,lnA常数值
Table 4 c, Q, lnA constant values
T/℃ c Q /(kJ·mol-1) lnA 950~1 010 3.077 474 763.507 18 70.533 9 1 040~1 100 1.020 228 231.357 85 17.892 1 -
[1] 田飞, 曾卫东, 马雄, 等.物理分析法与金相法测定BT25钛合金相变点[J].材料热处理学报, 2011, 32(5):1-5. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_jsrclxb201105001 [2] 王杨, 曾卫东, 马雄, 等. BT25钛合金在两相区变形过程中的显微组织定量分析[J].中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(7):1861-1865. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97361X/201307/47078230.html [3] MA X, ZENG W D, TIAN F, et al. Modeling constitutive relationship of BT25 titanium alloy during hot deformation by artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering Perormance, 2012, 21(8):1591-1597. doi: 10.1007/s11665-011-0061-7
[4] 蔡钢, 雷旻, 万明攀, 等.加热速度对BT25钛合金α→β相变的影响[J].稀有金属, 2016, 40(1):8-13. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_rcl200904007 [5] 张喜燕, 赵永庆, 白晨光.钛合金及应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2005. [6] 胡赓祥, 蔡珣, 戎咏华.材料科学基础[M].上海:上海交通大学出版社, 2010. [7] 戚运莲. Ti600高温钛合金的热变形行为及加工图研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10699-2007058341.htm [8] 王方, 李鑫, 鲁世强, 等.变形态Ti40合金的高温流变应力模型研究[J].锻压技术, 2012, 37(2): 134-138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJE201202035.htm [9] SHI-QIANG L U, OUYANG D L, CUI X, et al. Dynamic recrystallization behavior of burn resist ant titanium alloy Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(4):1003-1010. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64197-3
[10] 沈昌武. TA15、TC11钛合金热变形材料本构模型研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10699-2007056983.htm [11] RAO K P. Development of constitutive relationships using compression testing of a medium carbon steel[J]. Journal of Engineering Materials & Technology, 1992, 114(1):116-123. doi: 10.1007/s12598-011-0202-z
[12] 王琪, 文智, 王斌, 等.粉末冶金TA15钛合金的高温塑性变形行为[J].粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2013, 18(5):647-654. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/3295676e0b4c2e3f572763e6.html [13] ZENER C, HOLLOMON J H. Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1944, 15(1):22-32. doi: 10.1063/1.1707363
[14] MALLOL J, SARRAGA M C, BARTOLOME M, et al. Hot working behavior of near-α alloy IMI834 [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2005, 396(1/2):50-60. http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/handle/00001903-5/271927
[15] 周伟, 葛鹏, 赵永庆, 等. Ti-5553合金的高温变形行为[J].中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(增刊1):11-13. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92850X/201208/43111732.html [16] 孙二举, 边丽虹, 刘东, 等.热加工条件下Ti60高温钛合金的本构关系[J].航空材料学报, 2012, 32 (3): 40-45. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_hkclxb201203007 [17] CHEN H S, LIU X H, LIU G F, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo titanium alloy[J].Rare Metal Materials & Engineering, 2016, 45(4):901-906. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875537216300972




 下载:
下载: