Effects of hot rolling finishing temperature on the properties of QBe2 alloy sheet’s deformation-aging state
-
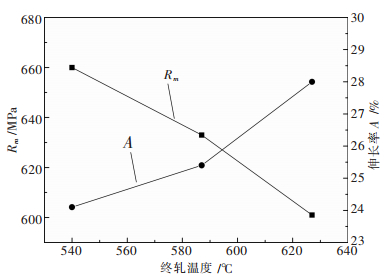
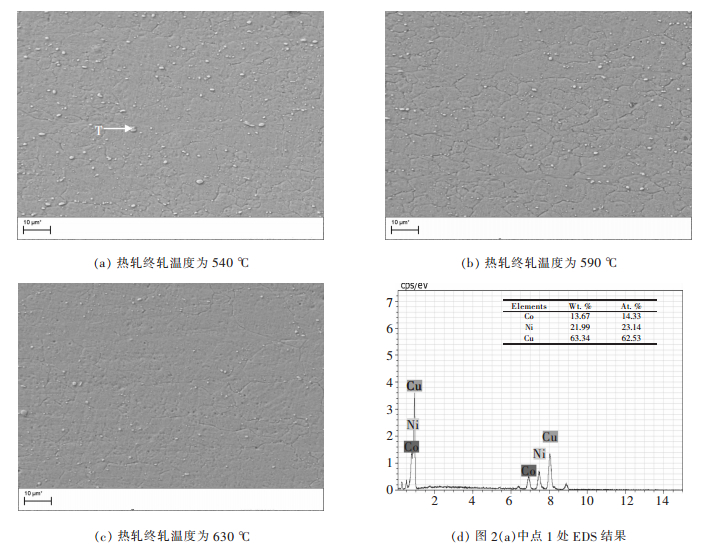
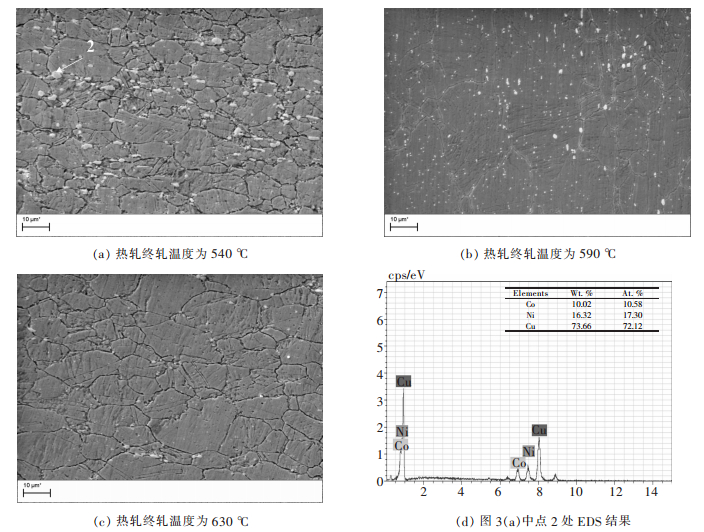
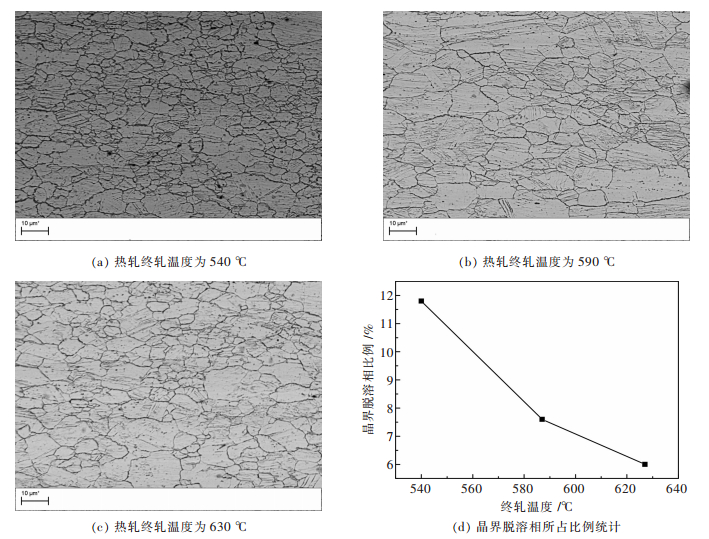
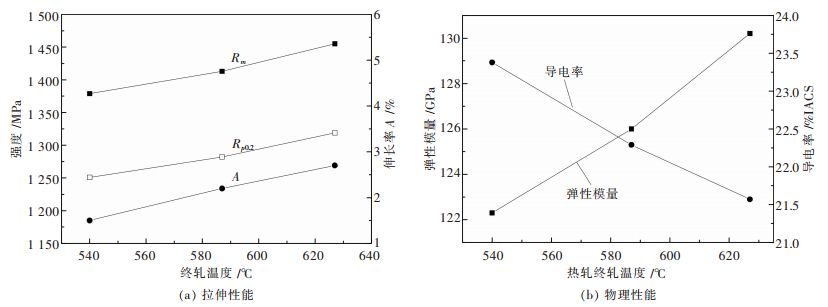
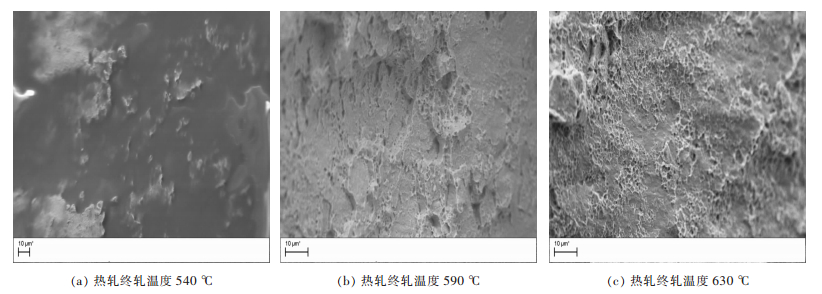
摘要: 通过对QBe2合金薄板的力学及物理性能进行测试,结合其不同热处理状态下的扫描电镜组织,研究了热轧终轧温度对形变时效状态QBe2合金薄板性能的影响.结果表明:热轧终轧温度在540~630 ℃范围内,较低终轧温度(540 ℃)的QBe2合金薄板经过形变时效热处理后显微组织中β相含量较高,并且析出物沿晶界局部脱溶的现象更为严重.热轧终轧温度从540 ℃升高到630 ℃,形变时效态下QBe2合金薄板的强度提高80~90 MPa,伸长率提高1.2%,弹性模量提高近10 GPa,导电率降低1.8%.造成不同热轧终轧温度的形变时效状态QBe2合金薄板性能不同的主要原因是显微组织中β相含量不同.Abstract: In order to study the effect of hot rolling finishing temperature on the properties of deformation-aging state QBe2 alloy sheet, the mechanical and physical properties of QBe2 alloy sheets are measured, combined with scanning electron microscope (SEM) microstructure of different heat treatment state. The results show that the deformation-aging state QBe2 alloy sheet with a lower hot rolling finishing temperature (540 ℃) contains larger amount of β phase and presents a more severe phenomenon of grain boundary desolvation when the hot rolling finishing temperature ranges from 540 ℃ to 630 ℃. When the hot rolling finishing temperature increases from 540 ℃ to 630 ℃, the strength of deformation-aging state QBe2 alloy sheet increases approximately 80~90 MPa. The elongation increases by 1.2% and the Young’s modulus increases approximately 10 GPa while the conductivity decreases by 1.8%. Due to different contents of β phase in the microstructure, the properties of deformation-aging state QBe2 alloy sheets with various hot rolling finishing temperatures are different.
-
由于没有对陕西某钒矿其矿山的不同生产区域的初始爆破参数及时调整优化,导致爆破效果不佳,矿石块度不能满足选矿要求;在高分段,大间距的情况下前排炮孔起爆对后排炮孔破坏严重,导致后续装药困难,爆破生产效率降低;在放矿过程中凭借经验出矿,放矿管理不科学,导致放出矿石损失贫化严重[1].为了有效控制爆破成本,提高生产效率和经济效益,本文在爆破试验的基础上进行了爆破参数的优化设计.
1 工程背景和岩石特性
工程地质调查发现,矿区以砂岩、砂砾岩型矿岩为主要成分且矿化规模大,产出稳定,形成细脉状,微细浸染状矿石,矿床工业类型为砂(砾)岩型层控矿床.矿区矿体的节理发育多为钙质、多具团块状构造,工程地质特性复杂多变,结构较不完整,矿体具有碎裂岩体的特征,稳定性差.顶底板岩性复杂,主要以青石化白云岩和粗砂岩主,这类岩石在风化和外界扰动的情况下易软化,导致抗压强度较低,稳定性较差.
2 爆破漏斗试验
标准爆破漏斗实验选用YGZ-90型凿岩机打孔,钻头的孔径是60 mm,在巷道内垂直向上打扇形炮孔,初始炮孔间排距1.5 m.矿山炸药是粉状铵油炸药,装药直径为65 mm,炸药的密度为0.98 g/cm3,采用导爆管雷管起爆,试验具体方案见表 1.
表 1 爆破的试验数据炮孔序号 装药量/kg 堵塞长度/m 漏斗半径/m 设计抵抗线/m 实测抵抗线/m 爆破效果 1 0.75 0.7 0.81 0.62 0.65 均匀块度 2 0.75 0.7 0.86 0.62 0.63 均匀块度 3 0.75 0.7 0.84 0.62 未测到 冲泡 4 0.75 0.7 0.85 0.62 0.61 均匀块度 5 0.75 0.7 0.71 0.62 0.53 大块、碎块多 6 0.75 0.7 1.03 0.62 0.71 大块多 对爆破完成后炮孔,取8个不同方向的平均值作为漏斗半径和实测最小抵抗线[2],从表 1经过剔除后求得爆破漏斗半径的平均值为0.84 m,最小抵抗线的平均值为0.62 m,实际的爆破漏斗n值为1.35,最初选择的炸药q为1.84 kg/m3,根据鲍列斯阔夫公式Q=(0.4+0.6n3)qW3,化简可得到式(1)校正初选炸药单耗[3].
$$q = q'/\left( {0.4 + 0.6{n^3}} \right)$$ (1) 式(1)中:q为试验计算炸药单耗,kg/m3;q′为初选炸药单耗,kg/m3;n为实际爆破漏斗作用指数.
校正后得到更为合适的炸药单耗q是0.981 kg/m3.
3 正交试验法优化扇形深孔的爆破参数
3.1 炮孔密集系数以及扇形深孔排距、孔底距优化
排距的大小对凿岩成本、爆破效果、回采进度和成本均有很大影响[4].小排距虽然能够改善爆破效果,但是降低了施工效率,增加了爆破成本,而排距过大则容易导致大块率高,甚至是出现“爆破墙”,严重影响爆破效果[5].炮孔的密集系数、排距、孔底距三者之间的关系式为:炮孔密集系数M=孔底距a/最小抵抗线W.
最小抵抗线的大小可根据经验公式计算,也可根据与扇形炮孔直径的关系,从相关矿山的实际资料中参考选取.
$$W = d\sqrt {7.85\frac{{\Delta \psi }}{{mq}}} $$ (2) 式(2)中:Δ为装药密度,kg/dm3;d为炮孔直径,dm;ψ为平均装药系数值;q为炸药单耗,kg/m3;m为炮孔密集系数.
3.2 扇形孔排距、孔底距试验方案
相同炸药单耗下,不同孔底距和排距爆破效果试验结果见表 2.
表 2 不同排距、孔底距布置矿得爆破效果编号 炸药单耗/(kg·m-3) 孔底距/m 排距/m 炮孔密集系数 大块率/% 1 0.981 1.9 1.5 1.27 2.5 1.9 1.6 1.19 2.8 1.9 1.7 1.12 3.2 1.9 1.8 1.06 3.5 1.9 1.9 1.00 4.1 2 0.981 2.0 1.5 1.33 2.7 2.0 1.6 1.25 2.6 2.0 1.7 1.18 3.2 2.0 1.8 1.11 3.5 2.0 1.9 1.05 3.9 3 0.981 2.1 1.5 1.40 2.6 2.1 1.6 1.31 2.5 2.1 1.7 1.24 2.6 2.1 1.8 1.17 3.1 2.1 1.9 1.11 3.9 4 0.981 2.2 1.5 1.47 2.5 2.2 1.6 1.38 2.4 2.2 1.7 1.29 2.6 2.2 1.8 1.22 3.1 2.2 1.9 1.16 3.8 5 0.981 2.3 1.5 1.53 3 2.3 1.6 1.44 3.5 2.3 1.7 1.35 3.8 2.3 1.8 1.28 4.2 2.3 1.9 1.21 4.4 由表 2的记录情况,可以发现当孔底距保持不变时,爆破后大块率与密集系数m成反比,当密集系数m保持在一定范围时,大块率与孔底距成正比关系.这是由于孔底距和排距都增大,导致孔网密度变稀,由于每个炮孔装药量一定,根据体积原理,在装药量没有改变情况下,爆破岩石体积增多,大块产出率必然随之增大.与此同时,由于是采用分段崩落法回采,在挤压崩落围岩的条件下爆破的落矿同样也增加了大块率.综合比较得出排距在1.6~1.85 m之间合理,孔底距在2~2.2 m之间合理.在此情况下,凿岩工程量大为减少,极大地加快了施工进度.爆破后,回采进路眉线保持平整,巷道掉块和片帮较少,后排炮孔变形破坏程度较轻,大块产出率也低[6-7].
3.3 崩矿步距的优化
崩矿步距是无底柱分段崩落采矿方法的重要落矿参数之一,由于该方法在覆岩下放矿,矿石损失贫化与崩矿步距之间具有很大的相关性.所以控制矿石的损失和贫化应该从爆破参数的优化和放矿方式的改进两方面来着手.
最佳崩矿步距可根据理论计算、数值模拟放矿、室内物理模拟放矿和现场工业性试验等方法来确定.当矿区回采巷道间距、分层高度都已确定,在采矿过程中很难再进行调整,而崩矿步距却不一样,可以随时进行灵活的调整.合理崩矿步距L是按三者最佳配合原则来确定,当三者最佳配合时回采效率能够达到最大,贫化率也较小,此时的崩矿步距为最佳值[8-9].通过理论计算并结合现场工业试验统计回收率与贫化率之差来确定最优的崩矿步距.
3.4 崩矿步距的理论计算
回采效率的表达式为:
$$\lambda = \frac{{{V^2}}}{{{V_{\rm{f}}}{V_{\rm{h}}}}}$$ (3) 式(3)中:λ为回采效率:Vh为混入废石体积;V为矿石体积;Vf为放出体体积.
放出的矿体在矿石脊平面的切割作用下,放出矿体体积Vf、矿石体积V与混入废石体积Vh,如图 1所示,有以下关系:
$$\begin{array}{l} {V_{\rm{f}}} = \frac{2}{3}{\rm{ \mathsf{ π} }}abc + {\rm{ \mathsf{ π} }}abc\frac{{a{\rm{tan}}\theta }}{{\sqrt {{a^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{tan}}\theta } + {{\rm{c}}^2}}}[1 - \frac{{{{(a\tan \theta )}^2}}}{{3({a^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta + {c^2})}}]\\ \;\;\;{V_{\rm{h}}} = {\rm{ \mathsf{ π} }}\mathit{abc}[2 - \frac{{L - a\tan \theta }}{{\sqrt {{a^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta + {c^2}} }}(1 - \frac{{{{(L - a\tan \theta )}^2}}}{{3({a^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta + {c^2})}}) - \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\frac{{2M}}{{\sqrt {{a^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta } + {c^2}}}(1 - \frac{{{M^2}}}{{3({a^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta + {c^2})}})]\\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;M = \frac{1}{{2(B - K)}} + (1 + H + a)\tan \varphi \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;V = {V_{\rm{f}}} - {V_{\rm{h}}} \end{array}$$ (4) 式(4)中:L为崩矿步距;θ一般取4.5°左右;φ一般在15°~20°;M为漏斗母线在Z轴方向上所截的线段长度;B为进路间距;K为回采进路宽;H为分段高度.
V是L的函数,将式(4)中各相关函数代入式(3)中并对L求一阶导数,求λ的极值,可得到回采效率最大时的崩矿步距为:
$$L = \frac{1}{{10}}[9a\tan \theta + \sqrt {81{a^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta + 60{c^2}} ]$$ (5) 化简后的崩矿步距表达式为:
$$L = a\tan \theta + 0.77c$$ (6) 由式(5)可知,求得长半轴a的值和纵短半轴c的值就可求得崩矿步距L.
$$\mathit{a} = \frac{{{k^2} + 4{H^2}_{\rm{f}}\left( {1 - {\varepsilon ^2}} \right)}}{{8{H_{\rm{f}}}\left( {1 - {\varepsilon ^2}} \right)}}$$ (7) $$\mathit{b} = \frac{{{k^2} + 4{H^2}_{\rm{f}}\left( {1 - {\varepsilon ^2}} \right)}}{{8{H_{\rm{f}}}\left( {1 - {\varepsilon ^2}} \right)}}$$ (8) $$\varepsilon = \frac{{\sqrt {{\mathit{a}^2}{\rm{ - }}{\mathit{b}^2}} }}{\mathit{a}}$$ (9) $${H_{\rm{f}}} = 2H - K$$ (10) 式(9)、式(10)中:Hf为放矿高度;ε为放出体偏心率.
将Hf为26 m,ε为0.93~0.95代入到式(7)、式(8)、式(9)可得:
a=13.57~13.79 m;b=4.31~6.3 m;c=4.13~6.09 m
将上述a、c和θ值代入到式(6)中,求得最佳崩矿步距为4.26~5.78 m.
根据上述理论计算最佳崩矿步距的结果,结合矿石的碎胀系数1.4,一次崩矿3排时正好在最佳崩矿步距理论计算的范围内.
3.5 正交工业试验确定崩矿步距
崩矿步距的试验要求与生产期具有相同的放矿环境[10],即在覆岩的条件下出矿,回采进路扇形孔孔底距均为2.1 m,回采进路中的扇形孔具有不同范围(1.6~1.85 m)的排间距.因此,工业试验布置在19#勘探线的回采进路中,放矿设计要求矿石回收率不低于75 %,贫化率不超过12 %.表 3为试验统计结果.
表 3 不同崩矿步距正交试验情况编号 排间距/m 崩矿间距/m 崩落矿量/t 出矿量/t 实际回收率/% 贫化率/% 回贫差/% 1 1.80 1.80 968.6 890 73.1 21.2 51.8 2 1.80 1.80 968.6 911 71.2 25.7 45.5 3 1.60 3.00 1 722.7 1 360 69.2 18.7 50.5 4 1.70 3.20 1 846.2 1 424 71.7 8.73 63.0 5 1.60 4.90 2 543.6 2 355 81.2 9.6 71.6 6 1.85 3.70 1 991.4 1 876 77.8 17.3 60.5 7 1.80 3.60 1 927.8 1 723 75.4 15.4 60.0 8 1.75 5.25 2 825.8 2 761 83.4 14.6 68.8 9 1.75 5.25 2 825.9 2 347 76.7 7.6 69.1 10 1.75 3.50 1 883.0 1 639 70.9 18.5 52.4 11 1.80 5.40 2 906.5 2 386 76.2 7.1 69.1 12 1.80 5.10 2 906.5 2 576 80.3 9.3 71.0 13 1.70 5.40 2 099.1 1 869 74.1 16.7 57.4 表 3中编号为第5、9、11、12组放出体在回收率和控制贫化方面都满足放矿要求,第8组放出体虽然回贫差较大,但是放矿时端部混入废石多导致贫化率高,没有达到设计的生产要求.总体来说崩矿步距为4.8~5.4 m,一次出矿量控制在2 400 t左右,矿石回收率和贫化率都较好,能够满足生产效率和经济效益要求.
正交试验表明当选择的最佳崩矿步距在4.8~5.4 m之间时,放出体的形态与爆破堆积体形态相对吻合,若加强放矿管理,能够有效改善矿石的损失和贫化率,提高原矿质量、满足生产实际要求[11-12].
4 结论
1)通过标准抛掷爆破漏斗试验能够较为准确地获得适合该矿区的炸药单耗值,经过计算炸药单耗选用0.981 kg/m3更为合适,运用正交试验来确定扇形孔的排距和孔底距是一种较为准确的方法,试验优化后的排距为1.6~1.85 m,孔底距为2~2.2 m.
2)根据放矿理论对20 m×15 m的间距情况下进行最佳崩矿步距的理论计算与不同崩矿步距放矿的工业试验.通过理论计算并结合现场工业试验统计回收率与贫化率之差来确定最优的崩矿步距,可以得出崩矿步距在4.8~5.4 m范围内为宜,小崩矿步距虽然能够增加矿石的回收,但是矿石贫化严重,容易形成悬顶,大崩矿步距虽然能够降低矿石贫化,但是端部矿体难以放出导致回收率低.
-
表 1 QBe2合金的主要成分/wt%
元素名称 Be Ni Co Cu 含量 1.7~2.0 0.2~0.3 0.1~0.2 Bal. -
[1] 王伟. 铍铜合金的生产和应用前景分析[J]. 有色金属加工, 2014, 43(2): 9-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJF201402003.htm [2] Cooley J C, Aronson M C. Origins of paramagnetism in beryllium-copper alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1995, 228(2): 195-200. doi: 10.1016/0925-8388(95)01894-8
[3] Behjati P, Vahid Dastjerdi H, Mahdavi R. Influence of aging process on sound velocity in C17200 copper-beryllium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 505: 739-742. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.06.128
[4] 史斌, 朱焕刚. 铍铜合金在汽车冲压成型模具上的应用[J]. 装备维修技术, 2010(4): 51-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBWX201004017.htm [5] 朱兴水. 高等级铍铜合金的应用与发展趋势[J]. 科技创新导报, 2014(4): 81-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXDB201404055.htm [6] 陈乐平, 周全. 铍铜合金的研究进展及应用[J]. 材料热处理技术, 2009, 38(22): 14-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY200922005.htm [7] 符留念. 铍青铜的时效处理[J]. 热处理, 2010, 25(5): 55-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RACL201005014.htm [8] 丁雨田, 施永奎, 胡勇, 等. 热处理对QBe2合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2007, 36(24): 62-65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY200724021.htm [9] 卢越焜, 刘涛, 李阿妮, 等. 铍青铜(QBe2)的分级时效工艺[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2009(4): 67-68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHCG200904018.htm [10] Levent Yagmur. Effect of microstructure on internal friction and Young’s modulus of aged Cu-Be alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 523: 65-69. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.05.047
[11] 阎永, 汪治军, 董超群. 我国铍铜产业科技进步回顾与展望[J]. 稀有金属, 2003, 27(1): 66-68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXJS200301012.htm [12] Chakrabarti D J, Laughlin D E, Tanner L E. The Be-Cu (Beryllium-Copper) System[J]. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1987, 8(3): 269-282. doi: 10.1007/BF02874919
[13] Ryoichi Monzen, Tomoyuki Hasegawa, Chihiro Watanabe. Effect of external stress on discontinuous precipitation in a Cu-2.1wt%Be alloy[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2010, 90(10): 1347-1358. doi: 10.1080/14786430903352631
[14] Rioja R J, Laughlin D E. The Sequence of Precipitation in Cu-2wt%Be Alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1980, 28, 1301-1313. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(80)90086-3
[15] 丁宗业, 贾淑果, 邓猛, 等. Cu-0.36Cr-0.03Zr合金的时效动力学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(7): 1879-1884. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201307014.htm [16] 崔天成, 李述军, 郝玉琳, 等. 热处理对Ti2448合金冷轧板组织和性能的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2008, 22(3): 225-229. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJB200803002.htm [17] 余伟, 李保成, 黄文辉. 变形温度对7A04-T5铝合金组织与性能影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2011, 40(2): 51-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201102014.htm



 下载:
下载: