Abnormal aggregation of infrared high temperature points in the process of siltstone failure
-
摘要: 临破裂岩石热图像存在高低温区域空间分异,为定量研究岩石红外温度场的高温区空间分布聚集程度变化特征,进行了粉砂岩单轴压缩下的红外监测实验,先以红外温度场的第95百分位数为高温阈值,识别、提取高温点;又结合点密度样方分析法,以扩散系数定量衡量红外高温点的聚集程度,重点对粉砂岩加载过程中红外高温点聚集程度变化特征进行了研究,结果表明:加载过程中,粉砂岩红外温度场高温点扩散系数的波动性较弱、递增趋势明显,阶段特征表现为快-慢-快的反“S”型变化;其中,在塑性-峰后破坏阶段,红外高温点扩散系数的快速升高特征可作为岩石失稳的异常前兆,该前兆稳定出现,频率可达80 %.研究结果对丰富红外异常前兆,以及岩石灾变的红外监测及预警具有一定的工程应用价值.粉砂岩; 高温点; 聚集程度; 样方分析; 灾变预测Abstract: The high and low temperature region spatial anomalies of thermal image exists approaching rock failure under loading. In order to make quantitative study on the variation of aggregation degree of high temperature point, the infrared experiment was carried out in the condition of uniaxial compression, with the high temperature point being extracted according to the ninety-fifth percentile of the infrared temperature field and analyzed through the method of quadrat analysis. Using the diffusion coefficient to quantitatively measure the aggregation degree of high temperature points, the variation characteristics of the spatial distribution of high temperature points in the loading process of siltstone was studied. The results show that: in the process of loading, the fluctuation of the diffusion coefficient is weak, the increasing trend obvious and the stage characteristic is fast-slow-fast change like reverse "S"; in the stage of plastic deformation and post peak, rapid rise characteristics of diffusion coefficient of infrared high temperature points can be used as a precursory anomalies of rock steady loss, whose occurrence probability can be up to 80 %.
-
我国是采矿大国,与岩石受力灾变有关的矿山灾害频繁发生,如冲击地压(岩爆、矿震)、瓦斯突出、地表塌陷、边坡失稳等,危及生产、生活安全.(钱鸣高院士)指出“对岩石灾变过程进行有效监测与前兆识别,是岩石灾变预警与防灾减灾的重要基础.岩石受力灾变现象复杂,其特征与可测物理量表现为多模式、多层次、多尺度,包括红外辐射在内的电磁辐射是岩石破裂前兆研究的重要内容”.
前人对不同物理力学条件下岩石破裂失稳过程的红外辐射异常特征进行了大量的探索性研究并取得了许多重要成果.文献[1]通过实验研究发现, 煤岩和砂岩受压破裂过程中, 具有热图像和平均红外温度(AIRT)异常前兆,且晚于声发射和电阻率前兆出现.文献[2]指出,岩石破裂红外前兆包括AIRT时序特征异常和热像异常2种表征形式;前者分为降温、升温加速和降温转升3种类型;后者分为高温条带和低温条带2种类型.文献[3]利用接触式测温仪和红外热像仪对花岗岩和大理岩在单轴加载过程的温变特征进行了研究,表明岩石在破坏前存在温度奇变点.文献[4]对岩石破裂前红外热像的时空演化特征分析的结果表明,岩石在塑性变形阶段随着微破裂的产生而出现的热图像空间分异现象、临失稳前热图像整体短暂降温现象可分别作为岩石宏观破裂的早、晚期红外前兆.文献[5]认为,识别位于应力应变曲线上峰值点和快速失稳点之间的亚失稳阶段是岩石灾变短临预报的关键,亚失稳阶段的红外温变特征可作为识别出亚失稳阶段的重要标志.文献[6-8]进行了岩石灾变过程的红外异常前兆与声发射异常前兆相关性研究.文献[9-12]分别研究了隧道围岩、冲击倾向性煤失稳、岩爆发生的红外异常前兆.文献[13]基于灰色关联聚类分析定量研究了岩石破裂失稳过程的AIRT变化的共性特征.文献[14]通过热像方差刻画其分异程度,对岩石在加载过程中辐射温度场产生的分异现象进行了定量研究,认为岩石加载过程中热像的分异现象越明显,温度场偏离其均值的程度就越大,方差就越大.
然而,笔者也通过热像方差对单轴加载下的粉砂岩红外温度场分异特征进行了分析,结果不够理想.因为方差为数据点到均值的平均距离,通过平均处理,可以突出必然趋势,却也会弱化偶然突变.岩石灾变前由自身变化引起的红外温度场明显异常往往集中于某一较小区域内,如果对整个温度场进行分析、平均处理,容易弱化甚至隐匿此局部突变.鉴于此,为探究岩石破裂的红外异常现象,这里侧重于对红外温度场的某一局部—高温区域的突变特征进行分析,运用百分位法确定阈值,从红外温度场中识别、分离红外高温点,又结合点密度样方分析法,对高温点的聚集程度变化特征进行定量研究,研究结果对丰富红外异常前兆,以及岩石灾变的红外监测及预警具有一定的工程应用价值.
1 分析方法
1.1 基于百分位法识别红外高温点
将红外温度场中温度超出某临界值的采样点称为高(或低)温点,该临界值称高(或低)温阈值.可见,确定高温阈值是识别、提取高温点的关键,为此,引入了百分位法以确定阈值.
用99个点,将按大小升序排列的观测值划分为100个等分,则这99个点就称为百分位数.采用百分位确定阈值是目前国际上在气候极端变化研究中最常用方法,它将某一百分位数作为阈值,用以定义极端事件[15].本文亦利用百分位定义红外温度高温点.
每张热图像都对应一个红外温度矩阵,将红外温度矩阵各元素按大小升序排列,得到序列$\left\{ {x\left( i \right), i=1, 2, 3, \cdots, n} \right\}$,则α百分位数计算公式[16-17]如下:
$$ {x_{\rm{\alpha }}}=\left( {1 - {\rm{\alpha }}} \right){x_j} - {\rm{\alpha }}\;{x_{j + 1}} $$ (1) 式(1)中:j为xj在{x(i)}中的排列序号,j=floor(p(n+1)), floor()为向下取整函数;p为{x(i)}中所有小于等于xα的频率,即p=N{xj < xα}/n;a为权重系数,a=p(n+1)-j;α介于0~99之间取整.如果有30个值,那么第90百分位数为排序后的x27和x28的线性插值.采用该方法来估计百分位值,不但计算方便,而且避免了对序列分布的任何假设.
1.2 基于样方法度量高温变点聚集度
1.2.1 样方分析
样方分析是进行空间点模式分析的最常用的直观方式,其基本思想是通过空间上点分布密度的变化来评定空间分布模式,一般使用随机分布模式作为理论上的标准分布,将QA计算的点密度统计分布和理论分布做比较,判断点模式属于聚集分布、均匀分布还是随机分布.
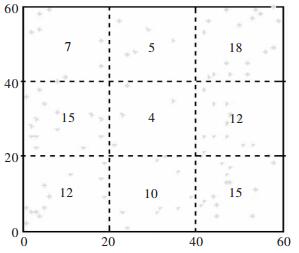
为便于分析高温点聚集程度变化情况,样方分析可按以下步骤展开:首先,将研究区域划分为规则的正方形网格区域(如图 1);其次,统计落人每个网格中点的数量(如图 1),并按大小升序排列成样方点量数列餐$\left\{ {X\left( k \right), k=1, 2, 3, \cdots, M} \right\}$(M为样方数).由于点在空间上分布的疏密性,有的网格中点的数量多,有的网格中点的数量少,有的网格中点的数量甚至为零.最后,计算出{X(k)}的统计特征参数—扩散系数,并观察其时变特征.
当使用样方法分析空间点分布模式时,样方的尺寸会影响到点的观测频次和分布.根据Griffith等人的多年研究,最优的样方尺寸的计算公式[18]:
$$ l=\sqrt {\frac{{2A}}{N}} $$ 其中,A、N分别为研究区域的面积和其中点的总数.
1.2.2 扩散系数
点要素空间分布聚集程度的度量,在生态学中习惯上采用的是方差与平均数的比值,即扩散系数(C)[19]:
$$ C=\frac{{{S^2}}}{{\bar X}} $$ 式(2)中,S2、X分别为所有样方点量数列{X(k)}的方差和均值.
因为在Poisson分析中,方差与均值相等,利用该性质的可方便地对分布情况进行评定.即,
1)当C < 1时,为均匀分布;
2)当C=1时,为随机分布(Poisson分布);
2)当C > 1时,为聚集分布.
均匀分布的极限(即全部样方的点数相同)是C=0,聚集分布的极限(即一个样方中包括全部个体)是C=M. C越大、越靠近样方数,则说明每个样方内分布的点数与整个研究区内样方点数的均值相差就越大,点要素就越趋于簇状分布,其聚集程度就越高[20].利用扩散系数可进一步研究试件加载过程中的红外高温点空间分布聚集程度变化特征.
2 实验
随着开采深度增加,矿井环境温度不断上升.根据量测,常规情况下的地温梯度为30℃/km[17],照此计算开采深度在1.5~2km范围内,地温可达50 ℃左右.不仅如此,实际地壳中的岩石多含有水,地下水作用不仅可能造成深部矿井突水灾害,还会软化围岩使其强度降低甚至导致岩体失稳灾变.深部矿井高温水浸透会对岩石的力学性能造成一定影响,尤其是粉砂岩受水的影响更大,而粉砂岩等细粒沉积岩常与煤岩伴生,探究高温水渗透下粉砂岩失稳的红外前兆对保障深部煤矿安全具有重要意义.因此,为模拟实验研究深部高温水渗透下粉砂岩破裂失稳过程的红外特性,进行了50 ℃温水浸透下粉砂岩单轴压缩下红外监测试验.
2.1 试件制备及处理
镜鉴试验结果表明,所选粉砂岩属于碎屑岩类,其石英含量63 %,方解石和绢云母含量5 %,泥质含量可达32 %,从物质组成和胶结方式来看粉砂岩含水后易软化;制备50 mm × 50 mm×100 mm规格的标准柱体试件5块,分别表号为S1、S2、S3、S4、S5,仔细研磨两端,使上下表面平等度符合试验要求.对试件进行了50℃温水浸泡处理.地下岩石长期与水相互作用下常保持饱水状态,为保证试件浸水后达到饱和状态,采取以下处理方式:浸泡2 h→称重→浸泡2 h→称重,待试件表面干燥后,用保鲜膜密封. 表 1为试件编号、尺寸及含水情况信息汇总表,从表 1中可知,在温水中浸泡2 h、4 h后试件重量相差不大,说明浸泡2 h后,试件已经接近饱和.
表 1 试件编号、尺寸及含水情况信息汇总Table 1. Summary of specimen size, serial number and rate of water content试件
编号尺寸/mm 干重
M0/kg浸水
处理湿重
M1/kg湿重
M2/kg饱和含
水率/%S1 50×49.1×100.9 0.625 50℃温水浸泡 0.652 0.653 4.32 S2 50×50.3×102 0.598 50℃温水浸泡 0.646 0.648 8.03 S3 50×49.3×99.9 0.605 50℃温水浸泡 0.641 0.645 5.95 S4 50×50×100.2 0.59 50℃温水浸泡 0.625 0.628 5.93 S5 50×50.1×100.4 0.615 50℃温水浸泡 0.65 0.651 5.69 注: M1、M2分别为浸泡2h、4h后所称试件质量. 2.2 实验仪器
所用压力试验机型号为RLW-3000,可进行常规加载和双轴加载,最大轴向试验力3000kN,最大横向试验力1000kN,试验力测量精度±1%.红外热像仪采用美国SC3000红外实时成像系统,系统采用的空间分辨率为320×240像素,光谱范围在8~12 μm,温度灵敏度达到0.03 ℃,成像速率可达50 Hz.
2.3 实验过程
实验前,将试样置放于压力机上,在试样测试面的前方1.0 m附近安设红外热像仪(正前方)、数字快速照相机(斜前方);校对各计算机显示时间,使得压力机、红外热像仪、数字快速照相机同步采集数据.实验在RLW-3000型伺服试验系统上完成,采用位移控制方式加载,先预加载至1.5kN,以保证试件与加载面完全接触,减少受力不均造成的影响,随后以1.5mm/min匀速加载,红外实时成像系统进行同步监测,直到试件破坏.为抑制实验中环境因素对红外热成像仪监测数据的影响,关闭门窗并拉上窗帘,保持实验环境安静,同时禁止人员走动.试验现场及试件加载过程中的红外热像图如图 2、图 3所示:
3 实验结果与分析
3.1 温度场变化特征常规分析
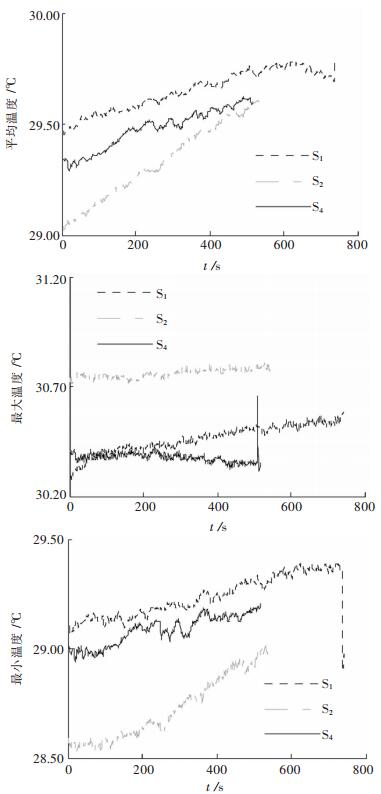
前人对岩石灾变的红外异常前兆的描述除热图像外主要借助红外温度场的均值、最大(小)值.本文旨在探寻岩石灾变的红外异常前兆,为便于对比而进行了红外温度场变化特征常规分析. 图 4为部分试件加载过程的平均、最大、最小红外温度随时间的变化曲线,从图 4中可以看出,加载过程中粉砂岩试件红外温度场的最大值基本稳定,最小值和均值逐渐增加,递增趋势特别明显,说明加载过程中温度场整体升温,呈现向高温区域迁移的趋势.
3.2 粉砂岩破裂过程的红外高温点聚集异常
对加载过程中粉砂岩的红外高温点聚集异常特征分析的同时,对红外低温点聚集程度变化特征也稍微有所涉及.红外低温点扩散系数可定量描述其空间分布的聚集程度.取不同低温阈值,作图、观察发现,加载过程中,各试件的红外低温点扩散系数变化特征较为类似,主要表现为在一定范围内波动,无明显变化趋势,加载后期,亦无明显共性的突变特征.限于篇幅,这里取低温阈值为低温点扩散系数时间序列的第5百分位数,只给出试件S2、S3、S5加载过程的扩散系数变化曲线(见图 5),不再详述.
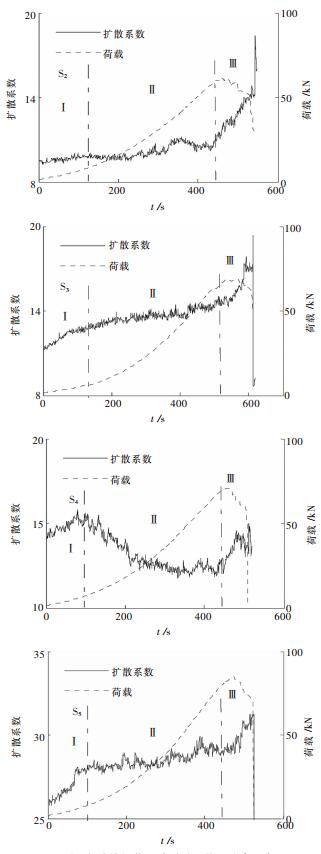
红外高温点扩散系数可定量描述其空间分布的聚集程度.取高温阈值为红外高温点扩散系数时间序列的第95百分位数百分位数,做出各试件加载过程的高温点扩散系数时序曲线,见图 6.经过对各试件加载过程中高温点扩散系数变化特征进行统计可得到表 2.根据荷载-时间曲线,可将应变过程分成压密阶段前期、压密-弹性阶段和塑性-峰后破坏阶段.由表 1可知,所统计的扩散系数变化特征及异常前兆出现概率均大于60 %,属于共性特征.据此将粉砂岩加载过程的红外高温点扩散系数变化的一般特征可概括为:曲线全过程呈反“S”型递增,可分为3个阶段;阶段Ⅰ递增且斜率较大,阶段Ⅱ递增但趋势平缓,阶段Ⅲ递增且斜率更大;失稳前存在快速上升的异常前兆,此前兆倾向于峰值应力附近或之后出现.
表 2 试件加载过程中红外高温点扩散系数变化特征统计Table 2. change characteristic of diffusion coefficient of the high temperature point during the loading of the each pecimen符号 应力应变阶段 扩散系数变化特征 出现频率 Ⅰ 压密阶段前期 递增且斜率较大 80% Ⅱ 压密-弹性阶段 递增但平缓 60% Ⅲ 塑性-峰后阶段 递增且斜率更大 80% P 塑性-峰后阶段 快速升高异常 80% 注:Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ代表不同阶段; P表示岩石灾变的红外高温点聚集异常. 该现象成因可解释为:微裂隙压密阶段前期,孔隙率较大的粉砂岩易于发生变形,变形中孔隙面发生相互错动,使摩擦热效应增强,进而导致高温区域聚集程度明显增加;在加载继续增加而又不太大的压密-弹性阶段,应力场不断调整,非均质的粉砂岩经过初步压密,强度分布非均匀性减弱,摩擦热效应弱于阶段Ⅰ,使得高温区域聚集程度递增相对平缓,甚至下降;进入塑性-峰后破坏阶段,荷载较大逐步接近极限强度,使应力集中状态再度激化,导致局部热效应增强,出现了高温点聚集程度加速增加的异常现象.
4 结论
以粉砂岩单轴压缩过程的红外监测实验为基础,以红外温度场的第95百分位数为高温阈值,识别、提取高温点;又结合点密度样方分析法,用扩散系数定量衡量红外高温点的聚集程度,对粉砂岩加载过程中红外高温点空间分布的聚集程度变化特征进行了研究,结果表明:加载过程中,粉砂岩的红外温度场高温点的扩散系数波动性较弱、递增趋势明显,阶段特征表现为快-慢-快的反“S”型变化;其中,塑性-峰后破坏阶段,发生的红外高温点扩散系数快速上升特征可作为岩石失稳的异常前兆,该前兆稳定出现频率可达80 %.研究结果对丰富红外异常前兆,以及岩石灾变的红外监测及预警具有一定的工程应用价值.
另外,本文侧重于通过红外数据处理方法的创新来探究岩石破裂过程的红外异常现象,结合图像观察的定性分析方法去发现异常,而对异常临界点科学的识别方法,还需要专门研究.
-
表 1 试件编号、尺寸及含水情况信息汇总
Table 1 Summary of specimen size, serial number and rate of water content
试件
编号尺寸/mm 干重
M0/kg浸水
处理湿重
M1/kg湿重
M2/kg饱和含
水率/%S1 50×49.1×100.9 0.625 50℃温水浸泡 0.652 0.653 4.32 S2 50×50.3×102 0.598 50℃温水浸泡 0.646 0.648 8.03 S3 50×49.3×99.9 0.605 50℃温水浸泡 0.641 0.645 5.95 S4 50×50×100.2 0.59 50℃温水浸泡 0.625 0.628 5.93 S5 50×50.1×100.4 0.615 50℃温水浸泡 0.65 0.651 5.69 注: M1、M2分别为浸泡2h、4h后所称试件质量. 表 2 试件加载过程中红外高温点扩散系数变化特征统计
Table 2 change characteristic of diffusion coefficient of the high temperature point during the loading of the each pecimen
符号 应力应变阶段 扩散系数变化特征 出现频率 Ⅰ 压密阶段前期 递增且斜率较大 80% Ⅱ 压密-弹性阶段 递增但平缓 60% Ⅲ 塑性-峰后阶段 递增且斜率更大 80% P 塑性-峰后阶段 快速升高异常 80% 注:Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ代表不同阶段; P表示岩石灾变的红外高温点聚集异常. -
[1] 吴立新, 王金庄.煤岩受压红外热像与辐射温度特征实验[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 1998, 28(1):41-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199801007.htm [2] 刘善军, 吴立新, 王川婴, 等.遥感-岩石力学(Ⅷ)—论岩石破裂的热红外前兆[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(10):1621-1627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200410006.htm [3] 邓志毅, 张东胜, 安里千.热探测法监测岩石应力变化的实验研究[J].中国矿业大学学报, 2006, 35(5):623-627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD200605011.htm [4] 刘善军, 吴立新, 张艳博.岩石破裂前红外热像的时空演特征[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 30(7):1034-1038. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX200907029.htm [5] 任雅琼, 刘培洵, 马瑾, 等.亚失稳阶段雁列断层热场演化的实验研究[J].地球物理学报, 2013, 56(7):2348-2357. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201307020.htm [6] 孙强, 薛晓辉, 朱术云.岩石脆性破坏临界信息综合识别[J].固体力学学报, 2013, 34(3):311-319. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTLX201303014.htm [7] 张艳博, 刘祥鑫, 梁正召, 等.基于多物理场参数变化的花岗岩巷道岩爆前兆模拟实验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(7):1347-1357. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201407006.htm [8] 梁鹏, 张艳博, 田宝柱, 等.岩石破裂过程声发射和红外辐射特性及相关性实验研究[J].矿业研究与开发, 2015, 35(3):57-60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK201503020.htm [9] 姜耀东, 吕玉凯, 赵毅鑫, 等.煤样失稳破坏的多参量监测试验[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(4):667-674. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201204004.htm [10] 陈智强, 张永兴, 周检英.开挖诱发隧道围岩变形的红外热像试验研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(7):1271-1277. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201207015.htm [11] 徐子杰, 齐庆新, 李宏艳, 等.冲击倾向性煤体加载破坏的红外辐射特征研究[J].中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(10):121-125. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201310022.htm [12] 肖福坤, 申志亮, 刘刚, 等.冲击倾向性煤样单轴加载红外探测研究[J].黑龙江科技大学学报, 2015, 25(1):6-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJI201501002.htm [13] 高祥, 吴贤振, 尹丽冰, 等.基于灰色关联度的砂岩加载过程中AIRT演化特征研究[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2015, 6(2):67-71. http://ysjskx.paperopen.com/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201502013 [14] 刘善军, 魏嘉磊, 黄建伟, 等.岩石加载过程中红外辐射温度场演化的定量分析方法[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(S1):2668-2976. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2015S1047.htm [15] 薛联青, 刘晓群, 宋佳佳, 等.基于百分位法确定流域极端事件阀值[J].水力发电学报.2013, 32(5):26-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFXB201305005.htm [16] 李庆祥, 黄嘉佑.对我国极端高温事件阈值的探讨[J].应用气象学报, 2011, 22(2):138-144. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX201102004.htm [17] 罗梦森, 熊世为, 梁宇飞.区域极端降水事件阈值计算方法比较分析[J].气象科学, 2013, 33(5):549-554. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX201305010.htm [18] 秦昆.GIS空间分析理论与方法[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社, 2010:194-195. [19] 邬祥光.昆虫生态学的常用数学分析方法[M].北京:农业出版社, 1963:502-503. [20] 刘湘南.GIS空间分析原理与方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 2005:82-83.



 下载:
下载: