Effect of basicity in high chromium vanadium-titanium magnetite on sintering process
-
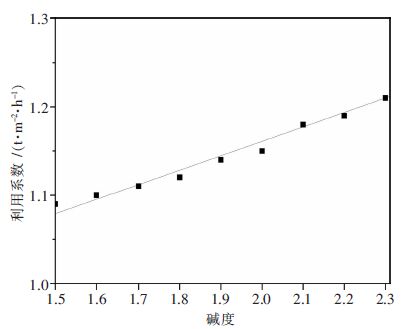
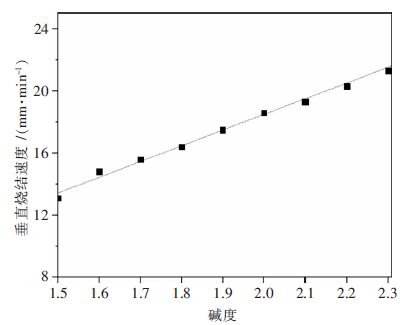
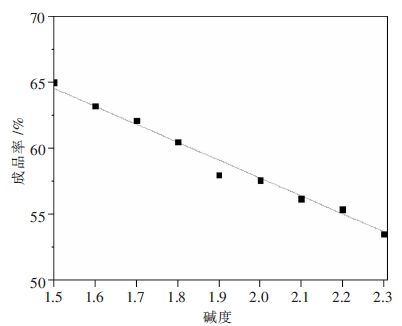
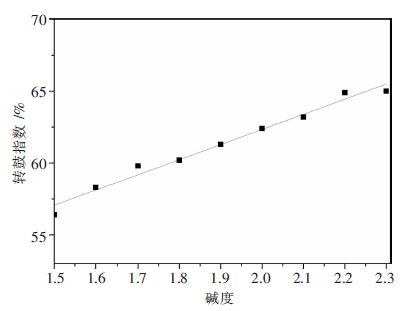
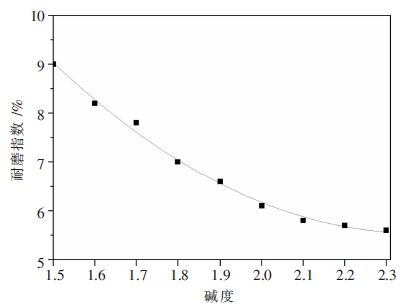
摘要: 针对某钢铁厂高铬型钒钛烧结矿适宜碱度的确定问题,利用烧结杯试验,在新的配矿条件下分别对高铬型钒钛磁铁烧结矿的生产指标、烧结矿强度以及烧结矿荷重软熔性能在不同碱度下进行了研究.结果表明:随着高铬型钒钛烧结矿碱度由1.5增加到2.3,烧结成品率、抗磨指数下降,垂直烧结速度、利用系数、转鼓强度均有提高;烧结矿的还原粉化指数RDI-0.5和RDI-3.15指标降低,而RDI+6.3提高;软熔带下移,软熔区间变窄,透气性提高,对于高炉顺行有积极的意义.通过分析不同碱度下烧结矿的各项指标,指出高铬型钒钛烧结矿碱度控制在1.9~2.0比较适宜.Abstract: In order to explore the suitable basicity of high chromium vanadium-titanium magnetite in a factory, the influence of different basicity in high chromium vanadium-titanium magnetite on production index、 sinter strength and the load softing property is studied by sintering pot test. The results show that the sintering yield、abrasion index、RDI-0.5 and -3.15 are decreased, while the vertical sintering speed、utilization coeffi-cient、tumbler strength and RDI+6.3 are increased with the increasing of sintering basicity. These is positive significance for blast furnace own to the shifting down of soft melting zone ,the turning narrow of soft melting and the permeability increasing. Analyzing all the indexing in the different basicity, the sinter basicity is more appropriate at 1.9~2.0.
-
Keywords:
- basicity /
- high chromium vanadium-titanium magnetite /
- sinter
-
岩石强度和变形特性一直是岩石力学研究的一个基础问题[1-9]. 长期以来对其研究主要是基于Mohr-Coulomb 强度理论[10-11]. 1910年,摩尔在库仑早期理论研究的基础上提出了摩尔强度理论,即在应力的作用下,土的破坏属于剪切破坏,并沿一定的剪切面产生剪切. 当沿该剪切面上的剪应力增大到极限值时,该单元土体就沿该剪切面发生剪切破坏. 近年来发现Mohr-Coulomb强度理论对于岩石在三向应力状态下的破坏也适用.岩石强度和变形特性是岩石力学与工程研究的重要课题之一. 随着试验设备和技术手段的不断改进和提高,岩石力学的试验水平有了很大的提升,尤其是岩石三轴常规实验得到了很大的改善[12-15],因而对岩石强度和变形特性方面的试验研究取得了一定的成果. 在岩土工程领域如隧道工程和地下采矿工程中,岩体均处于三向应力状态下[16],因而研究三向应力状态下岩石的强度和变形特性,对于了解和探明岩石的破坏机理[17-19],地下岩石破坏方式及变形机理等均有着重要意义,对工程实践意义更为显著. 文中通过以西部矿业锡铁山有限公司深部围岩为绿泥石英片岩为研究对象,采用英国GDS公司生产的RTS-500型岩石三轴流变仪试验系统进行常规三轴压缩试验,获得岩石三轴压缩下应力-应变曲线. 分析其不同深度及不同围压对岩样力学特性的影响. 为研究地下矿山深部围岩开挖稳定性,对绿泥石英片岩进行常规三轴压缩试验,研究绿泥石英片岩强度和变形特性,试图为矿山从事围岩和矿岩开挖工作设计以及岩石力学参数的选择提供参考依据.
1 三轴压缩试验
1.1 实验设备
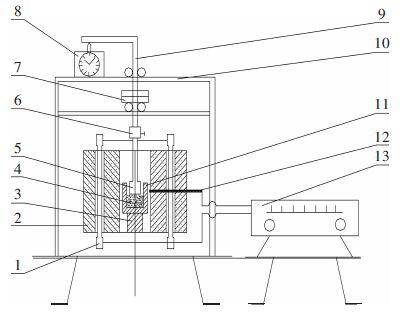
试验机选用英国GDS公司生产的RTS-500型岩石三轴流变仪试验机,RTS-500型岩石三轴流变仪是一款优质的高温高压岩石三轴测试系统,可施加大量程荷载,它是基于高压力荷载架的三轴实验系统,专门用于岩石试样的精准实验. GDS已经制造岩石高压自动三轴实验系统超过20年,被全世界尖端科研和商业机构所采用. 在中海油服等企业单位已得到较成熟的使用. RTS-500型岩石三轴流变仪可完成岩石单轴压缩试验、排水或不排水三轴压缩试验,单轴、三轴压缩流变试验,化学和温度耦合试验. 主要技术参数:高压岩石三轴流变仪最大轴向载荷400 kN,围压范围:0~32 MPa,对50 mm直径试样,可产生大于200 MPa偏应力,轴向力分辨率为1/10 000,位移分辨率为0.1 μm,行程100 mm.温度控制范围:25~65 ℃,用于测试温度控制精度0.1 ℃.实验系统及试件安装如图 1、图 2所示.
1.2 实验方法及试件加工
实验试件来自西部矿业集团锡铁山有限公司深部的岩石,锡铁山为中国目前储量最大的铅锌矿.矿山位于青海省柴达木盆地北缘,柴达木盆地为高原型盆地.故该矿山位于西部青海省柴达木盆地高原地区,因此对于高原地区的深部岩石,在三向应力状态下的力学性质和变形特性的研究尤为重要.取回来的岩石均为绿泥石英片岩经过加工为Φ50 mm×100 mm的标准试件,由于岩芯的贵重以及稀缺,这里有的高度不能达到要求,但不影响整体实验,经过打磨抛光处理,然后进行分组.在已加工好的试件中选取3组深度不同的共9个试件,详细的试件统计见表 1.
表 1 三轴压缩试验试件相关参数Table 1. Three axial compression test parameter组号 试件编号 试件尺寸/mm 标高/m 围压/MPa 直径 高 1 D-35 48.64 102.1 2 505.844 10 D-27 48.70 101.80 2 505.844 20 D-30 48.80 101.16 2 505.844 30 2 D-29 48.60 101.60 2 312.380 10 D-83 49.42 99.80 2 312.380 20 D-10 48.64 100.2 2 312.380 30 3 D-76 48.50 100.40 2 110.726 10 D-31 48.60 103.14 2 110.726 20 D-38 48.60 99.60 2 110.726 30 如表 1所示,实验共分为3组,每一组实验有3个试件,实验时各试样分别以围压10 MPa、20 MPa、30 MPa进行加载,每块试件轴向压力采用一级加载方式,轴向压力加载速率为0.2 kN/s,直至压坏为止. 要测出应力、应变曲线与时间的关系. 图 3所示为实验过程中的应力-应变曲线.
2 实验结果及分析
2.1 不同围压强度及变形特性
随着对能源需求量的增加和开采强度的不断加大,目前矿山的开采,地表浅部的资源已经开采殆尽,浅部资源日益减少,国内外矿山都相继进入深部资源开采状态.深部岩体由于受到高地应力、特别是侧向高应力的作用,使其具有不同于浅部岩石的特征.深部高应力围岩的岩石强度明显增加,岩体处于高压缩变形或破坏极限状态,我国很多矿山已经进入真正意义上的深部开采.随着开采深度的增加,矿山深部矿石的围压也会跟着增大,通过研究锡铁山矿山不同围压状态下围岩的强度变化规律,以及在围压状态下的岩石变形特征,根据实验数据画出了不同深度的3条应力-应变曲线,分别为10 MPa、20 MPa、30 MPa围压下的强度特性及变形,如图 4、图 5、图 6所示.不同深度的绿泥石英片岩的应力应变变化曲线如图 7、图 8、图 9所示.
由图 4、图 5、图 6可知,随着围压的增大,岩石的峰值应力也跟着增加,在三轴抗压强度下岩石的峰值应力出现前,即岩石没有发生破坏前,同一深度同一位置的岩石在围压不同的情况下,岩石应力-应变曲线的斜率几乎相同,也就是说岩石的弹性模量与外界所施加的围压无关,只与岩石本身的性质有关.低围压时岩样内部材料并未均匀化,岩石表现为脆性变化特性;而高围压时岩样内部材料强度由低到高逐渐屈服,变形趋于均匀,岩石出现了由脆性变形向塑性转化的趋势,变形呈线性增长.
在图 7、图 8、图 9中,在浅部地应力下,绿泥石英片岩主应力-应变曲线斜率随着围压的增加而明显变缓;深部高应力下,绿泥石英片岩承载后产生的变形及破坏形态与围压大小密切相关,其主应力-应变曲线斜率随着围压的增加而明显变陡,破坏荷载增高. 岩石的峰值应变与围压显著成正线性关系.
2.2 岩石的内聚力和内摩擦角
在三轴压缩试验中,围压不同的三轴试验,假设有n个不同的围压,第i个试验对应的峰值应力为σ1i,围压为σ3i,则根据Mohr-Coulomb 强度理论[20]有:
$$\frac{1}{2}\left( {{\sigma }_{1i}}-{{\sigma }_{3i}} \right)=c\cos \varphi +\frac{1}{2}\left( {{\sigma }_{1i}}-{{\sigma }_{3i}} \right)\sin \varphi $$ (1) 式(1)中:φ为内摩擦角;c为内聚力.
令${{y}_{i}}=\frac{1}{2}\left( {{\sigma }_{1i}}-{{\sigma }_{3i}} \right),{{x}_{i}}=\frac{1}{2}\left( {{\sigma }_{1i}}+{{\sigma }_{3i}} \right)$,则式(1)为:
$${{y}_{i}}=c\cos \varphi +x\sin \varphi $$ (2) 偏离程度采用式(3)来计算,即:
$$Q\left( c,\varphi \right)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{\left( {{y}_{i}}-c\cos \varphi -{{x}_{i}}\sin \varphi \right)}^{2}}}$$ (3) 由于Q(c,φ)是c,φ的非负二次函数,所以存在极小值,且是线性回归得到的抗剪强度直线和该直线与莫尔圆切点之间的距离平方和,如果距离平方和等于0,则说明抗剪强度直线与莫尔圆正好相切,但是抗剪强度不一定与所有试验得到的莫尔圆都相切,因此利用式(3)的极小值直线来作为抗剪强度直线.由式(3)根据极值原理可得:
$$\left. \begin{align} & \frac{\partial Q}{\partial c}=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{\left( {{y}_{i}}-c\cos \varphi -{{x}_{i}}\sin \varphi \right)\left( -c\cos \varphi \right)=0} \\ & \frac{\partial Q}{\partial \varphi }=-2\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{\left( {{y}_{i}}-c\cos \varphi -{{x}_{i}}\sin \varphi \right)\left( -c\cos \varphi -{{x}_{i}}\cos \varphi \right)=0} \\ \end{align} \right\}$$ (4) 求解式(4),可得到c,φ:
$$\varphi =\arcsin \left( \frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{x}_{i}}{{y}_{i}}-\bar{x}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{y}_{i}}}}}{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{x_{i}^{2}-\bar{x}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{x}_{i}}}}} \right)$$ (5) $$c=\frac{{\bar{y}}}{\cos \varphi }-\bar{x}\tan \varphi $$ (6) 式(6)中:$\bar{x}=\frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{x}_{i}},\bar{y}=\frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{1}{{{y}_{i}}}}$
由表 2可以得出,相同深度的岩石,岩石的抗压强度随着围压的增大而增大;随着深度的增加,相同的围压条件下,埋藏深度越深的岩石其抗压强度越强,符合地下岩石的发展规律;而且根据内聚力以及内摩擦角的计算结果,随着深度的增加,内聚力和内摩擦角也会跟着相应的增大.
表 2 不同标高试件三轴试验参数结果Table 2. Three different levels of axial test parameters试件编号 标高/m 围压/MPa 破坏荷载/kN 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/MPa 内聚力/MPa 内摩擦角$\varphi $/(°) D-35 2 505.844 10 75.31 43.44 104.431 D-27 2 505.844 20 282.08 149.13 97.912 4.173 2 21.111 5 D-30 2 505.844 30 312.93 164.47 98.123 D-29 2 312.380 10 278.10 141.70 100.234 D-83 2 312.380 20 298.54 152.05 93.617 10.752 7 47.461 3 D-10 2 312.380 30 369.82 193.99 102.121 D-76 2 110.726 10 317.69 168.52 24.343 D-31 2 110.726 20 24.96 174.59 105.304 16.362 2 51.163 4 D-38 2 110.726 30 416.82 219.98 104.769 3 结 论
1) 同深度同位置的岩石在不同围压条件下,岩石应力-应变曲线在峰值应力前阶段几乎重合,说明岩石的弹性模量与外界条件无关,只与岩石本身的性质有关.
2) 低围压时,变形不均匀,岩石表现为脆性特性;高围压时,变形趋于均匀,岩石出现由脆性向塑形特性转变的趋势.
3) 浅部低应力下,绿泥石英片岩应力-应变曲线斜率随着围压的增加而明显变缓;深部高应力下,其应力-应变曲线斜率随着围压的增加而明显变陡,绿泥石英片岩承载后产生的变形及破坏形态与围压大小密切相关,其破坏荷载增高.岩石的峰值应变与围压显著成正线性关系.
4) 相同深度的岩石,岩石的抗压强度随着围压的增大而增大;相同围压条件下,随着深度的增加,埋藏深度越深的岩石其抗压强度越强,内聚力和内摩擦角也会随着深度的增加而增加.
5) 根据深部岩石在三轴实验中的变形规律,对深部开采矿山高效、安全的回采具有一定的现实指导意义.
-
表 1 原料化学成分/%

表 2 燃料成分/%

表 3 烧结所用铁矿化学成分/%

表 4 低温还原粉化性能测定结果

表 5 不同碱度烧结混合料软熔温度测定结果

表 6 不同碱度烧结矿软熔性能测定结果

-
[1] Akimoto S,Katsura T. Magnetochemical study of the generalized titanomagnetic in volcanic rocks[J]. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity,1959(10):69-90.
[2] Katsura T. Generalized titanomagnetic in Hawaiian volcanic rocks[J]. Pacific Science, 1964,18(4):223-228. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0789d27d8a13b2c5e1a92b9f3e9e3145&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] 刘熙光,邱定辉,张其春,等. 关于钒钛磁铁矿综合利用可持续发展问题的探讨[J]. 中国矿业,2000(4):21-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA200104007.htm [4] 胡途. 钒钛磁铁精矿转底炉多层球还原基础研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2013. [5] 杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1996. [6] 王筱留. 钢铁冶金学炼铁部分[M]. 北京:冶金工业出版社,1995. [7] 周取定,孔令坛. 铁矿石造块理论及工艺[M]. 北京:冶金工业出版社,1992:12-14. [8] 王喜庆. 钒钛磁铁矿高炉冶炼[M]. 北京:冶金工业出版社,1994:5-6. [9] 唐贤荣,张青岑. 烧结理论与工艺[M]. 长沙:中南工业大学出版社,1992:23-235. [10] 闫利娥. 提高太钢烧结矿碱度稳定性的研究与实践[J]. 烧结球团,2009,34(4):44-47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJQT200904019.htm [11] 尚策,周明顺,翟立委. 鞍钢烧结矿冶金性能优化研究[J]. 中国冶金,2009,19(9):13-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYE200909004.htm [12] 韩淑峰,周明顺,沈峰满. 优化鞍钢烧结矿碱度及炉料结构的试验研究[J]. 材料与冶金学报,2013,12(3):163-168. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUJI201303003.htm [13] 何木光,易凯,张文德. 钒钛磁铁矿在高碱度下提铁降硅烧结性能研究[J]. 矿业工程,2013,11(2):33-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWKS201302013.htm [14] 张文山,吕庆,李福民. 碱度对钒钛烧结矿强度和烧结过程的影响[J]. 烧结球团,2006,31(5):11-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJQT200605002.htm [15] Matsuno, Nishikida Ikesaki. Strength deterioration of sample of iron ore 5 %~10 % CaO systems during the reduction at 550 degree C in 30 % CO-N2 gas[J]. Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan,1984(4):275-283.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 佟志芳,王佳兴,许聪聪,谢肇勋. TiO_2和碱度对CaO-MgO-Al_2O_3-SiO_2-Cr_2O_3-Fe_2O_3-TiO_2渣系黏度和结构及氧化铬溶解度的影响. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(03): 332-341 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 陈均优,张庆猛,周敏,赵艳芸. 不同TiO_2和Nb_2O_5含量对BaO-SrO-PbO-TiO_2-Nb_2O_5-SiO_2玻璃陶瓷介电性能的影响. 稀有金属. 2024(10): 1502-1509 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马行娟,徐昌华. 纳米材料制备的气体传感器对装饰环境中乳胶漆化学检测试验. 粘接. 2023(11): 87-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: