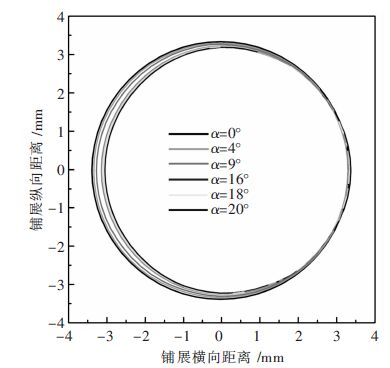
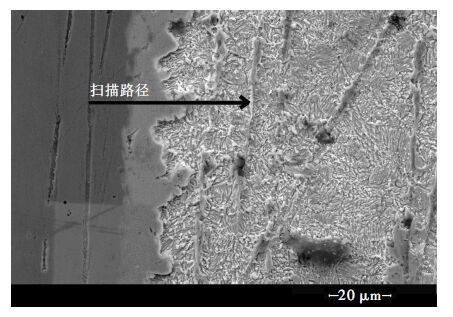
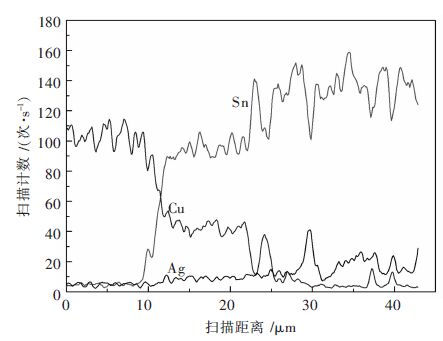
Simulation analysis on the surface morphology of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu melting on the inclined Cu substrate
-
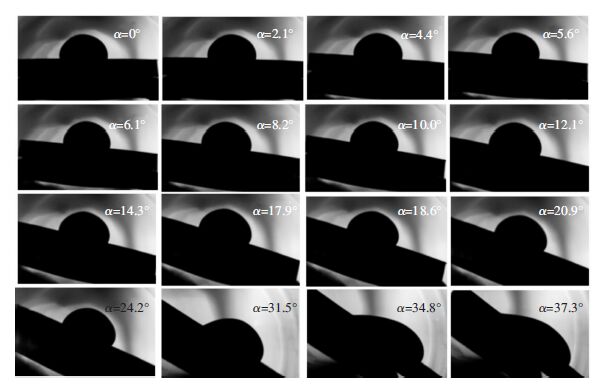
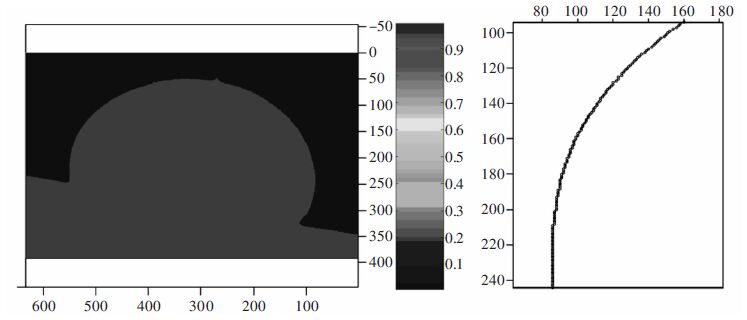
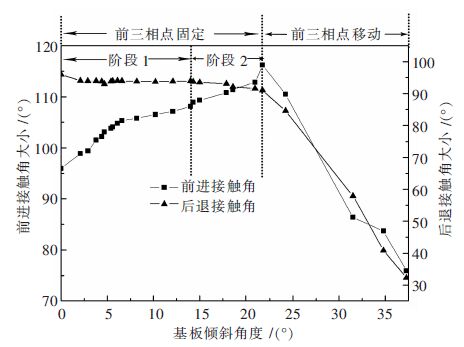
摘要: 通过润湿性实验,借助有限元软件Surface Evolver模拟研究了在490 K温度下熔融态的无铅焊料Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu在倾斜铜基板上的铺展行为及界面特性.根据经验方程拟合熔滴侧面轮廓曲线并获得三相点处的接触角大小.经计算发现,在基板的倾斜角度较小时,三相接触线几乎不发生移动,三相接触线的后三相点沿基板向前移动,前三相点保持不动,相应地,前进角逐渐增大并达到最大值.随着基板倾斜角度的继续增大,前三相点开始向前移动,导致前进角逐渐减小,最终熔滴从基板上滑落.通过模拟铺展过程表征了接触角的滞后现象;通过SEM及EDS手段分析界面微观结构,说明了在润湿过程中发生了界面化学反应,确定了金属间化合物Cu6Sn5生成并呈扇贝形分布.Abstract: To investigate interface properties of molten Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder melting on the inclined Cu substrate, numerical simulation is carried out by Surface Evolver at 490 K with wetting experiments. Profile curves of the droplets are fitted with empirical equation, which are proposed to obtain preferable contact angles. According to the experimental results, it is indicated that the contact line hardly moves at the very beginning and the rear point of triple line moves forward along the substrate subsequently, but the front point of triple line is still pinned on the substrate. Correspondingly"the advancing contact angle gradually increases to the peak value. When the inclined angle of the substrate continues to increase, the advancing contact angle decreases along with the front point of triple line moving forward, and finally the drop slides down from the substrate. In this paper, contact angle hysteresis is characterized by the numerical simulation. Furthermore, the interface microstructure is observed by means of SEM and EDS. It is illustrated that the interfacial chemical reaction happens in the wetting process which determines the formation of intermetallic Cu6Sn5 that distributes as the scallop shape.
-
Keywords:
- lead-free solder /
- surface morphology /
- hysteresis /
- numerical simulation
-
铅是非常重要的金属,由于其良好的金属性能被广泛应用于蓄电池、电缆屏蔽、造船和辐射防护等领域,同时也是制造各种合金的重要原料。目前,硫化铅精矿是生产铅的重要原料。然而随着高品位硫化铅精矿的快速消耗,难选的铅锌混合矿由于储量大已成为我国铅锌冶炼的重要原料。烧结-密闭鼓风炉炼铅锌工艺自20世纪60年代初投入工业生产,是目前唯一能直接处理铅锌混合矿的火法冶炼工艺。但铅锌混合矿的烧结脱硫工序存在能耗高、脱硫效率低以及烟气中低浓度SO2回收效率低等技术难题[1-3]。相较于烧结-鼓风炉工艺,熔池熔炼法被认为在能源消耗、环境保护以及有色金属回收方面存在优势[4-14]。富氧底吹炉由于能耗低、二氧化硫吸收率高等优点已经被广泛地应用于我国铅冶炼。现有的底吹炉对入炉原料有严格的限制(ω(Pb)>45%)[6],若用底吹炉直接处理铅锌混合矿,必然会使得氧化渣中铅质量分数降低和锌质量分数升高,炉渣成分的变化会导致熔渣熔点和黏度发生改变。ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)和ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)是火法炼铅过程中调节炉渣成分的重要手段,因此研究不同ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)和ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响显得十分重要。
文中提出了铅锌混合精矿氧气熔融脱硫清洁冶炼新思路,重点对ω(Zn)/ω(Pb)≈1的铅锌混合矿熔融脱硫过程进行了研究,研究了温度、氧气流量、炉料成分(ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)、ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2))对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响,确定熔池熔炼合适的入炉炉料成分和温度,为实现铅锌混合精矿直接清洁冶炼提供理论依据。
1 实验材料和实验方法
1.1 实验原料
选用甘肃某地铅锌混合矿成分如表 1所列,铅锌混合矿Pb质量分数为24.56%,Zn质量分数为28.5%,ω(Zn)/ω(Pb)=1.2。铅锌混合矿XRD图谱见图 1,铅锌混合矿中铅主要以PbS的形态存在,锌主要以ZnS、Zn3Fe2S5形态存在,铁主要以FeS2、Zn3Fe2S5形态存在。实验熔剂PbO、CaO、SiO2等均使用分析纯化学试剂。
表 1 铅锌混合矿主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical composition of lead and zinc mixed concentrate
1.2 试验步骤
表 2所列为铅锌混合矿氧气熔融直接脱硫实验物料配比,熔融脱硫温度分别为1 250 ℃、1 300 ℃、1 400 ℃。
表 2 铅锌混合矿喷吹氧气熔融脱硫方案Table 2. Scheme of oxygen desulfurization of lead and zinc mixed concentrates
喷吹氧气熔融脱硫装置示意图,如图 2所示。实验装置由电阻炉、气源装置、尾气处理装置组成。电阻炉升温元件为二硅化钼,升温程序由电脑控制。刚玉坩埚放置在刚玉平台上,通过设置在刚玉坩埚底部的热电偶测量温度,温度误差范围为±2 ℃。气源装置为高纯氩气和氧气。尾气处理装置包括烟尘收集瓶和二氧化硫收集瓶(双氧水)。
具体试验步骤:
1)熔剂按质量配制好,混匀后加入至氧化铝坩埚(直径为46(38)mm×120 mm),升温至预定温度熔融,将铅锌混合矿高温加入至氧化铝坩埚中并恒温5 min,铅锌混合矿和熔剂总的质量为150 g,为保证反应管内气氛,在升温过程中在炉体底部通入Ar(流量:600 mL/min)。
2)将氧化铝喷吹管(直径为8(5)mm×800 mm)插入至高温熔体内(熔池厚度为30~40 mm,插入深度为离坩埚底部5 mm处),喷吹氧气进行脱硫,氧气压力为0.2 MPa。
3)喷吹到预定时间,停止喷吹。用铁棒蘸取适量熔渣在水中淬冷,渣样用碳硫分析仪(AXS, G4, Germany)和XRD衍射技术(Bruker, D8 ADVANCE, 德国)分析其硫含量和物相。
脱硫率为铅锌混合矿脱硫效果的评价指标之一,文中脱硫率的计算公式如式(1)所示:

(1) 式中:m1为反应前炉料质量,m2为反应t时刻炉渣质量;CS1为反应前炉料S质量分数,CS2为反应t时刻炉渣S质量分数。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 O2流量和温度对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响
铅锌混合矿氧气脱硫可如下表示:

(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
(5) 
(6) 
(7) 
(8) O2流量对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响见图 3,随着O2流量的增加,炉渣含S量减少,铅锌混合矿脱硫速率增加。O2流量的增加,增加了气液反应界面,增大了气泡的表面更新速率,熔融渣氧化脱硫的动力学条件得到强化[15],使得铅锌混合矿脱硫速率加快。当O2流量为100 L/h时,炉渣S质量分数与120 L/h炉渣S质量分数无明显差别。因此,后续试验过程中O2喷吹流量均采用100 L/h流量进行。
温度对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响如图 4所示,由图 4可以看出,当反应时间为24 min时,铅锌混合矿在1 250 ℃、1 300 ℃、1 400 ℃时的熔渣S质量分数分别为3.24%、1.47%、1.11%,可以看出,反应温度的升高有利于炉渣S质量分数的降低,进而加快铅锌混合矿脱硫速率。而当温度升至1 300 ℃时,继续提高反应温度,铅锌混合矿炉渣含S降低并不明显。因此,为了提高铅锌混合矿脱硫速率和O2利用率,氧气熔融脱硫过程的温度应大于1 300 ℃。
2.2 ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响
图 5所示为不同ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)质量比时,熔渣S质量分数与时间关系图。由图 5可知,在反应温度(1 250~1 300 ℃)内,ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的降低有利于炉渣S质量分数的降低,加快铅锌混合矿脱硫速率。当反应温度为1 250 ℃,反应时间为30 min,ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)由0.62增加至1.14,炉渣S质量分数由1.09%增加至3.64%。图 6所示为1 300 ℃、反应时间为24 min时,入炉炉料ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的变化对脱硫率的影响。铅锌混合矿的脱硫率随着ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的降低而显著增加,当ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)由1.14降低至0.47时,脱硫率由95.3%增加至98.8%。
由上可知,ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)对铅锌混合矿脱硫速率和脱硫率影响显著。为了解ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)增加后的物相变化对脱硫率的影响,对不同ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的淬冷渣进行了XRD衍射分析。如图 7所示,当ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)=0.47时,熔渣中主要物相是铁橄榄石相,当ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)增加至0.78时,熔渣中开始形成尖晶石相(ZnxFe3-xO4+y),且随着ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的增加,尖晶石相的峰强逐渐增强。一些研究者研究了尖晶石相的形成对熔池熔炼的影响,研究结果表明尖晶石相的产生是泡沫渣形成的主要原因之一[16]。且熔渣中Fe含量的增加会导致熔渣中固相物质的增多[17],进而导致熔渣黏度增大。在之前的研究中[18],对ω(Pb)/ω(Zn)=1的氧化渣在1 300 ℃进行了黏度实验研究,实验结果如图 8所示,随着ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的增加,炉渣黏度逐渐增加,当ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)增加至1.17时,高铅锌渣黏度已经达到0.43Pa·s,不利于冶炼的顺利进行。以上分析说明铅锌混合矿随着ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的增加会导致脱硫速率和脱硫率的降低。
2.3 CaO/SiO2对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响
图 9所示为不同反应温度下,不同ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)质量比对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响。由图 9可知,当反应温度为1 250至1 300 ℃,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)的提高不利于熔渣S质量分数的快速降低,且反应温度越低,此趋势越明显。当反应温度提高至1 400 ℃时,反应时间为21 min时,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)=0.1,0.5的熔渣S质量分数分别为3.58%、1.12%,高温下(1 400 ℃)ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)提高有利于熔渣S含量的快速降低。ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)对铅锌混合矿脱硫率的影响如图 10所示,其规律与图 9一致,即在1 250~1 300 ℃,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)提高导致铅锌混合矿脱硫率的降低,当反应温度升高至1 400 ℃时,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)提高有利于铅锌混合矿脱硫率的提高。
熔渣中的CaO质量分数的变化会对熔渣的熔点和黏度产生很大的影响[19]。在此渣型下,由于熔渣中高熔点的铁、锌氧化物较多,CaO质量分数的增加会使熔渣熔点升高,熔渣中固相物质增多,熔渣黏度变大。使用Factsage热力学软件对铅锌氧化渣(炉渣成分:ω(Pb)/ω(Zn)=1,ω(Pb+Zn)=50 %,ω(Fe)/ ω(SiO2)=1.14,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)=0.1, 0.5)进行了相平衡计算,其熔点均在1 300 ℃以上,且在1 250 ℃,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)=0.5的熔渣中固相物质质量分数为14%高于ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)=0.1的熔渣中固相物质百分含量的13.8%,这可能是导致在1 250~1 300 ℃,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)的增加不利于铅锌混合矿脱硫的原因。当反应温度提高至1 400 ℃时,熔渣几乎没有固相物质析出,此时,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)的增加有利于解聚硅酸盐网状结构,加速复杂聚合离子团的分解,使得熔渣黏度的降低[20-21],进而使得ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)的增加有利于铅锌混合矿脱硫率的提高。
3 结论
研究了O2流量、反应温度、炉料成分对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响规律,得到以下结论:
1)O2流量的增加和反应温度的提高有利于铅锌混合矿脱硫。当反应温度为1 300 ℃时,铅锌混合矿熔融脱硫率可在24 min内达到95%以上,脱硫率远高于烧结脱硫。为保证熔池熔炼的顺利进行和O2的利用率,应将反应温度保持在1 300 ℃以上。
2)ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的提高不利于铅锌混合矿脱硫速率的加快和脱硫率的增加。由于ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)的增加导致熔渣中尖晶石相和固相物质增多,导致黏度增加,不利于铅锌混合矿脱硫反应的进行。因此,铅锌混合矿熔融脱硫ω(Fe)/ω(SiO2)应控制在0.78以下。
3)ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)对铅锌混合矿脱硫的影响较为复杂。当反应温度为1 250 ℃或1 300 ℃时,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)的降低有利于铅锌混合矿脱硫反应的进行,而当反应温度升高至1 400 ℃时,ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)的降低不利于铅锌混合矿脱硫反应的进行。因此,铅锌混合矿熔融脱硫ω(CaO)/ω(SiO2)应控制在0.5以下。
-
[1] Lai H, Duh J. Lead-free Sn-Ag and Sn-Ag-Bi solder powders prepared by mechanical alloying[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2003, 32 (4): 215-220. doi: 10.1007/s11664-003-0212-1
[2] Xu H, Yuan Z, Lee J, et al. Contour evolution and sliding behavior of molten Sn-Ag-Cu on tilting Cu and Al2O3 substrates[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2005, 359(1/2/3): 1-5.
[3] Allen S, Notis M, Chromik R, et al. Microstructural evolution in lead-free solder alloys. Part II. Directionally solidified Sn-Ag-Cu,Sn-Cu and Sn-Ag[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 19(5): 1425-1431. doi: 10.1557/JMR.2004.0191
[4] Krasovitski B, Marmur A. Drops down the hill: theoretical study of limiting contact angles and the hysteresis range on a tilted plate[J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21(9): 3881-3885. doi: 10.1021/la0474565
[5] Eustathopoulos N. Dynamics of contact angle phenomenon[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(7): 2319-2327.
[6] Whyman G, Bormashenko E. Oblate spheroid model for calculation of the shape and contact angles of heavy droplets[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009,331(1):174-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.11.040
[7] Abdelhadi O M, Ladani L. IMC growth of Sn-3.5Ag/Cu system: Combined chemical reaction and diffusion mechanisms[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 537 (5): 87-99.
[8] Suzuki S, Nakajima A, Tanaka K, et al. Sliding behavior of water droplets online-patterned hydrophobic surfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254 (6): 1800-1805.
[9] He B, Lee J, Patankar N A. Contact angle hysteresis on rough hydrophobic surfaces[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2004, 248(1/2/3): 101-104. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=59e6c5493439ec27cb28495a2248ee62&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] Parker A R, Lawrence C R. Water capture by a desert beetle[J]. Nature, 2001, 414: 33-34. doi: 10.1038/35102108
[11] Chou T, Hong S, Sheng Y, et al. Drops sitting on a tilted plate: receding and advancing pinning[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28 (11): 5158-5166. doi: 10.1021/la300257t
[12] Quéré D, Azzopardi M J, Delattre L. Drops at rest on a tilted plane[J]. Langmuir, 1998,14 (8): 2213-2216. doi: 10.1021/la970645l
[13] Yuan Z, Mukai K, Takagi K, et al. Surface tension and its temperature coefficient of molten tin determined with the sessile drop method at different oxygen partial pressures[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 254 (2): 338-345. doi: 10.1006/jcis.2002.8589
[14] Yuan Z, Mukai K, Huang W. Surface tension and its temperature coefficient ofmolten silicon at different potentials[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18 (6) : 2054-2062. doi: 10.1021/la0112920
[15] Bonn D, Eggers J, Indekeu J, et al. Wetting and spreading[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009,81: 739-805. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.739



 下载:
下载: