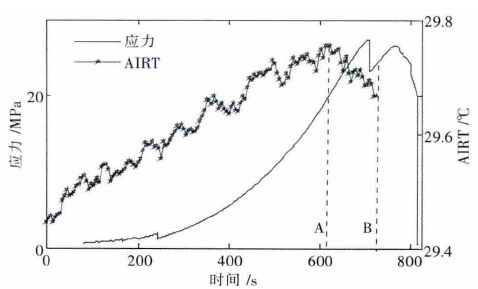
AIRT evolution features in the process of sandstone loading based on gray correlation
-
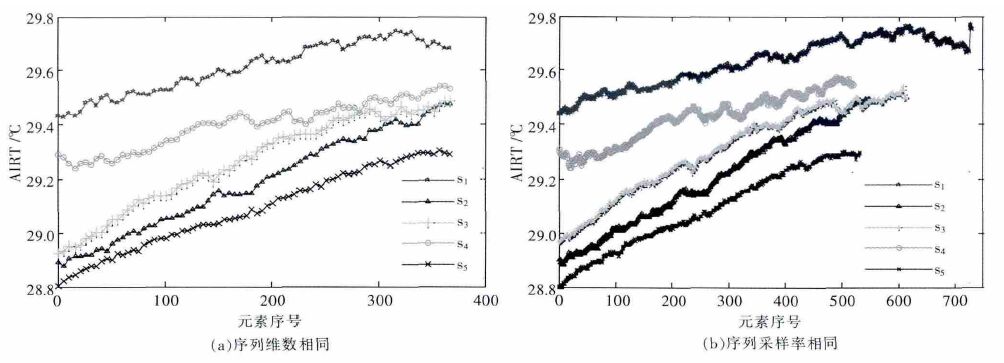
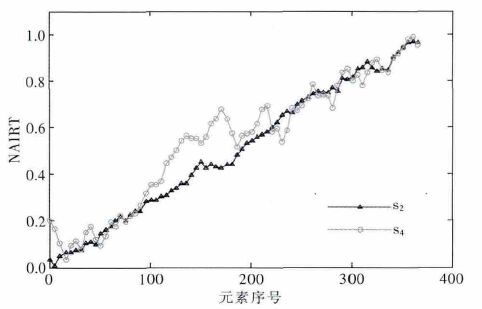
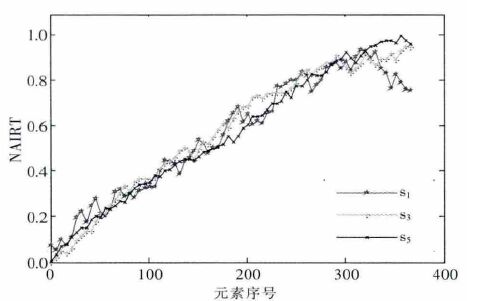
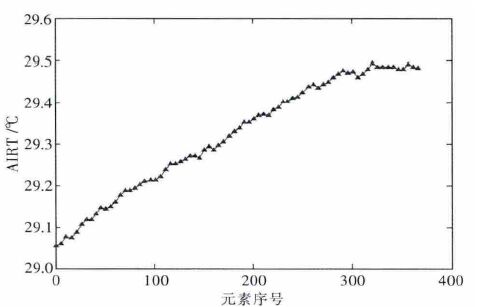
摘要: 在受力岩石的红外辐射效应研究中,AIRT 时序曲线应用广泛,但试件岩石成分、损伤分布不均又各向异性,导致AIRT 时序曲线形式多样,共性特征隐蔽,难以明确分类.文中以单轴压缩下粉砂岩红外观测试验为依托,对原AIRT 时间序列,先进行重采样和归一化处理,再进行灰色关联聚类分析,以序列间发展趋势的相似程度为定量指标,进行分类.结果表明:此次试验,临界值取0.7,可将AIRT 时序曲线分成2 类,其中,第Ⅰ类曲线占60 %,具明显的红外异常前兆,此种数据处理方法,对AIRT 演化特征及灾变前兆定量研究具有一定的参考意义.Abstract: In the study of the effect of stress rock infrared radiation, although AIRT temporal curve is used widely, due to uneven distribution and anisotropy of rock specimen composition and damage, the AIRT tempo - ral curve is always in a variety of forms with common features hidden and difficulty to be classified clearly. The paper, based on infrared observation experiment of siltstone under uniaxial compression, resamples and normalizes the original AIRT time series, then carries out grey correlation clustering analysis and classifies them with development trend of similar degree between sequences as quantitative indicators. Results show that for the test, when the critical value is 0.7, the AIRT temporal curve can be divided into two categories, the first class curve of which accounts for 60 % of all, with obvious infrared abnormal precursors, and the data pro - cessing method has very important reference significance for the AIRT evolution characteristics and catastro - phe precursor quantitative research.
-
钻爆法开挖工程岩体时,地应力和循环冲击载荷共同作用于围岩体. 已有的研究结果表明[1-5],不同的静载荷和循环冲击组合形式导致岩石具有不同动态力学特性,例如动态强度劣化、疲劳变形、能量耗散、损伤变量的定义方法、损伤累积演化特性和破坏模式等. 然而,上述研究没有研究静载荷与循环冲击作用下岩石的动态本构关系.
本构模型一直是岩石力学的重点研究领域之一,岩石在静态或准静态载荷作用下的本构模型已取得许多研究成果.由于岩石冲击动力学起步较晚,且岩石材料动态力学特性不仅与所受应力状态有关,而且与加载速率有关,因此对岩石冲击动态本构的研究相对较少.
岩石动态本构的研究大致可以分为2种方法:经验模型方法和理论分析方法. 经验模型方法主要基于实验结果总结得出岩石动态应力与应变率的经验关系[6]. 理论分析模型方法主要基于损伤力学理论并结合其他理论方法,将岩石看成由弹性元件、黏性元件和塑形元件中2个或2个以上通过串联或并联组成,再结合相关力学知识,建立岩石在动载荷作用下的本构模型. 20世纪80年代日本木下重教、佐藤一彦、川北稔以及于亚伦教授等根据岩石冲击实验结果,认为可以用宾厄模型来描述岩石的冲击本构特性,该模型的优点是可以描述峰后的变形,但不能反映弹性模量随应变率的变化特性. 郑永来等[7]建立黏弹性连续损伤本构模型,该模型的优点是能反映岩石强度和弹性模量的应变率效应,然而其参数较多,且确定参数时需要大量不同应变率的实验数据. 单仁亮等[8]提出岩石冲击破坏的统计损伤时效模型,该模型假设岩石单元同时具有统计损伤特性和黏性液体的特性,把岩石试件看成损伤体Da和黏缸ηb的并联体,将统计损伤模型和黏弹性模型结合起来,该模型的优点是表达式简单,参数确定较方便. 李夕兵等[9]在损伤时效模型的基础上,将统计损伤模型和黏弹性模型相结合,考虑了初始静应力的影响,该模型的最大特点是考虑了动静组合加载时岩石的本构关系,但其考虑的应变率范围较低,最大应变率为10-1量级. 刘军忠等[10]采用黏性体ηb和损伤体Da并联组合建模的方法,将统计损伤模型和黏弹性模型相结合,建立了基于Weibull分布的岩石冲击损伤本构模型,该模型的优点是在损伤体Da上考虑了围压的作用,然而该模型是没有考虑轴压和围压共同作用. 朱晶晶等[11-12]在统计损伤失效模型的基础上,研究一维轴向静应力和循环冲击组合下岩石的损伤本构模型,取得了较好的效果.
上述本构模型研究中,没有涉及到三维静载荷与循环冲击组合作用下岩石的本构关系研究. 文章将岩石试件看成是黏缸体ηb和损伤体Da并联而成的组合体,建立具有三维静应力时黏弹性损伤体的本构关系.基于已有的循环冲击组合作用下岩石损伤累积演化模型,得到循环冲击过程中岩石物理力学参数与损伤的关系,进而将循环冲击次数引进统计损伤失效模型. 探索模型中参数的变化对本构模型的影响规律.最后应用循环冲击试验数据验证该模型的正确性. 本模型的建立丰富了岩石动力学的理论研究内容,并为岩体工程安全,高效施工和运营提供重要的理论依据.
1 循环冲击下岩石弹模的变化规律
1.1 循环冲击作用下岩石损伤累积演化特性
文献[13]通过循环冲击试验,研究循环冲击作用下岩石的强度和变形与循环冲击次数的关系,并在此基础上,结合Logistic曲线方程,得出适合于表征具有不同静载荷的岩石在循环冲击作用下的损伤累积演化的模型. 该模型首先利用波阻抗计算的损伤随循环冲击次数的变化趋势,将岩石损伤简单的分为3个阶段,第1阶段为初始损伤阶段,第2阶段为低速阶段,第3阶段为加速阶段,接着与Logistic曲线进行对比,求原方程的逆函数,即得到描述岩石在循环冲击作用下的岩石损伤累积演化趋势的曲线方程:
$$D=\alpha -\beta \ln \left( \frac{\kappa }{n}-\rho \right)$$ (1) 式(1)中:D指岩石的累积损伤因子,n为循环冲击次数,α、β、κ和p为参数. 其中α为初始损伤因子,控制着曲线低速阶段中心点的损伤的大小;β为低速阶段的速度因子,控制着曲线低速阶段的损伤累积速度的大小,β的大小受围压的影响较大,围压越大,β值越小;参数κ表示岩石试件所受轴压大小;p表示曲线在加速阶段的损伤累积速度大小,与轴压有关. 最后,根据一定的岩石循环冲击试验数据,利用该损伤累积模型进行拟合,得出α、β、κ和p值的大小,即可得出具体的损伤累积模型.
1.2 岩石弹性模量与累积损伤的关系
在循环载荷作用下,岩石在出现强度劣化和疲劳变形的同时,往往内部会有微裂纹的孕育、萌生、扩展和贯通的过程.要研究载荷对岩体的破坏,就必须先确定岩体的初始损伤变量,这涉及如何合理的定义损伤变量,考虑爆破会对岩体的弹性常数产生影响.
根据应变等价原理有:
$$\varepsilon =\tilde{\sigma }/E=\sigma /\tilde{E}$$ (2) 由损伤理论得:
$$\tilde{\sigma }=\sigma /\left( 1-D \right)$$ (3) 结合式(2)、式(3)可得:
$$\tilde{E}=E\left( 1-D \right)$$ (4) 式(4)中${\tilde{E}}$和E分别为损伤材料和无损材料的弹性模量;${\tilde{\sigma }}$和σ为材料的应力和有效应力.
若要考虑岩石在每次冲击后的累积损伤与弹性模量的关系,则可将式(4)改写为:
$${{E}_{n}}={{E}_{0}}\left( 1-{{D}_{n}} \right)$$ (5) 式(5)中En和E0分别表示岩石在第n次冲击后的弹性模量和岩石在无损状态时的弹性模量;Dn则为岩石在第n次冲击后的累积损伤值,可利用式(1)进行求解. 这样也间接得出循环冲击次数与岩石弹性模量的关系.
2 岩石损伤本构理论模型
假设岩石是由大量微元体构成的集合体,微元一方面足够大,可以包含足够多的微节理、微裂纹等,另一方面又足够小,可以将其看作一质点来考虑,满足连续损伤力学理论的相关条件. 为便于对岩石损伤本构理论模型的分析研究,将加载过程中岩石的损伤看作是一个连续的过程.
2.1 基本假设
1)岩石单元同时具有统计损伤特性和黏性液体的特性,可将岩石试件看成是黏缸ηb和损伤体Da并联而成的组合体[14],如图 1所示:
2)损伤体的损伤特性为各向同性,在损伤之前为线弹性体,服从虎克定律.
3)黏缸没有损伤特性,遵循的本构关系为:
$${{\sigma }_{b}}=\eta \frac{d\varepsilon }{dt}$$ (6) 4)微元体的强度F服从Weibull分布,其概率密度函数为:
$$p\left( F \right)=\frac{m}{{{F}_{0}}}\times {{\left( \frac{F}{{{F}_{0}}} \right)}^{m-1}}\times \exp \left[ -{{\left( \frac{F}{{{F}_{0}}} \right)}^{m}} \right]$$ (7) 式(7)中,F为微元体强度的分布变量,m及F0为Weibull分布的2个参数,反应了岩石的物理力学特性.
由于岩石在损伤过程中,其微缺陷、微空洞等都具有随机性[15],根据微元体强度服从统计分布的假设,可用统计损伤变量进行表征. 因此,把岩石微元破坏的概率作为动态损伤变量D',则可得基于Weibull分布的动态损伤变量:
$${D}'=1-\exp \left[ -{{\left( \frac{F}{{{F}_{0}}} \right)}^{m}} \right]$$ (8) 2.2 微元体的强度
由于Drucker-Prager破坏准则克服了库仑-莫尔准则的主要弱点,既考虑静水压力的作用,又计入了中间主应力的影响,在岩体介质中运用广泛,且参数简单,基于该破坏准则的岩石微元强度为:
$$F=f\left( \sigma \right)=\alpha {{I}_{1}}+\sqrt{{{J}_{2}}}=k$$ (9) 式(9)中:α、k为与岩体黏聚力c和内摩擦角φ有关的参数,且α=sin φ/$\sqrt{9+3{{\sin }^{2}}\varphi }$;I1为应力张量的第一不变量,J2为应力偏量的第二不变量,与虎克定律相结合可得:
$${{I}_{1}}=\frac{\left( {{\sigma }_{x}}+\sigma +2{{\sigma }_{3}} \right)E\varepsilon }{{{\sigma }_{x}}+\sigma -2v{{\sigma }_{3}}}$$ (10) $$\sqrt{{{J}_{2}}}=\frac{\left( {{\sigma }_{x}}+\sigma -{{\sigma }_{3}} \right)E\varepsilon }{\sqrt{3}\left( {{\sigma }_{x}}+\sigma -2v{{\sigma }_{3}} \right)}$$ (11) 式(10)和式(11)中:σx为轴向静应力,σ3为围压应力(σ3=σ2),σ为轴向动应力,ε为轴向应变,E、v分别为岩石的弹性模量与泊松比.
2.3 本构模型的建立
由于本文研究的是在三维静载下岩石受循环冲击作用的岩石损伤本构模型,如图 1所示,故假定在岩石单元的x方向预先施加轴向静荷载σx,在y、z方向预先施加围压σy和σz. 由组合体的并联关系可知,黏性体的应变εb与损伤体的应变εa相等,即组合体的应变与两分体的应变相等;组合体的应力则等于两分体应力之和,因此损伤体与黏性体满足如下关系:
$$\varepsilon ={{\varepsilon }_{a}}={{\varepsilon }_{b}}$$ (12) $$\sigma ={{\sigma }_{a}}={{\sigma }_{b}}$$ (13) 式(13)中,σ为组合体在轴向的总冲击应力,σa和σb分别为损伤体和黏性体承受的冲击应力.
三轴条件下,由应变等效原理可得损伤体的本构关系为:
$${{\sigma }_{a}}=E\varepsilon \left( 1-{D}' \right)+v\left( {{\sigma }_{y}}+{{\sigma }_{z}} \right)-{{\sigma }_{x}}$$ (14) 将式(6)与式(14)代入式(13),即可得组合体的本构关系为:
$$\sigma =E\varepsilon \left( 1-{D}' \right)+v\left( {{\sigma }_{y}}+{{\sigma }_{z}} \right)-{{\sigma }_{x}}+\eta \frac{d\varepsilon }{dt}$$ (15) 考虑岩石在循环冲击作用下的本构关系,可将式(15)进行改写,并结合式(8)可得
$$\sigma =E\varepsilon \exp \left[ -{{\left( \frac{F}{{{F}_{0}}} \right)}^{m}} \right]+v\left( {{\sigma }_{y}}+{{\sigma }_{z}} \right)-{{\sigma }_{x}}+\eta \frac{d\varepsilon }{dt}$$ (16) 式(16)即为基于Weibull分布的岩石在静载荷与循环冲击组合作用下的损伤本构模型.
2.4 模型参数的求解
通过以上分析可知,要求解该本构方程,需要确定6个参数:En、α、F0、m、v及η. 这6个参数往往需要通过对实测的试验数据进行分析进而确定,并不可避免的需要进行一定的试算. 其中En的确定可通过累积演化模型,利用式(5)进行求解;黏性系数η的取值范围大致在0~2;α的变化范围大致在0~$\sqrt{3}$;Weibull分布的2个参数F0和m则可根据实测数据,采用曲线拟合的方法进行确定;应变ε和应变率dε/dt则应当采用实测数据.
3 试验验证
利用文献[2]中的岩石循环冲击试验数据验证式(16)的正确性和可行性. 根据循环冲击试验结果,结合式(16)的关系式,求解其中的参数值,可得其损伤本构理论模型曲线. 因为式(16)是一个隐函数,在Matlab中编写一个循环程序进行求解. 由于篇幅限制,在此仅给出围压为4 MPa、轴压为49 MPa的试件T1-4-2的结果. 表 1所示为该试件本构模型中参数的求解结果. 图 2为试验结果和理论结果的对比.
表 1 试件T1-4-2本构模型的参数值Table 1. Parameter values of specimen T1-4-2 in constitutive model循环次数 E/GPa v η/(MPa•s) F0/MPa m 1 64 0.27 1.75 196 -0.4 2 57 0.2 1.62 194 -0.34 3 53.5 0.194 1.39 191 -0.32 4 45 0.189 1.1 167 0.45 5 43 0.17 0.85 154.6 0.5 6 38 0.14 0.75 142.1 0.75 7 16.5 0.1 0.44 119.5 2.1 由图 2可以看出,实测曲线与理论模型曲线具有较好的一致性,说明式(16)可以用来描述静载荷与循环冲击组合作用下岩石的损伤本构关系,验证该模型的正确性和可行性.
由表 1可以看出,对具有三维静载的岩石试件(4 MPa围压和49 MPa轴压),利用式(16)所表示的损伤本构模型进行拟合时,随着循环冲击次数的递增,其中的参数m值逐渐增大. 具有三维静载荷的岩石在循环冲击过程中,其损伤程度逐渐增加[2, 16],且其破坏模式多呈圆锥(台)形式[17],因此可以推断在循环冲击过程中岩石试件的不均匀程度在增加.即循环冲击过程中,m值越大岩石试件越不均匀,其表示岩石的不均匀度. 这与岩石在静载荷和单次冲击下的均质度[18-20]不同.
结合式(8)解释m表示循环冲击过程中岩石的不均匀度的合理性. 式(8)中的F0表示岩石试件在单次冲击中的峰值应力,F表示岩石微元体强度,一般情况下认为,岩石的微元体强度高于其整体强度.假设岩石单次冲击时的F0=120 MPa,当不均匀度值逐渐增加时,根据式(8)计算的损伤值呈逐渐增大的趋势,如图 3所示. 不均匀值m的增加,表示循环冲击过程中岩石内的微裂纹逐渐萌生、贯通和成核,此时在循环冲击载荷作用下,在这些微裂纹处压缩应力波将发生斜入射,通过反射和透射产生纵波和横波,增加岩石进一步损伤破坏的概率,即对相同强度的微元体,不均匀度m值越大,其损伤值也越高. 因此图 3说明了表 1中m的拟合值的合理性,也说明了可以用m表示循环冲击过程中岩石的非均匀度.
4 参数对本构模型的影响
4.1 弹性模量En对模型的影响
从式(5)可知,参数En和E0分别表示岩石在第n次冲击后的弹性模量和岩石在无损状态时的弹性模量. 当固定其他参数不变而改变En时,应力-应变曲线的变化情况如图 4. 由图 4可以看出,随弹性模量En的减小,岩石的峰值强度也随之减小,峰值前的应力-应变曲线的斜率逐渐减小. 即随着冲击次数的增加,岩石的弹性模量则随之减小,同时岩石的峰值强度也在减小,岩石的弹性模量En的变化对应力-应变曲线的影响较大.
4.2 α对模型的影响
α和k是岩石黏聚力c和内摩擦角φ有关的实验常数. 当固定其他参数不变而改变α时,其实也即是改变内摩擦角φ的大小,应力-应变曲线的变化见图 5. 由图 5可以看出,随着α的减小,岩石的峰值应力反而有所增大,但增加的幅度较小. 由此可得,α的变化对应力-应变曲线有一定的影响,但影响不显著.
4.3 参数F0与m对模型的影响
F0和m作为Weibull分布的2个参数,反应岩石物理力学性质. 当固定其他参数不变而改变F0时,应力-应变曲线的变化情况如图 6. 由图 6可知,随着F0的减小,岩石的峰值强度也随之减小,即参数F0表示岩石试件在单次冲击中的峰值应力,反映了岩石的宏观平均强度;但F0对初始段应力-应变曲线的影响不显著.
当固定其他参数不变而改变m时,应力-应变的曲线变化如图 7. 由图 7可知,m值的越大,单次冲击时岩石的峰值应力越小,初始阶段应力-应变曲线的斜率增加,峰值应力对应的应变逐渐减小,即m对应力-应变曲线的影响较显著.
4.4 泊松比v对模型的影响
当固定其他参数不变而改变v时,应力-应变曲线的变化如图 8. 由图 8可知,随着v的增大,岩石的强度基本无变化,应力-应变曲线基本无影响.
4.5 黏性系数η对模型的影响
当固定其他参数不变而改变η时,应力-应变曲线的变化如图 9. 由图 9可知,随着η的增大,岩石的峰值应力也随之增大,峰值应力对应的应变逐渐减小. 可见η的变化对应力-应变曲线的影响显著,可以改变应力-应变曲线的形态.
5 结论
1)通过基于Logistic曲线方程的损伤累积模型计算岩石的累积损伤,考虑爆破冲击对岩体的弹性模量的影响,根据应变等效原理,导出了岩石弹性模量与累积损伤变量的关系,从而将循环冲击次数引入岩石损伤本构关系中.
2)将统计损伤模型和黏弹性模型相结合,并根据Drucker-Prager破坏准则,建立有轴压有围压时循环冲击作用下岩石的动态损伤本构模型.
3)通过实验验证,所建模型曲线与实测曲线具有较好的一致性,说明所建模型是合理的,且该建模型具有计算参数少,运用简便的特点,能够较好的描述一定静应力作用下的岩石在循环冲击作用的本构关系.
4)岩石的弹性模量、黏性系数等参数对循环冲击时岩石的应力-应变曲线影响较大;而岩石的摩擦角和泊松比等对具有三维静载岩石的冲击疲劳应力-应变曲线影响较小.循环冲击过程中,岩石的非均匀度逐渐增加.
-
表 1 NIART 序列关联矩阵上三角阵

-
[1] 耿乃光,崔承禹,邓明德.岩石破裂实验中的遥感观测与遥感岩石力学的开端[J].地震学报,1992,11(增刊1):645-652. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB1992S1013.htm [2] 崔承禹,邓明德,耿乃光.在不同压力下岩石光谱辐射特性研究[J].科学通报,1993,38(6):538-541. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199306016.htm [3] 耿乃光,崔承禹,邓明德,等.遥感岩石力学及其应用前景[J].地球物理学进展,1993,8(4):1-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ199304001.htm [4] 邓明德,耿乃光,崔承禹,等.岩石红外辐射温度随岩石应力变化的规律和特征以及与声发射率的关系[J]. 西北地震学报,1995,17(4):79-86. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ504.011.htm [5] 吴立新,王金庄.煤岩受压红外热像与辐射温度特征实验[J].中国科学(D 辑:地球科学),1998,28(1):41- 46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199801007.htm [6] 吴立新,刘善军,吴育华,等.遥感-岩石力学(I)———非连续组合断层破裂的热红外辐射规律及其构造地震前兆意义[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(1):24-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200401006.htm [7] 吴立新,刘善军,吴育华,等.遥感-岩石力学(IV)———岩石压剪破裂的热红外辐射规律及其地震前兆意义[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(4):539-544. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200404001.htm [8] 刘善军,吴立新.脆性岩石与有机玻璃受力红外辐射特征的比较[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(增刊2):4183-4188. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2007S2087.htm [9] 刘善军,吴立新,吴焕萍,等.多暗色矿物类岩石单轴加载过程中红外辐射定量研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2002,21(11):1585-1589. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200211001.htm [10] 刘善军,吴立新,张艳博,等.潮湿岩石受力过程红外辐射的变化特征[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2010,31(2):265-268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX201002029.htm [11] 张艳博,刘善军.含孔岩石加载过程的热辐射温度场变化特征[J].岩土力学,2011,32(4):1013-1017. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201104008.htm [12] 刘善军,吴立新,张艳博.岩石破裂前红外热像的时空演化特征[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2009,30(7):1034-1038. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX200907029.htm [13] 谭志宏,唐春安,朱万成,等.含缺陷花岗岩破坏过程中的红外热像试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,16:2977-2981. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200516031.htm [14] 吴立新,刘善军,吴育华.遥感岩石力学引论-岩石受力灾变的红外遥感[M].北京:科学出版社,2007:126-132. [15] 郑诚,欧阳为民,蔡庆生.一种有效的的时间序列维数约简方法[J].小型微型计算机系统,2002,23(11):1380-1383. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXWX200211027.htm [16] 孙晓立,莫海鸿,杨敏.抗拔桩荷载-位移曲线的归一化[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2008,36(11):114-120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNLG200811022.htm [17] 刘思峰,党耀国,方志耕,等.灰色系统理论及应用[M].(5 版).北京:科学出版社,2010:64-65.




 下载:
下载: