Molecular dynamics simulation of adsorption of polyacrylic acid on surface of dicalcium silicate
-
摘要: 采用分子动力学(MD)方法,模拟研究了聚合物抑制剂聚丙烯酸与β-硅酸二钙(110)晶面的相互作用行为。结果表明:聚丙烯酸与β-硅酸二钙(110)晶面间结合能为负值,在模拟范围内结合能随聚丙烯酸聚合度的增加而增大,聚丙烯酸分子能较好地吸附在β-硅酸二钙(110)表面。通过体系中各种相互作用、径向分布函数以及吸附构象图分析,发现聚丙烯酸主要是通过库仑静电作用吸附在β-硅酸二钙(110)晶面上。聚丙烯酸中不同位置羧基的分子动力学模拟结果差别也很大,链端羧基波动扭转比链中端羧基强度大得多,表明中端羧基与β-2CaO·SiO2晶体的吸附比链端更牢固因而更能有效地吸附在晶面上,达到抑制熟料二次反应的作用。Abstract: The interactions between polyacrylic acid (PAA) and β-dicalcium silicate (110) crystal face were simulated by molecular dynamics(MD).The results show that the binding energy for the polyacrylic acid polymer with β-dicalcium silicate (110) crystal is negative and increases with the increasing in the degree of polymerization of polyacrylic acid within simulation range, which indicate that the polyacrylic acid can be adsorbed well on the β-dicalcium silicate crystal face. The analysis of various interactions and pair correlation functions of all systems and adsorption conformation chart indicate that binding energies are mainly determined by coulomb interaction. The results of molecular dynamics simulation of carboxyl groups at different positions of polyacrylic acid also differs greatly. The strength of torsion fluctuation of the chain end carboxyl is larger than that of the mid-chain. Both of those indicate that the mid-chain carboxyl’s adsorption with β-2CaO·SiO2 crystals is firmer than the chain end carboxyl’s adsorption with β-2CaO·SiO2 crystals, and more effective. Thus, clinker secondary reaction can be inhibited.
-
在烧结法生产氧化铝的熟料溶出过程,熟料中的硅酸二钙(β-2CaO·SiO2)(约占熟料质量的30%左右)会与铝酸钠溶液发生二次反应,使部分己溶出的A12O3和Na2O重新析出进入赤泥而造成损失[1-3]。经过长期地实践总结出了一些抑制二次反应的措施[4-7],例如低溶出温度和低苛性比溶出、适当的碳酸钠浓度、二段磨快速分离赤泥等,但是氧化铝的损失仍然很重。近年来由于使用添加剂抑制熟料溶出的方法操作简单,且抑制二次反应发生的效果良好,因而越来越受到企业及研究者的重视.
关于抑制剂的筛选及抑制机理已开展了许多研究工作[8-10],张程忠[11]等研究认为富含醚、醇、羧基等多种官能团的腐殖酸钠能有效地抑制二次反应的发生,并通过红外光谱分析研究了其抑制机理,但由于其颜色深而无法实际应用。含有羧基的聚丙烯酸与含有羟基的PEG聚合物,都具有一定程度的抑制二次反应的能力,其中含羧基的聚丙烯酸的抑制能力较含羟基的聚合物PEG强。于海燕[12]等研究了聚合物PEG在硅酸二钙界面吸附行为的热力学和电化学行为,并探讨了其抑制机理。目前关于抑制剂的研究主要是采用宏观实验的方法,研究结论主要是在实验结果的基础上进行分析、推断,无法从分子微观结构的角度揭示抑制剂的结构与性能的关系,也很难从实质上解决抑制剂在界面吸附现象的机理性问题。伴随着计算机模拟技术的发展,通过分子动力学模拟,可以直观地观察体系的微观分子水平上动态行为,国内外学者利用分子动力学模拟开展了许多有意义的研究工作[13-15]。
目前,从微观分子水平上开展熟料抑制剂抑制二次反应机理的研究报道较少[16],因此,本文选取抑制效果较好的聚羧酸类抑制剂聚丙烯酸(PAA)为研究对象,运用分子动力学(MD)方法对其在硅酸二钙晶面上的吸附行为进行微观分子水平上动态模拟,探讨聚丙烯酸分子结构及功能团与硅酸二钙之间相互作用的本质,为阐明吸附抑制机理,继而为开发更加优良的抑制剂提供理论依据。
1 模型构建与模拟方法
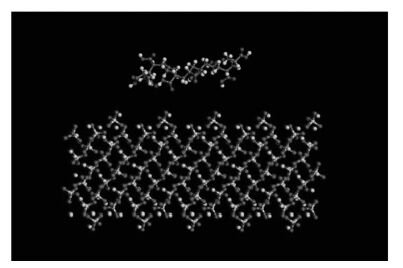
本文以Materials Studio 8.0软件为计算平台,选用COMPASS力场进行分子动力学模拟[17]。根据实验事实,采用分割切面的模式,研究PAA聚合物与β-硅酸二钙(β-2CaO·SiO2)晶体的相互作用机理。β-硅酸二钙为单斜六面体结构,晶胞属于P21/N空间群[18],晶胞参数为a=5.502Å,b=6.745Å,c=9.297Å;α=γ=90°,β=94.59°。前人研究表明[16],(110)面为β-硅酸二钙晶体的主要生长面,故在构建好的β-硅酸二钙晶体上切出(110)晶面,建立(110)晶面的超晶胞尺寸为46.694Å×43.589Å×17.698Å,含有2800个原子(O:1600;Si:400;Ca:800)。使用Amorphous Cell模块构建不同链长的聚丙烯酸链模型,对不同链模型进行能量最优化,优化后从中优选出能量最低的优势构象作为初始输入构型。将优选出的聚合物构象置于晶面上,真空薄层厚度取为3.0nm。PAA与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)面的初始构像见图 1。
本模拟实验采用总动量为0的正则(NVT)系综,COMPASS力场参数对多层不固定的硅酸二钙和聚丙烯酸进行描述;模拟中采用周期性边界条件,截断半径选择18.5Å,静电力及范德华力计算均采用Eward加和方法,各分子起始速度由Maxwell随机产生;模拟温度根据文献资料设定353K[10],选用Andersen方法控制,设定时间步长为1fs,模拟时间为200ps (前100ps用于体系平衡,后100ps为取样分析阶段),每400步记录一次体系的运动轨迹,用于平衡后体系动力学分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 聚合物与晶面相互作用的平衡
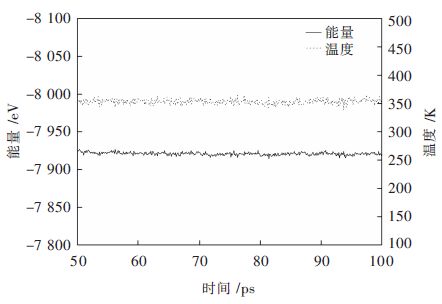
利用分子动力学模拟过程中温度和能量曲线来判别体系是否达平衡[19],以链长为10的PAA吸附模拟为例,PAA在β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面上的分子动力学模拟平衡阶段最后50ps的温度、能量波动曲线见图 2。由图 2可知,温度曲线上下波动幅度很小,近似趋于直线,表明PAA与β-2CaO·SiO2晶体组成的体系温度己达平衡。同样,从图 2中可知,能量曲线上下波动平缓,表明体系能量也已达平衡。综上所述,PAA与β-2CaO·SiO2晶体组成的体系己达平衡。
2.2 聚丙烯酸在β-硅酸二钙晶面上的相互作用能
聚合物在晶体表面的平均相互作用能Einter可表示为Einter=Etotal-(Esurface+Epolymer)[20],其中Etotal为晶体表面和聚合物的总能量,Esurface和Epolymer分别是晶体表面及聚合物的单点能。定义结合能为相互作用能的负值,即Ebinding=-Einter。结合能是衡量吸附过程中吸附强度的重要指标,若结合能为正值,表明不利于吸附过程的进行。反之结合能为负值,说明有利于吸附过程的进行。
MD模拟体系平衡后取样分析计算聚合物分子与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面相互作用的结合能、非键作用能等参数.表 1列出了不同聚合度聚丙烯酸分子与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面相互作用的能量模拟数据。由表 1可以看出,结合能均为负值,说明该结合过程放热,有利于PAA吸附在β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面上。非键作用能参数中体系范德华作用能变为正值,不利于聚合物与晶面的结合,而库仑作用能变为负值,说明库仑作用对聚合物与晶体的结合起促进作用。同时,库仑作用能变的绝对值远远大于范德华作用能变,说明体系非键作用能主要来自库仑作用能变的贡献。由结合能与非键作用能对比可以推测,PAA主要是通过聚合物与晶面间的库仑静电作用而吸附在β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面上,静电作用越大,则结合越紧密,趋近程度越大。
表 1 聚合物分子与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面相互作用的结合能和非键作用能(eV)Table 1. Binding interaction energies and non—bond interaction energies between polymers and(110)surface of β-2CaO·SiO2(eV)能量形式 不同链长的PAA 8 10 12 14 20 Etotal -6691.299 -7922.779 -6691.311 -7924.557 -7932.705 Esurface -6680.930 -7913.624 -6680.969 -7907.592 -7906.279 Epolymer -4.442 -2.341 -3.090 -2.682 -4.020 Einter -5.927 -6.813 -7.252 -14.283 -22.406 Ebinding 5.927 6.813 7.252 14.283 22.406 Enon-bond -6.882 -5.302 -10.145 -13.740 -21.473 Evdw 2.075 5.367 -2.601 -0.923 1.323 Ecoulomb -8.944 -10.660 -7.532 -12.808 -22.777 通过对比不同链长的PAA与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的结合能,可以看出随着PAA的链长增加,其结合能逐渐增强,这是由于聚丙烯酸(PAA)分子结构中含有羧酸基功能团,该功能团可通过静电吸引、离子键和氢键等多种方式与β-C2S表面直接作用而使PAA被吸附,链越长,其含有的羧酸基功能团也就越多,聚合物与晶面间的相互作用越强,越容易产生吸附。
2.3 PAA与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的径向分布函数和吸附构象
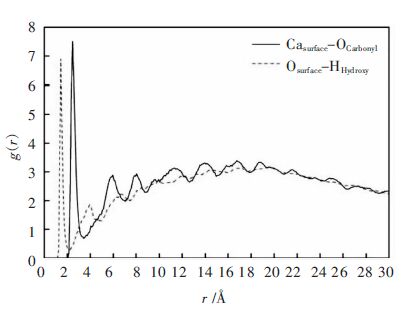
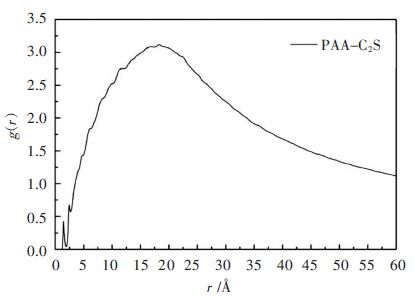
径向分布函数g(r)是反映流体微观结构特征的物理[21],其表示在一种元素周围距离为r的地方出现另一种元素的概率密度,g(r)值越大,说明一个原子与另一个原子吸引作用越强导致一个原子周围出现另一个原子的概率增加。一般来说,g(r)~r图中3.5Å以内的峰主要由化学键、氢键构成,3.5Å以外的则主要是库仑力、范德华相互作用为主。以链长为10的PAA为例,对其与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的MD模拟最终结果进行分析,得到相应的径向分布函数。图 3为晶面上O原子与聚合物中羟基H原子之间以及晶面上Ca离子与聚合物中羰基O原子之间的径向分布函数函数g(r).图 4为PAA与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面之间总的径向分布函数函数g(r)。
由图 3可以看出,Osurface-Hhydroxy曲线中聚合物在1.45Å附近出现最强峰(峰值为6.89),比O-H共价键长1.1Å略大,表明晶面上O原子与聚合物中羟基H原子之间形成了较弱的氢键。Casurface-Ocarbonyl曲线在2.45Å处有最强吸收峰(峰值为7.51),与Ca-O离子键长2.39Å相差不大,表明PAA羰基中的氧原子与β-2CaO·SiO2晶面上Ca离子之间形成了一定强度的离子键,此外,在4Å以后出现多个峰谷,可以理解为羰基O原子与多层晶体中Ca2+通过一些作用力所造成,这些作用力较弱,以库仑、范德华相互作用为主。从总的径向分布函数关系图 4可以看出,图 3中分别位于1.45Å、2.45Å处的峰在图 4中均有显示,但强度比3.5Å以外的峰要弱得多。故从整体上来看,聚合物与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的结合以库仑、范德华作用为主,与相互作用能分析结果一致。
图 5为整个体系进行MD模拟200ps得到的PAA分子与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的吸附构象。从图 5可以看出,聚丙烯酸(PAA)分子由于其羧酸基功能团中羰基O、羟基H原子与β-C2S晶面中Ca2+、O库仑静电相互作用而较好地吸附在晶面上,其中个别羰基O与晶面中Ca2+形成一定强度的离子键,而羟基H与晶面中O则形成氢键。PAA分子与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的吸附构象较好地佐证了径向分布函数分析。
2.4 PAA不同位置羧基在β-2CaO·SiO2(110)面的吸附动力学行为
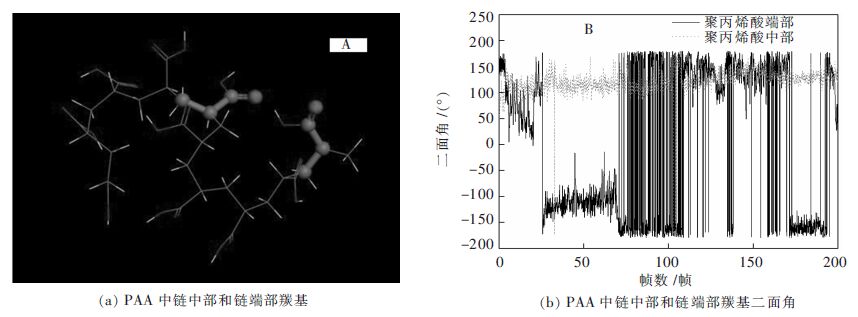
为了进一步了解聚丙烯酸中不同位置的羧基官能团在β-硅酸二钙表面上吸附情况,在MD模拟过程中,对链长为10的聚丙烯酸分子中不同位置羧基进行了分子动力学模拟分析。图 6为PAA链端、中端含羰基二面角(均以球棍模型标出其余原子以线模型显示)的角度随时间波动图(共200帧)。
由图 6可知,PAA链端二面角的振荡幅度比链中端二面角大得多,表明模拟过程中链端羧基比中端羧基波动扭转强度大。分析原因,主要是由于链端羧基较中端羧基受到的空间位阻要小,其受到的限制约束要少,在空间伸展更自由一些,从而引起更多的构象旋转。链端羧基波动扭转剧烈,导致其吸附在β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的能力降低,使得其与晶面结合不稳定,因而不能有效抑制二次反应。因此,在分子量为一定范围内时,聚合度高的聚丙烯酸因含有更多的链中端羧基会比聚合度低的抑制性能好,这与不同链长PAA与晶面相互作用能的分析结果一致,也与张程忠[11]等研究认为的抑制二次反应效果随聚丙烯酸的聚合度增加而更好的实验事实相符合。
3 结论
通过对聚丙烯酸在β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面吸附的分子动力学模拟计算,得出如下结论:
(1)聚丙烯酸与β-硅酸二钙晶体表面间的结合能均为负值,聚合物可较好的吸附在晶体表面。结合能随聚丙烯酸链增长而增加。体系结合能主要由非键作用能中的库仑静电作用提供。
(2)径向分布函数表明,β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面上O原子与聚合物中羟基H原子之间形成氢键,PAA羰基中的氧原子与晶面上Ca离子之间形成了一定强度的离子键,但两者强度比库仑、范德华作用能要弱得多。从整体上来看,聚合物与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面的结合以库仑、范德华作用为主。
(3)聚丙烯酸中不同位置羧基的分子动力学模拟差别很大,链端羧基波动扭转比链中端羧基强度大得多,说明中端羧基与β-2CaO·SiO2晶体的吸附比链端更牢固,从而达到抑制熟料二次反应的作用。
-
表 1 聚合物分子与β-2CaO·SiO2(110)晶面相互作用的结合能和非键作用能(eV)
Table 1 Binding interaction energies and non—bond interaction energies between polymers and(110)surface of β-2CaO·SiO2(eV)
能量形式 不同链长的PAA 8 10 12 14 20 Etotal -6691.299 -7922.779 -6691.311 -7924.557 -7932.705 Esurface -6680.930 -7913.624 -6680.969 -7907.592 -7906.279 Epolymer -4.442 -2.341 -3.090 -2.682 -4.020 Einter -5.927 -6.813 -7.252 -14.283 -22.406 Ebinding 5.927 6.813 7.252 14.283 22.406 Enon-bond -6.882 -5.302 -10.145 -13.740 -21.473 Evdw 2.075 5.367 -2.601 -0.923 1.323 Ecoulomb -8.944 -10.660 -7.532 -12.808 -22.777 -
[1] 陈滨,李小斌,徐华军,等. 氧化铝熟料溶出过程二次反应的热力学讨论[J].北京化工学报(自然科学版),2007,34(2):189-192. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJHY200702019.htm [2] 袁艺,项阳,黄芳,等. 铝酸盐烧结熟料溶出二次反应浅析[J].轻金属,1999(12):18-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS199912005.htm [3] LI X B, ZHAO Z, LIU G H, et.al .Behavior of calcium silicate hydratein aluminate solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2005,15 (5):1145-1149 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2349545729&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] 陈红武,周宗科.烧结法熟料溶出条件对二次反应影响分析[J].轻金属,2001(8):21-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200108003.htm [5] 陈滨,张淑英.烧结法熟料高浓度溶出过程二次反应的抑制[J].湖南工业大学学报,2011,25(3),8-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZGX201103005.htm [6] 张建.碱石灰铝土矿熟料高浓度溶出过程中二次反应的研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2008 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-2008164674.htm [7] 任根宽.二次反应对熟料中氧化铝溶出率的影响分析[J].轻金属,2007(4):16-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200704003.htm [8] 李太昌.二次反应抑制剂及其添加工艺技术研究[J].有色金属(冶炼部分),2002(1):26-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE200201007.htm [9] 任根宽.二次反应抑制剂及其添加工艺技术研究[J].轻金属,2008(5):16-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200805006.htm [10] 张程忠,于海燕,张立强,等.腐殖酸钠抑制氧化铝熟料溶出二次反应机理初探[J].化工学报,2008,59(2):526-530. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ200802042.htm [11] 张程忠.抑制熟料溶出二次反应添加剂的研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2007. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2609144788&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] YU H Y,PAN X L,DING T T,et.al.Electrochemical study on adsorption behavior of surfactants at β-2CaO?SiO2/NaAlO2 interface[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2013,8(23):214-219. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2044104895&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] Peng Xuan.Molecular simulations of the purification of toxic benzene gas on single-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2014,30(11):2000-2008.
[14] 倪哲明,夏明玉,施炜,等.糠醛在Pt(111)表面的吸附和脱碳反应[J].物理化学学报,2013, 29 (9):1916-1922. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLHX201309010.htm [15] MEI Q Q,HOU M Q,NING H, et.al.Microstructure and intermolecular interactions of [Bmim][PF6]+Water+ Alcohol Systems: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study[J].Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2014, 30 (12):2210-2215. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2369552101&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[16] 于海燕,王波,潘晓林,等.聚乙二醇在硅酸二钙表面吸附的分子动力学模拟[J].化工学报,2013,64(3):943-948. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201303023.htm [17] Sun H,Ren P,Fried J.R.The COMPASS Force Field:Parameterization and Validation for polyphosphazenes.Computational and Theoretical Polymer Science, 1998,8(1/2):229 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2024955711&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[18] K.H.Jost. B.Ziemer R.Seydel. Redetermination ofthe Structure of β-Dicaleium Silicate[J],Acta Cryst. 1997.B33:1696-1700.
[19] 黄玉成,胡应杰,肖继军,等.TATB基PBX结合能的分子动力学模拟[J].物理化学学报,2005,21(4):425-429. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLHX200504015.htm [20] 张曙光,王风云,雷武,等.水溶性聚合物与硬石膏晶体相互作用的分子动力学模拟[J].化学学报,2007,65(20):2249-2256. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB200720007.htm [21] 杨小震,分子模拟与高分子材料.北京:科学出版社,2002.



 下载:
下载: